Artist rendition of the Loss of the HMS Hood
Friends of Padre Steve’s World,
I am still working on my article on the Bismarck Class battleships which is the first of a series on the late Treaty and Post Treaty battleship. However, the research has been time consuming and Massive amounts of technical data on Bismarck and her contemporaries is making this a much more technologically wonk type of article than I expected. I am continuing to work on it, even though I had hoped to publish it before I went on to the history of Operation Rheinübung, the deployment of Bismarck and the heavy cruiser Prinz Eugen against British convoys in the hopes that they would sink and destroy a lot of ships and return to home safely as the Scharnhorst and Gneisenau had during Operation Berlin which sank 22 ships between February and March 1941, an operation commanded by Admiral Günther Lütjens who commander the Bismarck task force.
The Bismarck and Prinz Eugen set sail for Operation Rheinübung on 18 May 1941 over the protests of Lütjens’s protest to delay the operation until Scharnhorst could be repaired d Tirpitz was fully operational. However, this was not possible until early July, and Grand Admiral Erich Raeder had his own agenda. Of the participants in the operation, only he knew that Hitler had planned to attack the Soviet Union on 22 June 1941. That invasion, Operation Barbarossa gave the Kriegsmarine just a small supporting role compared to the Heer, Luftwaffe, and even the SS. So Raeder ordered Lütjens into action in order to score a success that would enable him to continue to argue the need for more battleships and surface forces. Reader instructed Lütjens to not reveal the planned operation to anyone, including Hitler, which Lütjens obeyed when Hitler visited Bismarck on 5 May without Raeder being present. Concerning the operation itself Raeder’s orders to Lütjens stressed that “The primary target in this operation is the enemy’s merchant shipping; enemy warships will be engaged only when that objective makes it necessary and it can be done without excessive risk.”
On 20 May the German ships were sighted numerous Swedish and Norwegian fishing boats, and by a scout plane from the Swedish Cruiser Gotland which reported their position to the Swedish Admiralty. This information was leaked to the British Naval Attaché and relayed to the British Admiralty: “Kattegat, today 20 May. At 1500, two large warships, escorted by three destroyers, five ships and ten or twelve planes, passed Marstrand to the northeast. 2058/20.”
They were also sighted by a Norwegian agent who sent a report of their presence. On 21 May the two ships arrived in Grimstadfjiord near Bergen in order to allow Prinz Eugen to refuel, however Lütjens elected not to top off Bismarck’s fuel tanks, which would prove to be a fatal mistake.
May 21st was a day where the skies were perfectly clear, and alerted to their presence of the German Force, the Royal Air Force sent reconnaissance aircraft to confirm that they were really on the move. At 1315 hours a Spitfire equipped with onboard high altitude cameras spotted the German Force and returned to Scotland where their photos were sent to the Admiralty. As a result the Royal Navy ultimately mobilized six battleships, three battlecruisers, two aircraft carriers, sixteen cruisers, thirty-three destroyers and eight submarines to find and kill the German ships and to protect the 11 convoys currently at sea or preparing to sail. It was the largest deployment of the Royal Navy for a single operation to that point in the war.
Since the daylight prevented an unobserved departure, Admiral Lütjens decided to depart under cover of darkness for his breakout into the North Atlantic. Likewise, Admiral John Tovey, commander of the Home Fleet began his deployment to find and sink the Bismarck. Not knowing which route the Bismarck would use to break out, Tovey sent the pride of the Royal Navy, the “Mighty” HMS Hood and the brand new King George V Class battleship HMS Prince of Wales and four destroyers to join the heavy cruisers HMS Norfolk and HMS Suffolk under the command of Rear Admiral Frederick Wake Walker to Guard the Denmark Strait, which Lütjens had used earlier in the year with Scharnhorst and Gneisenau, and sent the modern and powerful light cruisers Manchester and Birmingham to patrol the area southeast of Iceland. In addition he kept several light cruisers on station between the Faroe and Orkney Island Gap in case the Germans attempted a straight run through the British blockade.
Early on 22 May Tovey departed Scapa Flow with King George V, the new carrier HMS Victorious, and their escorts, which would soon be joined by the battlecruiser HMS Repulse. which was already at sea. The older battleships HMS Rodney, HMS Ramillies, and HMS Revenge were also at sea escorting convoys, from which they would be detached to seek out the Bismarck. Finally, Force H comprised of the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal, battlecruiser HMS Renown, the light cruiser HMS Sheffield and their escorting destroyers, under the command of Rear Admiral James Somerville, based at Gibraltar, were alerted for possible deployment to the North Atlantic, even though their primary mission was to counter the Italians in the Mediterranean.
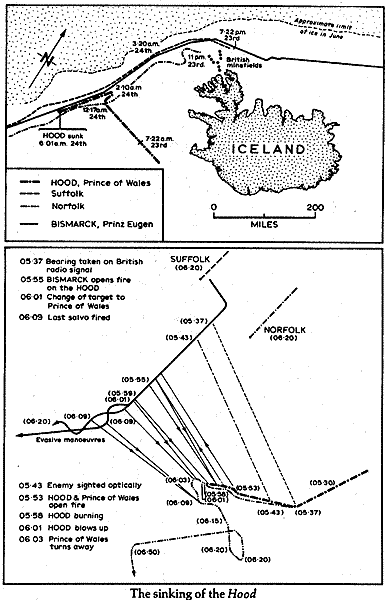
The 22nd of May was uneventful as each side sailed into the reaches of the North Atlantic, as was most of the 23rd as Bismarck and Prinz Eugen were able to use foul weather conditions to avoid British patrol aircraft, but but about 2000 hours they were detected by the radar of HMS Suffolk. Bismarck sighted and engaged Suffolk and Norfolk which returned fire and ducked into a fog bank as Suffolk continued to shadow Bismarck using her radar and continuing to send reports to Admiral Holland on Hood. However during the exchange Bismarck’s forward radar was damaged by the concussion of her main battery and Lütjens had Prinz Eugen take the lead. For the remainder of the night the ships continued to move through the Denmark Strait. Knowing his Force had been detected and surprise had been lost Lütjens could have reversed course and returned to Norway to await the availability of Scharnhorst and Tirpitz and a more favorable time to break out, but he continued on to a destiny that would result in the loss of the world’s two largest battleships in one of the most dramatic naval campaigns in history.
The first of the great ships lost would be the “Mighty Hood”, which was sunk by the Bismarck and Prinz Eugen during a very short and shocking engagement on the morning of 24 May. The news was broken to most of the world by American journalist Edward R. Murrow who in his radio broadcast reported:
“This is London, Ed Murrow reporting. This island, which is no stranger to bad tiding, received news today that HMS Hood largest warship in the British fleet and pride of the British navy, has been sunk by the German battleship Bismarck. From the Hood’s compliment of 1500 men, there were three survivors.”
The news of the sinking of the great ship stunned the world, and it is a tragic anniversary is something that I always mark. I first read about this battle in C.S Forrester’s little book Hunting the Bismarck when I was in 4th grade. That book was used as the screenplay for the 1960 film Sink the Bismarck.
This essay is in honor of the gallant HMS Hood and her crew. It is fitting for Memorial Day weekend although the HMS Hood and her killer, the German battleship Bismarck were not American. Both were great ships manned by gallant crews and the loss of both ships was tragic, especially from the aspect of the great loss of human life. I do hope and pray that we never forget the sacrifice of these men and all others who have gone down to the sea in great ships.
HMS Hood at Malta
There are some warships and naval engagements which assume legendary proportions. The Battle of the Denmark Strait on 24 May 1941 between the two largest battleships in commission at the time, the pride of the British Royal Navy the HMS Hood and the German behemoth Bismarck is legendary as are those two mighty ships. The battle came at a critical time as the Britain stood alone against the seemingly invincible German Blitzkrieg.
Hood in San Francisco on 1920s goodwill tour
Britain had been driven from Western Europe and Britain was being bombed regularly by Hermann Goering’s Luftwaffe. In the Balkans a British expeditionary force that had been sent to Greece had been defeated and it’s survivors withdrawn as Germans assaulted and conquered Crete with airborne forces, albeit with such heavy losses that Hitler forbade any more large airborne operations. In the Western Desert of North Africa, the Afrika Korps under Field Marshall Erwin Rommel had driven off a British counter-offensive on the Libyan-Egyptian frontier and were laying siege to Tobruk. In the Atlantic German U-Boats sank 66 Allied Merchant Ships of over 375,000 tons and the Royal Navy would lose 25 warships not including the Hood to surface action or U-Boats in the Atlantic alone. But before Hood the British had lost the aircraft carriers Glorious and Courageous and the battleship Royal Oak.
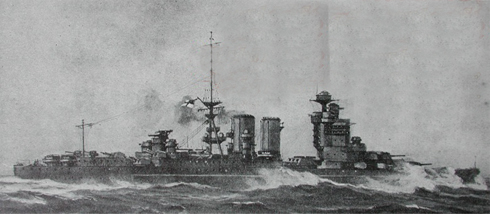
The Hood was the pride of the Royal Navy and was world famous due to her inter-war international presence and goodwill visits. She displaced 47,430 tons full load and she was armed with eight 15” guns in four twin turrets. Designed as a battle cruiser she was less heavily armored than contemporary battleships and had weak vertical protection from plunging shellfire. Her armored upper deck and armored deck had a combined 83mm of armor. This was a fault which was known but never rectified between the wars and when the war came the Royal Navy could ill-afford to take her out of service for the necessary improvements to her protection system. She was fast with a designed speed of 31 knots which been reduced to 28 knots by 1939 as a result of modifications which increased her displacement. This was further reduced by the wear and tear on her propulsion plant to 26.5 knots by 1940.
Hood was designed before the battle of Jutland (May 1916) where the weaknesses in the armor protection of British Battlecruisers was exposed as three, the HMS Invincible, HMS Queen Mary and HMS Indefatigable were destroyed by plunging fire which exploded their magazines. Though her design was modified during construction she still was vulnerable to plunging fire. She was scheduled for a major refit which would have included significant improvement in armor protection in 1941, but the war prevented Hood from receiving anything more than improvements to her anti-aircraft batteries.
Hood (nearly hidden by falling shells) in action at Mers-El-Kebir
During the war Hood was engaged in patrol and search operations against German raiders in the North Atlantic and in June 1940 joined Force “H” in the Mediterranean. As Flagship of Force “H” she took part in the sinking of French Fleet Units including the Battleship Bretagne at Mers-El-Kebir on 3 July 1940 following the French surrender to the Germans and remained in operation searching for the German Pocket Battleship Admiral Scheer and the Heavy Cruiser Admiral Hipper until she was withdrawn for a brief refit in January 1941.
Following another brief refit in mid-March, Hood was underway from mid-March searching for the German raiders Scharnhorst and Gneisenau and also false report of Bismarck breaking out into the Atlantic in April 1941. She returned to Scapa Flow on 6 May 1941.
Bismarck
Bismarck was slightly larger than Hood and mounted the same main armament but that was about all the two ships had in common. If the battle was a battle between heavyweight prize fighters Hood was the valiant but crippled champion and Bismarck the young and overpowering challenger. Bismarck was slightly faster than the limping Hood and was one of the most well protected ships ever built. Her gunnery officers and the men that manned her deadly 15” guns were like previous generations of German sailors, gunnery experts, working with some of the finest naval guns ever made.

Bismarck firing on Hood
The German ships were shadowed at a distance by the Norfolk and Suffolk. The German task force under the command of Admiral Gunther Lütjens emerged from the strait and were sighted by the British at 0537. Knowing his ships weakness in regard to plunging fire Admiral Holland desired to steer a direct course at the German ships in order to close the range quickly in order to narrow the range and prevent being hit by the same kind of plunging fire that doomed the British battle cruisers at Jutland.
However, events dictated otherwise and the British were forced to close the range much more slowly than Admiral Holland desired, and exposed both Hood and Prince of Wales to German plunging fire for a longer period of time. As such Holland then turned and tried to close the German ships faster. The result was that his gunnery was degraded by wind and spray coming over the bows of his ships compounded by his inability to bring his after turrets to bear on the German ships.
Hood, photographed from Prince of Wales moments before being hit and sunk by Bismarck
At 0553 Holland ordered his ships to open fire. Unfortunately, he dis so without the benefit of Suffolk and Norfolk being in position to engage the Prinz Eugen. Due to the similar appearance of the German ships Hood initially concentrated her fire on Prinz Eugen assuming her to be the Bismarck while Prince of Wales engaged Bismarck.
During the initial exchange of fire Prince of Wales drew first blood by hitting Bismarck three times with her 14″ guns. One hit damaged Bismarck’s seaplane catapult. A second did minor damage to machinery spaces, and a third which passed throughBismarck’s bow near the waterline and severed the fuel lines from her forward fuel tanks to her engines. The third hit would prove the might German Leviathan’s undoing.
Prinz Eugen
Both German ships opened fire at 0555 and concentred their fires on the Hood. Prinz Eugen immediately hit Hood with at least one 8” shell which set a large fire among the ready to use 4”ammunition stored in lockers near the mainmast. The hit started a large fire which Hood’s damage control teams raced to contain. At 0600, Admiral Holland ordered his ships to turn to port in order to bring the rear turrets of his battleships into the fight.
As the squadron executed the turn Hood was straddled by a salvo from Bismarck and observers on Prince of Wales observed an explosion between “X” turret and the mainmast of Hood. The hit set off the 4″ magazine and the resultant explosion consumed the Hood causing her bow to jut sharply out of the water before sinking beneath the waves in under 3 minutes time. Witnesses on both sides of the engagement were stunned by the sudden and violent end of the Hood.
With Hood now destroyed the Germans rapidly shifted their fire to the Prince of Wales, crippling the battleship and knocking her out of the action. Bismarck was now in a perfect position to finish off Prince of Wales but she did not do so. Against the advice of Bismarck’s Captain Ernst Lindemann, Admiral Lütjens refused to follow up his advantage to sink the crippled British battleship and instead broke off the action.
Hood blows up. Drawing by the Captain of HMS Prince of Wales J.C. Leach
Only three crewmen for Hood, Petty Officer Ted Briggs, Seaman Bob Tilburn and Midshipman Bill Dundas survived the cataclysm out of a total of 1415 souls embarked. They were rescued 4 hours later nearly dead of hypothermia. They stayed awake by singing “Roll out the Barrel” until they were rescued by the destroyer HMS Electra.
Briggs who died in 2008 recounted the sinking:
“Then she started listing to starboard. She righted herself, and started going over to port. When she had gone over by about 40 degrees we realised she was not coming back…” Briggs was sucked under the water “I had heard it was nice to drown. I stopped trying to swim upwards. The water was a peaceful cradle – I was ready to meet my God. My blissful acceptance of death ended in a sudden surge beneath me, which shot me to the surface like a decanted cork in a champagne bottle. I turned, and 50 yards away I could see the bows of the Hood vertical in the sea. It was the most frightening aspect of my ordeal, and a vision which was to recur terrifyingly in nightmares for the next 40 years.” (The Daily Telegraph 5 October 2008)
Ted Briggs
Bob Tilburn
The Admiralty reported the loss of the Hood later in the day saying Hood “received an unlucky hit in a magazine and blew up.” The official report of the sinking released later in the year said:
“That the sinking of Hood was due to a hit from Bismarck’s 15-inch shell in or adjacent to Hood’s 4-inch or 15-inch magazines, causing them all to explode and wreck the after part of the ship. The probability is that the 4-inch magazines exploded first.”
The commission’s findings have been challenged by a number of naval historians and there are several theories of how the magazines might have exploded. However, all theories point to a massive magazine explosion which may not have be caused by a plunging round but from a hit which detonated the unprotected 4” magazines or a hit from Bismarck that struck below Hood’s waterline and exploded in a magazine.
For forty years the Hood’s wreckage lay undiscovered. Her wreck was located in 2001 lying across two debris fields. The post mortem examination revealed that Hood’s after magazines had exploded. Hood’s resting place is designated as a War Grave by Britain and protected site under the Protection of Military Remains Act of 1986.
Bismarck sinking
Bismarck and her crew did not long survive her victory. When close to refuge in the French port of Brest on May 26th the great ship was crippled by a lucky aerial torpedo hit from a Fairley Swordfish bomber flying from the HMS Ark Royal.
The hit damaged Bismarck’s rudders and forced her to steer a course towards the approaching British fleet. Throughout the night Bismarck fought off attacks by British and Polish destroyers on the morning of May 27th 1941, after absorbing massive damage from the HMS King George V, HMS Rodney and several cruisers including HMS Dorsetshire, he plucky and persistent Norfolk and several destroyers, Bismarck was scuttled by her crew. When she went down she took with her all but 115 souls of her crew of over 2200 which included the Fleet Staff of Admiral Lütjens.
HMS Prince of Wales
A few months later, Prince of Wales would take Winston Churchill to Argentia Bay Newfoundland to meet with Franklin Roosevelt. At the conference that took place in August 1941, the Atlantic Charter was drafted. With the increased threat of Japanese expansion Prince of Wales reported to the Far East where she was sunk along with the Battlecruiser HMS Repulse on 9 December 1941 by a force of land based Japanese aircraft. The Prinz Eugen was the only heavy ship of the German Navy to survive the war and was taken as a prize by the US Navy when the war ended. She was used as a target during the Able and Baker nuclear tests at Bikini Atoll, but did not sink. She was too radioactive to be repaired and her hulk was towed to Kwajalein Atoll where she capsized and sank on 22 December 1946. Her wreck is still visible.
The loss of the Hood traumatized the people of Britain and the Royal Navy; she had been the symbol of British Naval power for over 20 years and people around the world were likewise stunned at her demise. The sinking of the Hood and the loss of her crew was a tragedy which all sailors assigned to large and prestigious ships and the nations that they sail for need to keep in mind.
No matter how mighty any ship may be, every ship has an Achilles heel and no ship is unsinkable, and human beings bear the brunt of such tragedies. Of the over 3600 officers and crew of the Hood and the Bismarck only 118 survived.
I will continue to remember the gallant Hood, her brave crew, especially my very distant relative Midshipman Bill Dundas who I never met. He left the Royal Navy with the rank of Lieutenant Commander in about 1960, and was killed in a car wreck in 1965. According to the Hood Association website he was troubled by the sinking for the rest of his life. I think that I could understand as I am still troubled by my far less traumatic experience of war in Iraq.
Until tomorrow,
Peace
Padre Steve+