Eugene Ely makes the first takeoff from USS Birmingham on November 14th 1910
Eugene Ely makes the first takeoff from USS Birmingham on November 14th 1910
On a blustery November 14th in the year 1910 a young civilian pilot hailing from Williamsburg Iowa became the first man to fly an aircraft off the deck of a ship. At the age of 24 and having taught himself to fly barely 7 months before Eugene Ely readied himself and his Curtis biplane aboard the Cruiser USS Birmingham anchored just south of Fort Monroe in Hampton Roads. Ely was there because he was discovered by Navy Captain Washington Irving Chambers who had been tasked with exploring how aircraft might become part of Naval Operations. Chambers had no budget or authority for his seemingly thankless task but hearing that a German steamship might launch and aircraft from a ship hustled to find a way to stake a claim for the U.S. Navy to be the first in flight. Weather was bad that day as is so typical for Hampton Roads in November and between rain squalls Ely decided to launch even though Birmingham did not have steam up to get underway to assist the launch. Ely gunned the engine and his biplane rumbled down the 57 foot ramp and as he left the deck the aircraft nosed down and actually make contact with the water splintering the propeller and forcing him to cut the flight short and land on Willoughby Spit about 2 ½ miles away not far from the southern entrance to the modern Hampton Roads Bridge Tunnel is. Chambers would talk Ely into making the first landing on a Navy ship the Armored Cruiser USS Pennsylvania in San Francisco Bay on January 18th 1911. Ely died in a crash at the Georgia State Fairgrounds on October 11th 1911.
 USS Langley CV-1
USS Langley CV-1
The Naval was slow to build upon the early achievements and the British and France would commission Aircraft Carriers well before the USS Langley CV-1 a converted Collier was commissioned. After Langley the Navy commissioned the converted Battlecruisers USS Lexington CV-2 and USS Saratoga CV-3 in the mid 1920s.
 USS Lexington CV-2 October 1941
USS Lexington CV-2 October 1941
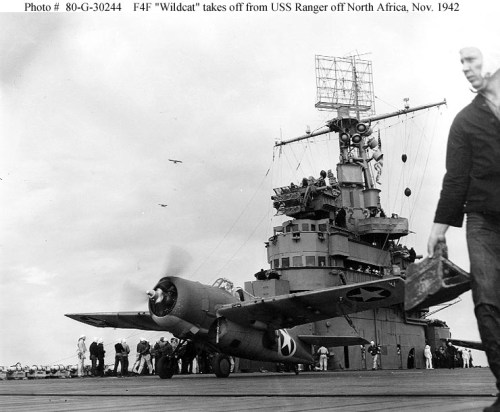
The three ships formed the nucleus of the Navy’s embrace of aviation and the pilots that they trained and the experience gained would be the foundation of the Navy’s success in the Second World War. They would be joined by the USS Ranger CV-4 the first U. S. Navy Carrier designed as such from the keel up in 1934.
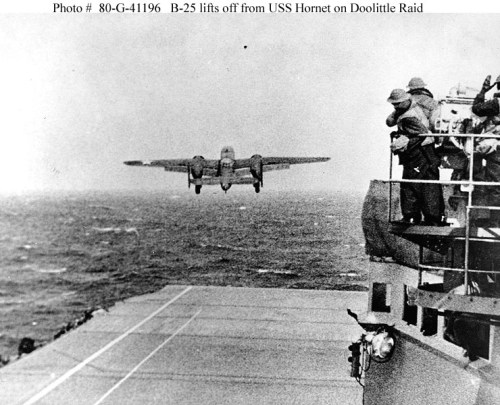
 USS Enterprise CV-6
USS Enterprise CV-6
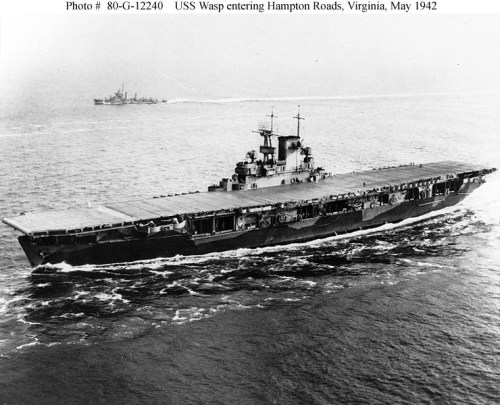
In 1937 the Navy commissioned the first of its true Fleet Carriers the USS Yorktown CV-5 which was followed by the USS Enterprise CV-6 in 1938, the USS Wasp CV-7 an improved version of Ranger in was commissioned in 1940 and the USS Hornet CV-8 in 1941. These ships would bear the brunt of US Navy operations in the first year of the war following the disaster at Pearl Harbor. Of these ships only the Enterprise and Saratoga would survive the first year of the war in the Pacific. Langley now a Seaplane Carrier was sunk during the Battle of the Java Sea in February 1942. Lexington would go down at Coral Sea in May 1942. Hornet would launch the Doolittle Raid against Japan on April 18th 1942. Yorktown, Enterprise and Hornet would take on and defeat the Japanese Carrier Strike force and sink the Akagi, Kaga, Soryu and Hiryu at Midway to avenge Pearl Harbor. Yorktown was sunk in the battle but Midway stopped the Japanese advance in the Pacific.
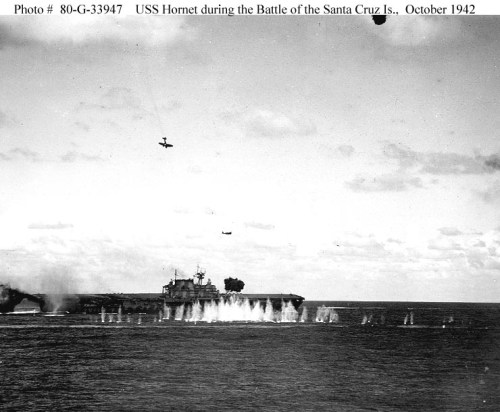
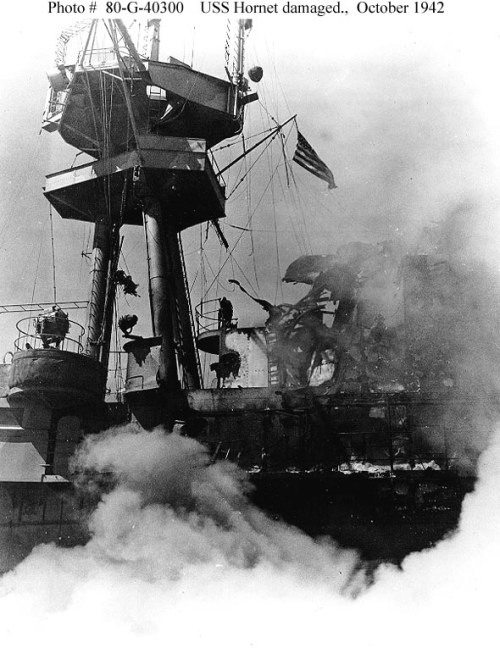
The U. S. went on the offensive in August invading Guadalcanal in the Solomons Islands. The Guadalcanal campaign and the numerous sea battles in the adjacent waterways would claim many American and Japanese ships. Wasp was sunk by a Japanese submarine on September 15th 1942 and Hornet was sunk at the Battle of Santa Cruz on 27 October 27th 1942. Saratoga spent much of 1942 in the yards having been torpedoed twice leaving the often battered Enterprise as the sole U. S. Navy Carrier facing the Japanese until Saratoga was repaired and the first of the Essex Class Fleet Carriers and Independence Class Light Fleet Carriers entered service and arrived in the Pacific.
 USS Yorktown CV-10 1944 a good example of the wartime Essex class ships below USS Cabot CVL-28 an Independence Class Light Fleet Carrier
USS Yorktown CV-10 1944 a good example of the wartime Essex class ships below USS Cabot CVL-28 an Independence Class Light Fleet Carrier

The Essex Class ships became the nucleus of the Fast Carrier Task Forces in the Pacific and with their smaller consorts of the Independence Class would dominate operations at sea from 1943 on. The Essex class would eventually number 24 ships with several more canceled before completion becoming the most numerous of any class of Fleet Carriers produced by the U. S. Navy. The Essex class would figure prominently in all offensive operations including the Battle of the Philippine Sea, Battle of Leyte Gulf, the campaigns at Iwo Jima and Okinawa and raids on the Japanese home islands. In the process they and their air groups would be instrumental in sinking hundreds of Japanese ships including the Battleships Yamato and Musashi and destroying thousands of aircraft. A number were heavily damaged by Kamikazes but none were lost with the epic story of the USS Franklin CV-13 and her survival after being hit by two bombs from a Japanese plane that slipped through the Combat Air Patrol. The resultant explosions and fires amongst her fueled and armed aircraft nearly sank her but for the heroic efforts of her crew including Chaplain Joseph O’Callahan who won the Medal of Honor caring for the wounded and dying and directing damage control teams. The ship lost 724 men killed and 265 wounded in the attack but survived though without power and dead in the water 50 miles off the Japanese coast.
 Murderers’ Row
Murderers’ Row
The Essex class were iconic and the ships etched their names in naval history. The Essex, Yorktown, Hornet, Wasp, Hancock, Ticonderoga, Franklin, Bunker Hill, Intrepid, Lexington and the other ships of the class had legendary careers. These ships became known as “Murderers’ Row” for their expertise in killing off Japanese ships and aircraft. Fittingly four of the ships, the Hornet, Yorktown, Lexington and Intrepid have found a second life as museum ships and Oriskany was sunk as an artificial reef off the coast of Florida where she is a favorite of recreational divers.

USS Croatan CVE-25 a Bogue Class Escort Carrier
During the war the Navy also built 118 Escort Carriers converted from merchant ships for use as convoy escorts, anti-submarine warfare and close air support for amphibious operations. 38 of these ships saw service in the British Royal Navy during the war.
 USS Hancock CVA-19 in 1969 showing the extent of the modernizations that brought the Essex Class into the jet age
USS Hancock CVA-19 in 1969 showing the extent of the modernizations that brought the Essex Class into the jet age
In the post World War II drawdown many carriers were decommissioned and the oldest, the Saratoga and Ranger disposed of. The three ship Midway class entered service after the war and incorporated design improvements learned from combat operations in the war. As the Navy entered the jet era it was found that the existing carriers would need significant modernization to handle the new aircraft. Among the improvements made to the Midway and Essex class ships was the angled flight deck, steam catapults, hurricane bows and improved landing systems. These improvements allowed these World War II era ships to remain front line carriers into Vietnam and in the case of the USS Midway and USS Coral Sea into the 1990s.
 Artists’ conception of USS United States CVA-58 a victim of Truman Era Air Force politics
Artists’ conception of USS United States CVA-58 a victim of Truman Era Air Force politics
The Navy began its first super-carrier the USS United States in 1949 but the ship and class was cancelled by Secretary of Defense Louis A. Johnson, not a fan of the Navy or Marine Corps due to opposition by the Army and the newly founded Air Force. The ship would have carried 12-18 nuclear capable bombers as well as 45-50 jet fighters and attack aircraft and been 1090 feet long and displaced 65,000 tons. It would not be until after the Korean War that the Navy would begin construction of its first super-carriers.
 USS Midway CVA-41 in 1971
USS Midway CVA-41 in 1971
During the Korean War most of the Essex class ships were called back into service with 15 modified to conduct jet operations while others were converted to serve as ASW Carriers and Helicopter Carriers (LPH) to support Marine amphibious forces. Likewise the Midway’s were modernized as the Navy began to construct the four-ship Forrestal Class which were 1036 feet long and displaced 56,000 tons and designed to carry 100 aircraft. The four ships, Forrestal CVA-59, Saratoga CVA-60, Ranger CVA-61, and Independence CVA-62 would all serve into the early 1990s before being decommissioned. In the past few months Forrestal and Saratoga have begun the journey to be scrapped, sold for a penny each to scrapyards in Brownsville, Texas.
 USS Ranger CVA-61
USS Ranger CVA-61
They were all heavily involved in the Vietnam War on Yankee and Dixie Station and both the Atlantic and Pacific during the Cold War. All four have been stricken from the Navy List and are awaiting disposal. Forrestal was programmed as an artificial reef but she, like Saratoga which had been on donation hold was approved for scrapping. Ranger is still on donation hold and the USS Ranger Foundation is attempting to raise the money to save her. Independence which had been programmed as an artificial reef project was approved for scrapping in 2008.In the past few months Forrestal and Saratoga began the journey to be scrapped in 2014, sold for a penny each to scrapyards in Brownsville, Texas.

USS John F Kennedy CV-67 a modified Kitty Hawk class ship
These ships were followed by the Kitty Hawk class consisting of Kitty Hawk CVA-63, Constellation CVA-64, America CVA-66 and John F. Kennedy CVA-67 which were improved versions of the Forrestal Class with a 60,100 ton displacement and 1047 foot length with the ability to carry 100 aircraft. Kitty Hawk had the distinction of being the last fossil fuel carrier in active U. S. Navy service being decommissioned and placed in reserve in 2009. Her sister the Constellation CV was decommissioned in December 2003 and in 2008 was programmed to be scrapped in the next five years. America was decommissioned in 1996 after not being given a Service Life Extension Program (SLEP) refit in the 1990s due to budget cuts. America was involved in much of the Cold War, Gulf War and Vietnam including responding to the Israeli attack on the USS Liberty in 1967, the Intervention in Lebanon in 1983 and the conflict with Libya in the Gulf of Sidra in 1985. She was sunk as a test bed to see how modern carriers would be affected by battle damage and to incorporate those lessons into future carrier design in May of 2005. John F. Kennedy was originally planned to be a nuclear ship equipped with 4 A3W reactors. This plan was shelved and she was completed as a fossil fuel ship. “Big John” served in Vietnam as well as throughout the Cold War and Gulf War and also engaged the Libyans in 1985. She was placed in the Reserve Force in the 1990s to save money and also served as a training carrier. Like America she did not receive the necessary maintenance and by 2002 she needed emergency repairs in order to deploy in support of Operation Enduring Freedom. Kennedy made three deployments in support of the War on Terror and decommissioned in 2007. She was placed in donation hold and currently two groups are making progress to acquire her as a Museum ship. Like the Forrestal’s the Constellation’s served in Vietnam, the Cold War, Operation Desert Shield and Desert Storm and three continued their service into Operation Iraqi Freedom. Constellation began her journey to the scrapyard in August 2014.
 USS Enterprise CVN-65
USS Enterprise CVN-65
As the Navy continued to develop the capabilities of the aircraft carrier it commissioned the nuclear powered USS Enterprise CVAN-65. The added capability of nuclear power enabled her to operate without dependence on fossil fuel which in addition to her range and speed allowed her to carry more aviation fuel and munitions than the fossil fuel ships. Unique among the Nuclear Carriers she produces 280,000 SHP and is powered by 8 Westinghouse (A2W) Reactors driving geared turbines, 4 screws with a classified top speed in excess of 35 Knots and is the quickest carrier going from all stop to full speed. At 1101 feet long and 75,700 ton (93,000 Full Load) displacement she was larger than any other carrier. She served in Vietnam, the Cold War, the Gulf War and Operation Enduring and Operation Iraqi Freedom. She was and was decommissioned in 2013.

USS Theodore Roosevelt CVN-71 of the Nimitz class
The Nimitz Class of nuclear powered carriers is the most numerous class of capital ship in the U.S. Navy since the Essex Class. Slightly smaller than Enterprise with a 1088 overall length and 91,000 full load displacement the Nimitz CVN-68 and her sister ships are the mainstay of the U. S. Navy carrier force. These ships have been the symbols of American naval power for three decades and will continue to be for the foreseeable future. Each of the ships has embodied successive improvements gained from the previous ships and the latest ships of the class the USS Ronald Reagan CVN-76 and USS George H. W. Bush CVN-77 incorporate technologies that were not known when Nimitz was on the drawing board. Thus whenever a ship is taken in for their Refueling and Complex Overhaul (RCOH) it is upgraded to the capabilities of the newest ship. The class consists of the Nimitz, the USS Dwight D. Eisenhower CVN-69, USS Carl Vinson CVN-70, USS Theodore Roosevelt CVN-71, USS George Washington CVN-72, USS Abraham Lincoln CVN-73, USS John C. Stennis CVN-74, USS Harry Truman CVN-75 as well as the previously mentioned Reagan and Bush. They can carry 90% more fuel and 50% more ordnance than the Forrestal class. Carrying 90 or more aircraft they pack a mobile offensive punch that is not matched by any other surface ship. The have served in every major military and many humanitarian missions since Nimitz was commissioned in 1974.
 Artist conception of USS Gerald R Ford CVN-78
Artist conception of USS Gerald R Ford CVN-78
The Nimitz class will be joined by the USS Gerald R. Ford CVN-78. The Ford is the first ship of an entirely new class. While approximately the same size as the Nimitz class at 1092 feet long and approximately 100,000 tons full load displacement the Ford class of which three are currently authorized and one under construction will feature many improvements over their predecessors. Among improvements are an advanced arresting gear, automation, which reduces crew requirements by several hundred from the Nimitz class carrier, the updated RIM-162 Evolved Sea Sparrow missile system, the AN/SPY-3 dual-band radar (DBR), as developed for Zumwalt class destroyers an Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System (EMALS) in place of traditional steam catapults for launching aircraft, a new nuclear reactor design (the A1B reactor) for greater power generation, advanced stealth features to help reduce radar profile and the ability to operate the new F-35C Lightning II. If the class is built as programmed on a one ship every five year rate with the Ford commissioning in 2015 then 6 ships of the class will be in commission by 2040. The next two ships have been named, the John F Kennedy and Enterprise.
Of course as with any military technology the future never is certain. In 1918 no one would have thought that the all-big gun Dreadnought Battleships would be eclipsed by the Aircraft Carrier in less than 25 years. While the Carriers have ruled the waves since Midway there are threats to them both military and financial. Countries such as China while building their own carriers have are developing weapons such as guided ballistic missiles designed to destroy carriers. As of now there is no defense against such a weapon if a carrier is within range. While China has not yet deployed the weapon it could be a game changer in the Western Pacific. Likewise there is the ever present threat posed by new and advanced submarines even those deployed by 2nd and 3rd world nations. Finally there is the financial cost which could derail the procurement of more carriers in an era of austerity. The cost of the Ford is currently estimated to be $9 Billion Dollars which if stretched end to end would probably reach Vulcan where the Vulcans would come up with an answer to our current problems.
At the same time the carriers have defied those who predicted their demise since the Truman administration. Currently no sea based platform has the multitude of capabilities of a carrier and its associated air wing and battle group and thus they should remain the Queens of the Sea for some time to come and the United States Navy which has led the world in their development and operation should continue to lead the way.
The next installment which will appear later this week will discuss the aircraft employed by the United States Navy not only those from carriers, but seaplanes, rotor-wing aircraft and lighter than air ships.
Peace
Padre Steve+
 Japanese Aircraft preparing to launch at Pearl Harbor
Japanese Aircraft preparing to launch at Pearl Harbor