This is the last of a three part series about the USS Yorktown Class Aircraft Carriers. It is the story of the USS Enterprise CV-6, the legendary “Big E” and possibly the most celebrated American warship of the Second World War.
The USS Enterprise CV-6, the second ship of the Yorktown class was ordered by the Navy on 3 August 1933 as authorized under the National Industrial Recovery Act of 16 June 1933. She was laid down just under a year later and launched on 3 October 1936 at Newport News Shipbuilding and Drydock Company, Newport News Virginia. She was commissioned on May 12th 1938 to begin one of the most celebrated careers of any US Navy ship in history. Displacing 25,500 tons full load Enterprise like her sister ships were designed for fast carrier operation working in conjunction with other carriers not tied to the battle line. With good protection and speed the Enterprise incorporated the lessons learned in the preceding carriers.
After her shakedown cruise she operated in the Atlantic and Caribbean until April 1939 when she was transferred to the Pacific Fleet and based a Pearl Harbor. As the flagship of Task Force 16 under Rear Admiral Bill “Bull” Halsey Enterprise conducted training operations and shuttled aircraft to various US island bases in the Central Pacific one such mission to Wake Island which had her out of Pearl Harbor when the Japanese attacked on December 7th 1941. Following the attack Enterprise and Task Force 16 would cover the Hawaiian Islands and then be used to conduct raids against Japanese bases in the Marshalls and protect convoys bound for Samoa.
 Rare photo of the Enterprise at Midway
Rare photo of the Enterprise at Midway
In April she escorted the newly arrived USS Hornet CV-8 to conduct the famed “Doolittle Raid” on Tokyo. Five days after returning to Pearl Harbor Enterprise was dispatched to the Coral Sea but could not arrive before that historic carrier battle. She returned to Pearl Harbor on May 26th and with Halsey sick departed two days later as flagship of TF-16 under the command of Rear Admiral Raymond A Spruance in company with Hornet, 6 cruisers and 10 destroyers with orders “to hold Midway and inflict maximum damage on the enemy by strong attrition tactics.”
 TBD Devastator landign on Enterprise May 1942
TBD Devastator landign on Enterprise May 1942
They would be joined 2 days later by the hastily repaired USS Yorktown flagship of Rear Admiral Frank “Jack” Fletcher and TF-17 escorted by 2 cruisers and 6 destroyers. Fletcher the senior officer assumed tactical command of this comparatively small force which represented the bulk of US naval power in the Pacific.
This tiny force would face 4 fleet (CV) and 2 light fleet (CVL) carriers, 7 battleships, 10 heavy (CA) and 2 light (CL) cruisers and 42 destroyers. Additionally the Japanese had an additional 2 carriers, 4 battleships, 3heavy cruisers 4 light cruisers and 23 destroyers involved in some way the simultaneous invasion of the Aleutian Islands which could be called into the fight if Admiral Yamamoto desired.
 SBD Dauntless Dive Bombers over Enterprise
SBD Dauntless Dive Bombers over Enterprise
The Battle of Midway was an epic of warfare and Enterprise and her Air Group 6 would play a pivotal role. Torpedo Six under LCDR Max Leslie in its obsolete, underpowered and under armored TBD Devastators was chopped to pieces as they attempted torpedo attacks on the First Carrier Strike Force of Admiral Nagumo losing 10 of 14 aircraft. As the gallant air crews of Torpedo Six along with Yorktown’s Torpedo 3 and Hornet’s ill-fated Torpedo Eight made their attacks Bombing Six under the command of CDR Wade McCloskie and Scouting Six under the command of LT Dick Best attacked and mortally wounded the Japanese Flagship Akagi and the Soryu. Later in the day aircraft from Enterprise would help sink the Hiryu and the following day helped mortally wound the Heavy Cruiser Mikuma. The Enterprise was not damaged by the Japanese at Midway.
 Flight Operations on Enterprise
Flight Operations on Enterprise
Following the Miracle at Midway the Enterprise took part in the Guadalcanal campaign participating in the invasion as well as the Battles of Santa Cruz and the Eastern Solomons. In each of these actions she was seriously damaged but her air group was instrumental in the campaign at sea and ashore. Following the sinking of the Wasp, Hornet and damage to Saratoga Enterprise was the only US carrier in action in the fall of 1942.
 Enterprise under attack at the Battle of Santa Cruz Islands
Enterprise under attack at the Battle of Santa Cruz Islands
 Bomb Explosion on Enterprise at the Battle of Eastern Solomons
Bomb Explosion on Enterprise at the Battle of Eastern Solomons
In November she took part in the Naval Battle of Guadalcanal where her aircraft helped to finish off the Japanese battleship Hiei and participated in the sinking of 16 Japanese ships including transports which carried troops, equipment and supplies to the Japanese defenders of Guadalcanal. After another 6 months of action in the Solomons supporting the US advance Enterprise returned first to Pearl Harbor at which time she was awarded the Presidential Unit Citation by Admiral Chester Nimitz, the first carrier awarded the citation in the Second World War and then to Bremerton for a badly needed overhaul.
Enterprise was back in action by November 1943 and participated in the US offensives in the Gilberts, Marshalls and the Marianas taking part in numerous raids, support to Marines ashore and in the Battle of the Philippine Sea, the Marianas Turkey Shoot. After a month long refit at Pearl Harbor she participated in the attacks on the Volcano, Bonin and Palau including strikes on Yap and Ulithi followed by the fast carrier raids on Japanese facilities on Okinawa, Formosa and the Philippines which culminated in her participation in the Battle of Leyte Gulf, the largest naval battle in history. Her aircraft would participate in strikes on each of the Japanese surface forces hitting battleships, cruisers and other Imperial Navy units in the epic naval battle.
Enterprise made a short return trip to Pearl Harbor in December 1944 where she embarked an air group trained in night operations. Rejoining the fleet she took part in sweeps against Japanese bases, ships and facilities in Indochina, the Philippines, Formosa and Okinawa prior to the invasion of Iwo Jima.
During this operation her aircraft worked night and day to provide air strikes and air defense to the fleet. She then joined the raids against Honshu, Kyushu and the Inland Sea where her aircraft provided night strikes against Japanese targets ashore as well as air defense to fleet units. She was damaged by a Japanese bomb on the 18th of March and on 11 April damaged by Kamikazes off Okinawa and again on 5 May prior to her last wound of the war on 14 May when a Kamikaze struck forward elevator necessitating repairs at Bremerton.
 Kamikaze Damage or forward elevator
Kamikaze Damage or forward elevator
Returning to the fleet to late for the final actions of the war Enterprise took part in Operation Magic Carpet returning US troops to the United States at the end of hostilities. She was decommissioned on February 17th 1947. While she was in reserve the Enterprise was redesignated first as an Attack Aircraft Carrier (CVA), and then as Anti-submarine Carrier (CVS).
 Enterprise Fleet Week New York 1945
Enterprise Fleet Week New York 1945
As the super-carrier entered the scene and the Essex and Midway Classes were modernized to accommodate jet aircraft the Enterprise was determined to be in excess of Navy needs. Despite attempts by some to save her as a Naval Museum the money could not be raised, even with the support of the dying Fleet Admiral Bill Halsey. Enterprise which Secretary of the Navy Forrestal said was “the one vessel that most nearly symbolizes the history of the Navy in this war” was sold for scrap on 1 July 1958 and scrapped at Kearney New Jersey from September 1958 to March 1960. Like so many ships which serve their country so well she was casually disposed of by a nation which had forgotten its past.
 Enterprise alongside new CVA 1958
Enterprise alongside new CVA 1958
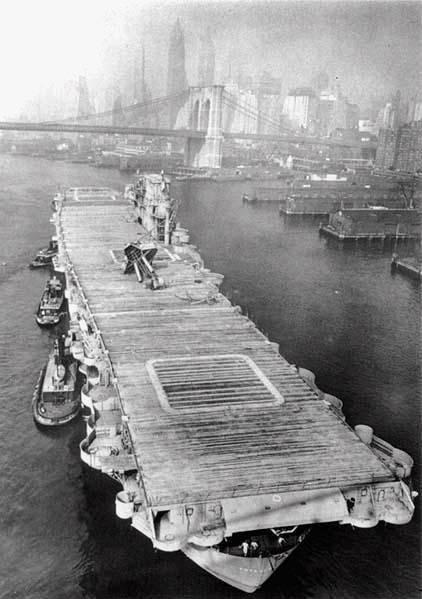 Enterprise on the way to the breakers
Enterprise on the way to the breakers
Enterprise was the only ship to receive both the Presidential and Naval Unit Citations for her service in World War Two and she was awarded the Asiatic-Pacific Campaign Medal with 20 battle stars. Her place in the carrier force would be taken by a new Enterprise, CVN-65, the First Nuclear carrier which after nearly 50 years of service is still in commission. The Enterprise is so significant that her legacy continues in Hollywood Science fiction in the various Star Trek series as the Federation Starship Enterprise NCC-1701, 1701-A, 1701-B, 1701-D and 1701-E, so much so that NASA named the first experimental Space Shuttle Enterprise.




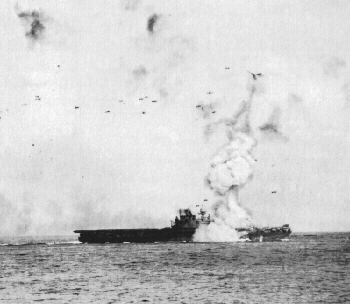
































 Aircraft over Saratoga
Aircraft over Saratoga USS Langley CV-1 The “Covered Wagon”
USS Langley CV-1 The “Covered Wagon”  Langley after conversion to AV-3
Langley after conversion to AV-3 USS Lexington CV-2
USS Lexington CV-2 USS Saratoga CV-3
USS Saratoga CV-3 Lexington Burning and Sinking
Lexington Burning and Sinking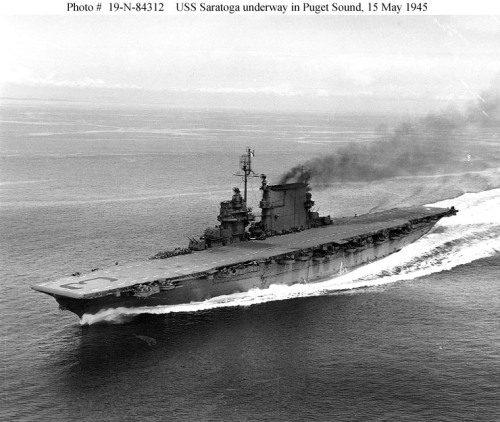 Saratoga 1945
Saratoga 1945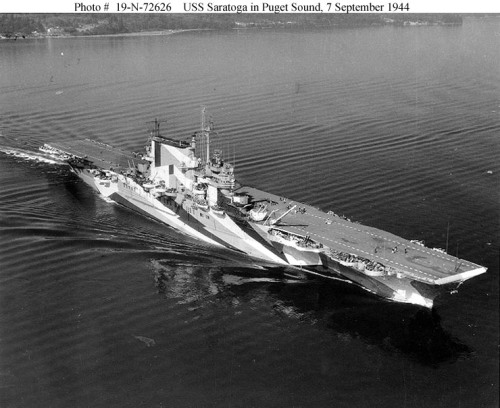 Saratoga September 1943
Saratoga September 1943 Saratoga burning after Kamikaze hits in 1945
Saratoga burning after Kamikaze hits in 1945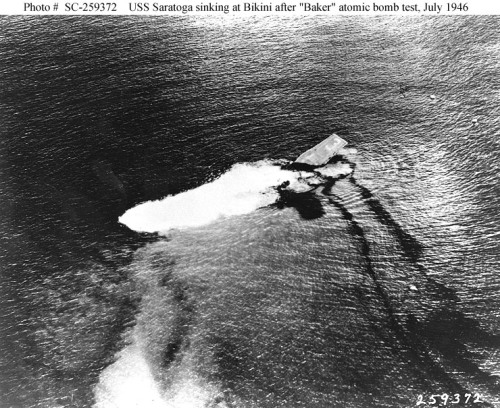 The End of an Era- Saratoga goes down at Bikini
The End of an Era- Saratoga goes down at Bikini Easter aboard USS Hue City CG-66 off the Horn of Africa 2002
Easter aboard USS Hue City CG-66 off the Horn of Africa 2002