Friends of Padre Steve’s World
This is the final part of my rendition of the great naval tragedy in three acts involving the German Battleship Bismarck. The first part was the sinking of the legendary and graceful pride of the Royal Navy, the Battle Cruiser Hood. The second part was the seemingly futile hunt and chase of the Bismarck by units of the British Home Fleet. What seemed hopeless changed when hours from the protection of night Bismarck was discovered and then torpedoed in a last ditch effort by Swordfish torpedo planes from the HMS Ark Royal. Today, the final act, the sinking of the Bismarck.
I have written about this before and this is an edited version of that article. As I have mentioned before I have long been fascinated with this naval tragedy. I call it that because I have served at sea and in combat ashore; and because I understand that amid all the technology and weaponry that ultimately it is the men who suffer the terrors of war, and who suffer and die who matter. Soldiers, Sailors, Marines and Airmen seldom get a choice in the wars that the leaders of their nations send them to fight. Thus for me, even the Sailors of the Bismarck, the pride of Adolf Hitler’s Kriegsmarine are as much victims of war as the British Sailors aboard the HMS Hood.
Peace
Padre Steve+
HMS King George V (above) and HMS Rodney (below)
The torpedo from the Swordfish from the HMS Ark Royal that struck the Bismarck in her stern, jammed her rudders and wrecked her steering gear at last light on May 26th 1941, doomed that remarkable ship and her crew. It was an astounding turn of events, as just minutes before both the Germans and the British were expecting Bismarck to reach safety to fight again.
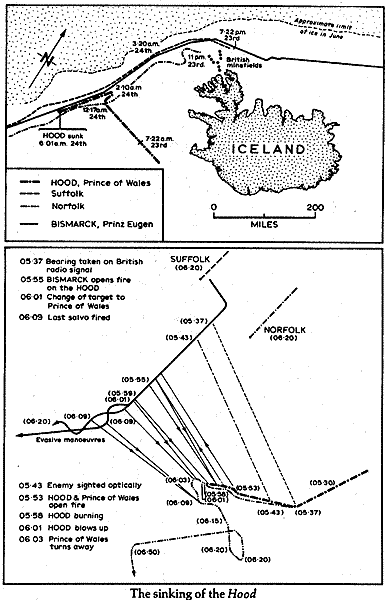
Just days before Bismarck had sunk the legendary British Battle Cruiser HMS Hood in minutes and had she persisted in her attack could have sunk the new Battleship HMS Prince of Wales. Instead, Vice Admiral Gunther Lutjens in command of the Bismarck and her consort the Heavy Cruiser Prinz Eugen decided to break off contact and make for safety in the French port of Brest.
Bismarck slipped her pursuers and allowed Prinz Eugen to escape. It seemed that nothing that the British could do would stop her from gaining the safety of the French port and with it the knowledge that she had sunk the most powerful ship in the Royal Navy and gotten away. Then out of nowhere Bismarck was spotted by a Royal Air Force Coastal Command PBY Catalina seaplane piloted by an American Naval Officer. Hours later a relatively small and slow torpedo dropped from an obsolescent Swordfish torpedo bomber, a stringbag hit the Bismarck in in her stern, wrecking her rudders and steering gear. Remarkably it was perhaps the only place that such a torpedo could have changed the developing narrative of a great German naval victory into defeat.
As darkness fell on May 26th, Bismarck, unable to steer towards Brest due to her damage and the following seas steered toward the oncoming British armada at a reduced speed. Her crew, now exhausted from countless hours on watch and at their battle stations knew that they were doomed.
Despite this the officers and sailors aboard Bismarck still labored trying in vain for a way to repair and save their their ship. As Bismarck’s engineers and damage control personnel sought at way to repair the damage on that dark night Royal Navy destroyers under the command of Captain Phillip Vian harassed her, closing to fire torpedoes and keep the exhausted crew of the mighty German ship engaged at their battle stations throughout the long night. Knowing that the end was near the Captain of the Bismarck ordered the contents of the ship’s store to be given to crew members.
Bismarck under Fire from King George V and Rodney
As light broke on the morning of May 27th the remaining heavy units from the Home Fleet which still had enough fuel in their tanks to continue the action, the Battleships HMS King George V and HMS Rodney along with the Heavy Cruisers HMS Norfolk and HMS Dorsetshire which had broke from its convoy escort duties on the 26th closed in for the kill. Norfolk had been in on the hunt since the beginning when she and her sister ship the HMS Suffolk had discovered Bismarck and Prinz Eugen as the transited the Denmark Strait on the night of May 23rd and 24th.
Bismarck from Dorsetshire
Warily the British ships closed the crippled but still powerful German battleship. At 0847 Admiral Tovey ordered British Battleships to open fire on Bismarck. The crippled German ship replied with accurate salvos and straddled Rodney. However, the British shells hammered the Bismarck. 16” shells from Rodney destroyed the command center of Bismarck and her main fire control stations. Within 30 minutes the mighty guns of the Bismarck which had sunk the Hood days before were silenced. With no opposition from the stricken German ship the British battleships and cruisers pounded Bismarck from point blank range with 16”, 14”, 8” and 6” shells as well as torpedoes.
The end of the Bismarck
The British ships scored at least 400 hits on Bismarck and though they had silenced her and reduced the German ship to smoking ruins, the Bismarck remained afloat, defying her attackers. She was burning and certainly doomed but undaunted. The British battlewagons pounded Bismarck, until finally, with their adversary obviously doomed and their own fuel supplies dangerously low, Admiral Tovey ordered the battleships to break off the action. As he did this the British cruisers continued to fire their guns and torpedoes at the blazing helpless ship.
Bismarck Survivors being hauled aboard Dorsetshire
The Bismarck’s First Officer, Fregattenkapitan (Commander) Hans Oels ordered her Chief Engineer Korvettenkapitan (Lieutenant Commander) Gerhard Junack to prepare the ship for scuttling and ordered the crew to abandon ship. The watertight doors were opened by Bismarck’s damage control teams and engineers as the scuttling charges fired at about the same time as HMS Dorsetshire launched her torpedoes at Bismarck. 1039 the Bismarck slipped beneath the waves. To this day those who claim the Bismarck sank because her crew scuttled her, and those who believe the the fish fired by Dorsetshire decided the fate of the ship, but truthfully it doesn’t matter. No matter what happened Bismarck was going to sink and no German forces could save her, or her crew.
HMS Dorsetshire 1941
With the great ship headed to the depths of the North Atlantic, hundreds of survivors bobbed about in the cold Atlantic waters. Of these men, 110 were rescued by British ships, mostly by Dorchester. Then lookouts aboard the cruiser spotted the periscope of a U-Boat, and the British ships broke off their rescue operations leaving hundreds more survivors to die of exposure or their wounds in the Atlantic. In a cruel twist of fate, the U-Boat they believed they spotted had expended all of its torpedoes and was not a threat to them. A few more of the Bismarck’s survivors were rescued later by German ships or U-boats, but about 2200 German sailors went down with their ship or died awaiting rescue that never came. When it was all over just 2 officers and 113 men survived the sinking of the Bismarck, combined with the three men who survived the sinking of the Hood nearly 3700 British and German Sailors perished.
Artist’s image of the Wreck of the Bismarck
Subsequent investigations of the wreck of the Bismarck would show that all the British shells and torpedoes did not sink the Bismarck, and that it was indeed the scuttling charges that sent the mighty ship to the bottom of the Atlantic. But even had she not been scuttled, she was doomed, and the damage that she had sustained would have sent her to the bottom within 12 to 24 hours had Commander Oels not ordered Lieutenant Commander Junack to scuttle the ship.
Within a year the Ark Royal, Prince of Wales, and Dorsetshire would also lie at the bottom of the seas. Prince of Wales along the HMS Repulse was sunk by Japanese land based bombers off Malaya in 1941, Dorsetshire was sunk near Ceylon by Japanese Carrier aircraft in April 1942, and Ark Royal was torpedoed by the U-Boat U-81 in November 1941 not far from Gibraltar. Of the destroyers that harassed Bismarck the night before her sinking only one, the Polish Destroyer ORP Piorun would survive the war.
The tragedy of mission of the Bismarck is that nearly 3700 sailors died aboard the two mightiest ships in the world, and while legendary the losses of the two ships did not materially alter the course of the war. Hood’s loss though tragic did not alter the strategic equation as more new battleships of the King George V class entered service. Likewise the surfing German capital ships were harassed by RAF bomber sorties and attacks by the Royal Navy’s Fleet Air Arm. With few exceptions these ships remained confined to ports in France, Germany or Norway and slipped into irrelevance as the war progressed as the German U-Boat force took the lead in the Battle of the Atlantic.
As an officer who has served at sea on a cruiser at war which came within minutes of a surface engagement with Iranian Revolutionary Guard patrol boats in the Northern Arabian Gulf in 2002 I have often wondered what would happened in the event of an engagement that seriously damaged or sank our ship. Thus I have a profound sense of empathy for the sailors of both sides who perished aboard the Hood and the Bismarck in the fateful days of May 1941.
I hope that no more brave sailors will have to die this way, but I know from what history teaches that tragedies like this will happen again.
Peace
Padre Steve+





































































 USS Pensacola
USS Pensacola HMS Exeter
HMS Exeter USS Houston with President Roosevelt Aboard
USS Houston with President Roosevelt Aboard Prinz Eugen
Prinz Eugen HMS Suffolk
HMS Suffolk USS San Fransisco Returning After the Naval Battle of Guadalcanal
USS San Fransisco Returning After the Naval Battle of Guadalcanal