Friends of Padre Steve’s World,
It has been a very busy couple of days so I am reaching back deep into the archives to re-post an old article about the British King George V Class battleships of the Second World War. These ships and their brave crews were of great importance to the Allied cause. Sadly, like so many great ships of that war all the surviving ships were scrapped due to measures of austerity and obsolescence and none preserved to honor their service or crews.
Hope to post something fresh tomorrow,
Peace’
Padre Steve+
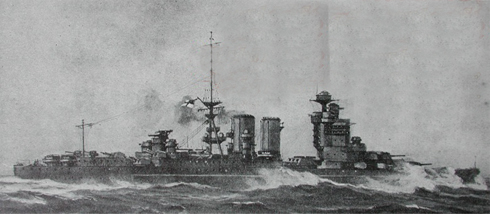
HMS King George V
This is the third in a series of five articles on the battleships built under the provision of the Washington and London Naval Treaty limitations in the 1930s. I am not including the ships which were completed in the immediate aftermath of the Washington Treaty limitations. This series looks at the modern battleships that the World War II combatants would produce in the 1930s which saw service in the war. This article covers the British Royal Navy King George V Class battleships. Part one covered the Italian Vittorio Veneto class entitled The Pride of the Regina Marina: The Vittorio Veneto Class Battleships. Part two French Firepower Forward: The unrealized potential of the Dunkerque and Richelieu Class Battleships covered the French Dunkerque class and Richelieu class Battleships. Part Four the American North Carolina and South Dakota Classes. I have already published the final part which covers the German Scharnhorst Class entitled Power and Beauty the Battle Cruisers Scharnhorst and Gneisenau. The German Bismarck, Japanese Yamato, British Vanguard and American Iowa Classes will be covered in a subsequent series.
HMS King George V in 1941
In the wake of the First World War the major naval powers entered into an agreement restricting the construction of capital ships and limiting the numbers that treaty signatories were allowed to keep. As a result numerous ships were scrapped or disposed of and the majority of planned ships were either cancelled while building or never laid down. In some cases to comply with treaty restrictions ships such as the Royal Navy’s Nelson Class which was a compromise design which sacrificed speed for protection and firepower. By the late 1920s the Royal Navy’s battle force was comprised of the Nelson’s, the fast Battlecruisers Hood, Renown and Repulse and 10 ships of the Queen Elizabeth and Revenge classes all designed before the First World War.
King George V Class Quad Turret being built
The Royal Navy began planning for a new class of battleships in 1928 but the plans were shelved with the signing of the London Naval Treaty which continued the “building holiday” on capital ship construction as well as size and armaments until 1937. With the realization that its battle force was becoming dated as other nations laid down new classes of battleships the Royal Navy recommenced planning in 1935. The Navy planned to build to the maximum of the 35,000 displacement limitation and placed a great measure of emphasis on armor and protection. The ships were designed to achieve a 28 knot speed which made them faster than all British battleships although slower than the Battlecruisers.
The planners had alternative designs to use 14”, 15” or 16” guns with the Navy favoring the 15” models which had equipped all of their other ships with the exception of the Nelson’s. However the Admiralty to use 14” as the government was endeavoring to negotiate with other powers to impose a 14” limitation on armament for new battleships. While the Americans and French agreed to the limit neither the Japanese nor Italians followed suit and as a result all new battleships of other powers had larger guns than the King George V Class ships with the French and Italians opting for 15”on the Richelieu and Vittorio Veneto Class, the Americans 16” on the North Carolina, South Dakota and Iowa Classes and the Japanese 18” guns for their Yamato Class. The Germans who were not a signatory built their Scharnhorst Class with 11” although they were planned as 15” ships and would equip the Bismarck Class with 15” guns. The Royal Navy attempted to rectify this by placing more guns on the ships than those of other navies but the planned armament of twelve 14” guns mounted in quadruple turrets but this was impossible on the 35,000 platform without compromising protection or speed. Thus the Admiralty compromised on 10 guns mounted in 2 quadruple and 1 twin turret.
ONI Drawing of King George Class
The ships displaced a full load displacement of 42,237 tons in 1942 which had increased to 44,460 tons in 1944. The were 745 feet long had a beam of 103 feet, a top speed of 28 knots with a cruising range of 5,400 nautical miles at 18 knots. Their relatively poor endurance limited their operations in the Pacific and even nearly caused King George V to have to abandon the chase of the Bismarck in May 1941.
The main batteries of the ships proved problematic in combat with the quadruple turret design causing all the ships problems. This was demonstrated in the engagement of the Prince of Wales against the Bismarck as well as the King George V in its duel with the German behemoth when A turret became disabled and completely out of action for 30 minutes and half of the main battery being out of action for most of the engagement for mechanical reasons. The Duke of York achieved excellent results against the Scharnhorst but even in that engagement the main battery was only able to be in action 70% of the time. One of the other drawbacks of the design was that in order to replace a gun due to wear that the turret itself had to be dismantled in order to remove and replace the guns.
The main secondary armament of 5.25” dual purpose guns in twin mounts suffered from poor rate of fire and slow traverse well below their designed standards.
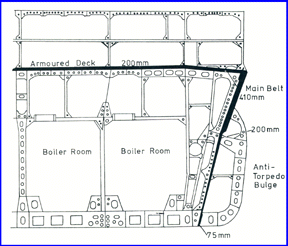
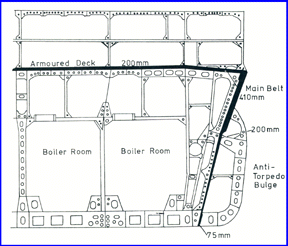
The mounting of the armament was designed to provide protection against turret explosions which could potentially detonate the ship’s magazines. The main side and underwater protection scheme was sound and protected the ships well in combat. The vertical protection was also sound as was the protection afforded to the turret barbets and placement of the magazines to shield them from plunging fire. Only the Prince of Wales was lost due to enemy action had later examination of her wreck revealed that the culprit was a torpedo which detonated in a propeller shaft outside of the armored belt which caused uncontrolled flooding when she was attacked by Japanese aircraft on 8 December 1941.
HMS Anson conducting gunnery exercises
The propulsion systems developed problems after 1942 when fuel oil quality was decreased because of the need for aviation gas. The new mixtures which were higher viscosity and contained more water than the boilers could effectively burn increased maintenance costs and decreased efficiency. To compensate the Admiralty designed new higher pressure fuel sprayers and burners which returned the boilers to full efficiency.
The lead ship of the class the King George V was laid down on 1 January 1937, launched on 21 February 1939 and commissioned on 11 December 1940. As the flagship of the Home Fleet she took part in the unsuccessful search for the Scharnhorst and Gneisenau and in the hunt for the Bismarck in which she earned lasting fame in helping to sink that ship. She took part in the Murmansk convoy protection as well as Operation Husky, the invasion of Sicily before sailing to the Far East for operations against the Japanese. She finished the war with the British Pacific Fleet and was present at the Japanese surrender in Tokyo Bay. She returned as flagship of Home Fleet until she was decommissioned in 1949. She was subsequently sold for scrap in 1957.
Prince of Wales pulling into Singapore, December 1941
The second ship the Prince of Wales laid down on 1 January 1937, launched on 3 May 1939 and commissioned 19 January 1941 although she was not officially completed until March 1941. Her initial operation came in May 1941 when she sailed with the HMS Hood to intercept the Bismarck. When she sailed she still had shipyard technicians aboard. Damaged in the action she did score an important hit on Bismarck which cut a fuel line making her forward tanks inaccessible and causing her to make her run for Brest which she did not complete. Another hit damaged her aircraft catapult and a third an electric dynamo.
Church Service on Prince of Wales at Argentia Bay with Churchill and Roosevelt in attendance
Following repairs she carried Winston Churchill to the Argentia Bay Newfoundland where he met with Franklin D. Roosevelt and together drafted the Atlantic Charter. She accompanied the HMS Repulse to Singapore to bolster the British presence in the Far East but without air cover was sunk by Japanese aircraft which struck her with 4 torpedoes and a bomb, the key hit being a lucky hit on her propeller shaft which caused flooding that caused a loss of power to pumps and anti-aircraft defenses.
Prince of Wales sinking and being abandoned
The third ship the Duke of York was laid down 5 May 1937, launched on 28 February 1940 and commissioned 4 November 1941. She provided convoy escort for the Lend Lease convoys to the Soviet Union as well the sinking of the Scharnhorst on 26 December 1943 during the Battle of North Cape. She was transferred to the Pacific in 1944 and served at Okinawa. She was decommissioned in 1949 and scrapped in 1957.
Duke of York
The fourth ship of the class the Howe was laid down on 1 June 1937, launched 9 April 1940 and commissioned on 29 August 1942. She served with the Home Fleet and in the Mediterranean until she was transferred to the Pacific in August 1944. She was stuck by a Kamikaze in May 1945 and Howe was sent for refit at Durban South Africa. She was still in refit when the war ended. She returned home and was placed in reserve in 1950 and scrapped in 1958.
HMS Howe
The last of the class the Anson was laid down 20 July 1937, launched 24 February 1940 and commissioned on 22 June 1942. She operated in the Mediterranean and the North Atlantic and was sent to the Pacific in 1945 where she accepted the surrender of the Japanese Forces at Hong Kong. She returned to Britain and was decommissioned in 1951 and scrapped in 1957.
HMS Anson
The ships had rather unremarkable careers for the most part with the exception of the Prince of Wales and King George V in the hunt for the Bismarck and the Duke of York sinking the Scharnhorst. They had a number of technical problems which limited their operations in the war. However they and their brave crews deserve to be remembered as helping to hold the line against the Axis in the early years of the war and sank two of the four German Battleships lost during the war. This alone was as remarkable achievement as of their contemporaries only the USS Washington sank an enemy battleship in combat.
The End: HMS Howe Being Scappped 1958