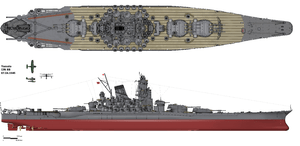
Friends of Padre Steve’s World,
After spending the time to take two days each to write two detailed articles on issues related to the novel Coronavirus 19 I needed a break. I could have started another COVID 19 article tonight but I needed a break, especially after I listened to today’s COVID 19 Task Force Press conference, which was more of a cheerleading fan rally than anything seriously informative. But I have to leave that here for now, I don’t have the emotional energy to write about it right now, after all there will be plenty of other chances to chronicle this and more.
So tonight I am going back to different classes of naval warships. This is another in a series of six articles on the battleships built under the provision of the Washington and London Naval Treaty limitations in the 1930s. I am not including the ships which were completed in the immediate aftermath of the Washington Treaty limitations. This series looks at the modern battleships that the World War II combatants would produce in the 1930s which saw service in the war. The first deal that the German Scharnhorst class and another covered the Italian Vittorio Veneto class. In between my commentary on current events, as well as the Holocaust, I plan to go back to the French Dunkerque and Richelieu classes, the British King George V class, and the United States South Dakota class. The German Bismarck, Japanese Yamato, British Vanguard and American Iowa classes will be covered in a subsequent series.I will probably write about the battleships that each of these nations planned but either did not complete or never left the drawing board, including the fantastical German ships of the various H classes.
So until tomorrow, I hope that you enjoy this.
Peace,
Padre Steve+
 Turret base of USS Washington being lowered into barbet
Turret base of USS Washington being lowered into barbet
The United States finished the First World War as the rising economic and potential military power in the world. The British Empire was economically reeling beset by massive debts, heavy loss of life and an empire which was beginning to smell the fresh breezes of independence. The United States retreated into isolationism and a naïve and unfounded optimism that war could be outlawed while turning its back on the one organization that might have helped bring nations together, the League of Nations. In this environment the United States sponsored the Washington Naval Conference of 1922 which produced the Washington Naval Treaty. The treaty stipulated limitations on total battleship tonnage, main armament and the maximum tonnage allowed per ship. Ships already in existence could not be replaced until they reached the age of 20 years. A battleship “building holiday” of 10 years was mandated with the major signatories allowed to complete a few ships that were already under construction. Whole classes of new construction were cancelled and many ships under construction were scrapped on the ways or completed only to be scrapped or sunk as targets. The Royal Navy completed two ships of the Nelson Class, the United States completed the 3 ship Maryland Class using a 4th vessel the incomplete USS Washington as a target and the Japanese were allowed to complete two ships of the Nagato Class. The Royal Navy completed the Battleship Eagle and Battle Cruisers Furious, Glorious and Courageous as Aircraft Carriers, the U.S. Navy the incomplete Battle Cruisers Lexington and Saratoga and the Japanese the Battle Cruiser Akagi and Battleship Kaga as carriers. The treaty limits of the Washington Conference were renewed in the London Treaty which also sought to limit the main batteries of new battleships to 14 inch guns.
 North Carolina Class 16″ Gun Turret
North Carolina Class 16″ Gun Turret
The U.S. Navy began a study of new designs for a fast battleship class to comply with the treaty restrictions in May to July of 1935. A minimum of 35 different designs were submitted and reviewed by the Navy and also reviewed by the faculty of the Naval War College. These designed included everything from an improved version of the Standard Type which had culminated in the Maryland Class and the never built South Dakota Class.
The Type VII Design, a Return to the Standard Battleship
After a considerable amount of debate a design called the Type XVI was selected. The design originally called for twelve 14” guns mounted in three quadruple turrets. Other designs considered called for twelve 14″ guns in triple turrets. When the Japanese opted out of the treaty and the Italians began building the Vittorio Veneto Class with 15” guns the U.S. Navy officially adopted the “escalation clause” and the design was modified to mount nine 16” guns in triple turrets primarily due to the expectation that the Japanese Imperial Navy would mount larger guns in its new ships.
 Initial Type XVI design with 14″ guns
Initial Type XVI design with 14″ guns
The Navy worked to achieve the maximum speed, armament and protection that it could within the 35,000 ton limitations of the Washington and London Naval Treaties. There was debate among Admirals and designers as to how to solve the problem with some factions leaning toward greater speed and lighter armor and armament and others weighing in on a slightly slower ship with greater firepower and protection.
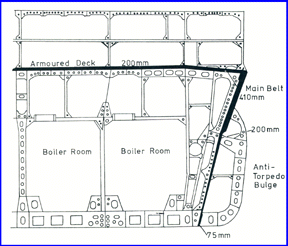
The Type XVI (modified) design original called for a main battery of twelve 14” guns in quadruple turrets, but this was changed to nine 16” guns in triple turrets. The main armor belt was 12” inclined 15 degrees with 16” armor on the turret faceplates and barbets having 16” side armor. Their conning tower was also protected by 14” armor. This gave them heavier armor than the Italian Vittorio Veneto Class. They had a lighter belt than the British King George V Class but were afforded more protection to their turrets, barbets and conning tower. Likewise, they had slightly less armor than the French Richelieu class due to the Design of the class which placed all main battery guns forward, using all or nothing armor protection. However, the design was a compromise and the armor could not have protected the ships from 16” shellfire, and there were weaknesses in the anti-torpedo defenses which were shown when North Carolina was torpedoed during the Guadalcanal campaign along with the USS Wasp.
 View of USS Washington Conning Tower showing Mk 38 5″ gun directors and SG Surface Search Radar
View of USS Washington Conning Tower showing Mk 38 5″ gun directors and SG Surface Search Radar
Their top speed of 27 knots was slower than their European counterparts but their range was far superior to all being able to steam over 20,000 miles at 15 knots and 6,610 miles at 25 knots. Their top speed and ranged decreased slightly during the war with the addition of more anti-aircraft guns and sensors.
Other designs were considered in the selection process, but most of the designs considered had speeds from 27-30 knots depending on whether the designers sacrificed speed for armament and protection, or protection and firepower for speed. One design, the Type VII resembled earlier classes of battleships with a speed of only 23 knots in favor of much heavier protection on a shorter hull.
The North Carolina Class was comparable in many ways with the Japanese Nagato Class in speed, protection and armament, but they had a far greater cruising range which made them excellent for operations in the Pacific either parts of Fast Carrier task forces, the Battle Line of the Third or Fifth Fleet, or centerpieces of surface action groups.
The North Carolina’s also were superior to their contemporaries in their anti-aircraft armament as well as their electronics, radar and fire direction suites which were all continuously upgraded throughout the war.
The construction of the ships was slow due to material shortages in the late 1930s. Likewise, the design change to 16” guns from the original 14” guns, as well as labor issues which not only lengthened the time of their construction and raised their cost from $50 million to $60 million dollars each.
 North Carolina during underway replenishment in the Pacific
North Carolina during underway replenishment in the Pacific
USS North Carolina was laid down on 27 October 1937, launched on 13 June 1940 and commissioned 9 April 1941. However, it was months before she was operational due to severe longitudinal vibration of her propeller shafts which was corrected by a modified propeller design. Despite the efforts to keep to the treaty limitations the ships displaced 36,600 long tons and had a full load displacement of 44,800 long tons. By 1945 the ships full load displacement had increased to 46,700 long tons for North Carolina and 45,370 long tons for Washington.
 Torpedo Damage to North Carolina
Torpedo Damage to North Carolina
When North Carolina completed her shakedown cruise she was sent to the Pacific where she joined Task Force 16 and the USS Enterprise on 6 August 1942. She defended Enterprise during the Battle of the Easter Solomons on 24 August and during an 8 minute period she shot down between 7 and 14 Japanese aircraft. On 15 September she was badly damaged by a torpedo from the Japanese submarine I-15 which necessitated her withdraw to Pearl Harbor for repairs.
The gravity of the damage from the hit sparked great debate in the Navy regarding her protection with some wondering if too much had been sacrificed in her design, despite this no modifications were made to the ships of the Iowa class.
Upon her return to service she operated with TF 38 and TF 58 protecting the carrier task forces in their operations against the Japanese as well as with TF 34 the Fast Battleship Task Force under the command of Vice Admiral Willis Lee. Serving throughout the Pacific campaign she took part in every major operation in the Central Pacific except Leyte Gulf and against the Japanese mainland. Her Marines and Sailors took part in the initial occupation of Japan. She was decommissioned and placed in reserve on 1 June 1960 and survived scrapping to be bought by the State of North Carolina for $250,000 and turned into a memorial at Wilmington North Carolina. She remains a National Historic Landmark and is maintained by the USS North Carolina Battleship Commission. She is exceptionally well maintained and much of the ship is open for tours.
 USS Washington BB-56 on high speed run in 1945
USS Washington BB-56 on high speed run in 1945
The USS Washington was laid down 14 June 1938 launched on 1 June 1940 and commissioned 15 May 1941 though like North Carolina had propeller shaft vibrations which delayed her operational availability. She became the first U.S. Navy Battleship to take an active part in the war when she joined the British Home Fleet in March 1942 operating with the Royal Navy escorting Arctic convoys bound for the Soviet Union against possible forays of the Battleship Tirpitz and other heavy German surface units until 14 July when she returned to the United States for a brief overhaul.
Following her overhaul, Washington was deployed to the South Pacific to join U.S. Forces operating against the Japanese at Guadalcanal and became the Flagship of Rear Admiral Willis Lee. During the Naval Battle of Guadalcanal on the night of 14-15 November she and the USS South Dakota sailed with 4 destroyers to intercept a Japanese task force. The Japanese force led by the Battleship Kirishima included 2 heavy and 2 light cruisers as well as 9 destroyers. The Japanese hit the Americans hard early in the battle sinking 3 of the 4 American destroyers and inflicting significant topside damage to South Dakota which caused a power outage and knocked her out of the action. Washington sailed on undetected by the Japanese and opened a devastating barrage against Kirishima. Washington scored hits on Kirishima with at least 9 of her 16” shells and over 40 5” shells. Kirishima was mortally wounded. despite the best attempts of her crew to save her, she was scuttled the following day. After mauling Kirishima, Washington then drove off the other Japanese ships sparing Henderson Field from certain heavy damage.
 Washington blasting Kirishima at the Naval Battle of Guadalcanal 14-15 November 1942
Washington blasting Kirishima at the Naval Battle of Guadalcanal 14-15 November 1942
 Washington’s victim the IJN Battleship Kirishima
Washington’s victim the IJN Battleship Kirishima
Washington continued operations in the South and Central Pacific until she was damaged in a collision with USS Indiana which resulted in her losing nearly 60 feet from her bow on 1 February 1944. She received temporary repairs before returning to the Puget Sound Naval Shipyard to receive a new bow and other modernizations returning to action in May 1944. She remained in operation against the Japanese the rest of the war. She was decommissioned in 1947 and struck from the Naval Register on 1 June 1960 and sold for scrap.
North Carolina and Washington in Reserve
Various improvements and ideas were suggested while the ships remained in reserve as some in the Navy wished to reactivate them to include lightening them to increase their speed, and conversion into Helicopter Carriers all of which were rejected. The rejection of these attempts to modernize and recommission the ships ensured their fates.
 Fireworks over the North Carolina in Wilmington (US Navy Photo)
Fireworks over the North Carolina in Wilmington (US Navy Photo)
Though the North Carolina class was a compromise design they performed admirably throughout the war. They and their brave crews are remembered in Naval History and the preservation of North Carolina has ensured that they will never be forgotten.