
I read a lot of political commentary and as a historian as well as a theologian I try to carefully examine mass movements such as the modern Tea Party Movement from a historical, theological and moral point of view. To do this as dispassionately as I can I look to history and attempt to find parallels to other movements and ideologies in the country concerned. For example if I am examining a movement in France, I look to French history for precedent, the same for any other country or region.
In regard to the Tea Party movement I have watched it since its inception in the fall of 2008 not long after I returned from Iraq. At the time I saw it as a protest against the massive failure of the American economy during the housing and stock market collapse involving the big banks and investment firms on Wall Street. I honestly did not believe that it would be a movement that has lasted as long as it has or would gain the amount of influence it has in the Republican Party. But then I saw it as a political and social protest and did not know enough about its leaders and their actual political ideology to make a serious connection to other political and social movements in U.S. History.
That being said, over the past six years I have had time to examine the movement, and while it is not monolithic there are within it many connections to previous American political movements, most of which would be classified as radically conservative. The movement is a curious combination of Libertarian leaning conservatives that preach a Libertarian form of unbridled Capitalism. There is also a religiously conservative element primarily composed of, but not limited to Evangelical Christians and conservative Roman Catholics focused more on social morality issues, particularly in regards to women’s issues, especially reproductive rights, abortion and homosexuality and LGTB rights and equality. There is also a collection of Second Amendment, or gun ownership proponents, anti-public education and pro-home school proponents, as well as others that advocate a number of conservative political beliefs, especially that of limited government. There is a highly volatile nativist element which has a nearly xenophobic world view, and a growing separatist militia movement that actively seeks confrontation with the Federal government.
However the movement does tend to mobilize over issues that they feel threaten their personal liberty, even if those issues have no actual effect on how they live their lives. This is particularly the case in terms of women’s issues and LGBT equality. This movement is particularly effective in taking political power at the local and state level and in many states have worked to roll back voting rights of minorities, particularly African Americans and uses the legislative and judicial process to advance their agenda, especially in terms of imposing a conservative Christian moral code on non-Christians or Christians that do not agree with them through the law, and this movement called Christian Dominionism is deeply ingrained in the personal philosophy and religious beliefs of many Tea Party leaders, both elected and unelected.
While many individual Tea Party members are moderate in their views, many are not and some advocate secession or overthrow of the present Federal government and are particularly united in their hatred of President Obama and any political official that will not completely embrace their agenda, thus Republican Tea Party members work to defeat moderate or conservative Republicans in primaries.
The thing is that none of this is new and that much of the current theology and philosophy in the Tea Party movement comes out of similar thought of the John Birch Society and well as the ante-Bellum South. While most Tea Party members would out rightly reject slavery, there often is a fair amount of racism displayed at their rallies, in their writings and in the declared goals of some groups. That is why that it is important to look to history, because the personal, religious, social and economic rights that many in the Tea Party embrace are directly concerned with limiting or rolling back the freedoms of minorities, women, immigrants and gays, thus the bridge to looking at the political, social, racial and religious issues that help to precipitate the American Civil War.
While the focus of this is on slavery, the same people who promoted the continued existence as well as expansion of slavery built a culture in which discrimination and the elevation of a political and social aristocracy was the goal. In addition to African Americans the leaders of the Southern states, especially the religious leaders fought tooth and nail against women’s suffrage, immigration, universal education and voting rights, especially for poor whites, who also for the most part were condemned to menial employment and hardscrabble farming whose social status was only just above that of African Americans. Those subjects, which are also very much a part of the modern Tea Party lexicon, each, could be addressed in its own article. But today I am focusing on the ideological differences between the North and the South related to the “particular institution” of slavery and briefly touch on other issues.
In his book Decisive Battles of the U.S.A. 1776-1981 British theorist and military historian J.F.C. Fuller wrote of the American Civil War:
“As a moral issue, the dispute acquired a religious significance, state rights becoming wrapped up in a politico-mysticism, which defying definition, could be argued for ever without any hope of a final conclusion being reached.” [1]
That is why it impossible to simply examine the military campaigns and battles of the Civil War in isolation from the politics polices and even the philosophy and theology which brought it about. In fact the cultural, ideological and religious roots and motivations of conflict are profound indicators of how savage a conflict will be and to the ends that participants will go to achieve their ends.
Thus the study of the causes of the American Civil War, from the cultural, economic, social and religious aspects which divided the nation, helps us to understand how those factors influence politics, policy and the primal passions of the people which drive them to war.
The political ends of the Civil War came out of the growing cultural, economic, ideological and religious differences between the North and South that had been widening since the 1830s. The growing economic disparity between the slave and Free states became more about the expansion of slavery in federal territories as disunion and war approached. This was driven by the South’s insistence on both maintaining slavery where it was already legal and expanding it into new territories and the vocal abolitionist movement. This not only affected politics, it affected religion and culture.
As those differences grew and tensions rose “the system of subordination reached out still further to require a certain kind of society, one in which certain questions were not publicly discussed. It must give blacks no hope of cultivating dissension among the whites. It must commit nonslaveholders to the unquestioning support of racial subordination….In short, the South became increasingly a closed society, distrustful of isms from outside and unsympathetic to dissenters. Such were the pervasive consequences of giving top priority to the maintenance of a system of racial subordination.” [2]
Edmund Ruffin
The world was changed when Edmund Ruffin a 67 year old farm paper editor, plantation owner and ardent old line secessionist from Virginia pulled the lanyard which fired the first shot at Fort Sumter. Ruffin was a radical ideologue. He was a type of man who understood reality far better than some of the more moderate oligarchs that populated the Southern political and social elite. While in the years leading up to the war these men attempted to secure the continued existence and spread of slavery within the Union. Ruffin was not such a man. He and other radical secessionists believed that there could be no compromise with the north. He believed that in order to maintain the institution of slavery the slave holding states that those states had to be independent from the North.
Ruffin’s views were not unique to him, the formed the basis of how most slave owners and supporters felt about slavery’s economic benefits, Ruffin wrote:
“Still, even this worst and least profitable kind of slavery (the subjection of equals and men of the same race with their masters) served as the foundation and the essential first cause of all the civilization and refinement, and improvement of arts and learning, that distinguished the oldest nations. Except where the special Providence and care of God may have interposed to guard a particular family and its descendants, there was nothing but the existence of slavery to prevent any race or society in a state of nature from sinking into the rudest barbarism. And no people could ever have been raised from that low condition without the aid and operation of slavery, either by some individuals of the community being enslaved, by conquest and subjugation, in some form, to a foreign and more enlightened people.”[3]
The Ante-Bellum South was an agrarian society which depended on the free labor provided by slaves and in a socio-political sense it was an oligarchy that offered no freedom to slaves, discrimination against free blacks and little hope of social or economic advancement for poor and middle class whites. Over a period of a few decades, Northern states abolished slavery in the years after the United States had gained independence. In the years the before the war, the North embraced the Industrial Revolution leading to advances which gave it a marked economic advantage over the South. The population of the North also expanded at a clip that far outpaced the South as European immigrants swelled the population.
The divide was not helped by the various compromises worked out between northern and southern legislators. After the Missouri Compromise Thomas Jefferson wrote:
“but this momentous question, like a fire bell in the night, awakened and filled me with terror. I considered it at once as the knell of the Union. It is hushed indeed for the moment, but this is a reprieve only, not a final sentence. A geographical line, coinciding with a marked principle, moral and political, once conceived and held up to the angry passions of men, will never be obliterated; and every new irritation will mark it deeper and deeper.”[4]
The trigger for the increase in tensions was the war with Mexico in which the United States annexed nearly half of Mexico. The new territories were viewed by those who advocated the expansion of slavery as fresh and fertile ground for its spread. Ulysses S Grant noted the effects of the war with Mexico in his memoirs:
“In taking military possession of Texas after annexation, the army of occupation, under General [Zachary] Taylor, was directed to occupy the disputed territory. The army did not stop at the Nueces and offer to negotiate for a settlement of the boundary question, but went beyond, apparently in order to force Mexico to initiate war….To us it was an empire and of incalculable value; but it might have been obtained by other means. The Southern rebellion was largely the outgrowth of the Mexican war.”[5]
In the North a strident abolitionist movement took root. It developed during the 1830s in New England as a fringe movement among the more liberal elites, inspired by the preaching of revivalist preacher Charles Finney who “demanded a religious conversion with a political potential more radical than the preacher first intended.” [6] Finney’s preaching was emboldened and expanded by the American Anti-Slavery Society founded by William Lloyd Garrison “which launched a campaign to change minds, North and South, with three initiatives, public speeches, mass mailings and petitions.” [7] Many of the speakers were seminary students and graduates of Lane Seminary in Cincinnati, who became known as “the Seventy” who received training and then “fanned out across the North campaigning in New England, Pennsylvania, New York, Ohio, Indiana and Michigan” [8] where many received hostile receptions, and encountered violence. Garrison used his newspaper, The Liberator to “pledge an all-out attack on U.S. slavery.” [9]
Frederick Douglass
Garrison frequently traveled and conducted speaking engagements with Frederick Douglass, the most prominent African American in the nation and himself a former slave. Douglass escaped slavery in 1838 and in 1841 he was “recruited by an agent for the Massachusetts Anti-Slavery Society; four years later he published his Narrative of the Life of a Frederick Douglass, an American Slave. Within a decade he had become the most famous African American on the continent, and one of slavery’s most deadly enemies.” [10]
The abolition movement aimed to not only stop the spread of slavery but to abolish it. The latter was something that many in the North who opposed slavery’s expansion were often either not in favor of, or indifferent to. The movement was given a major boost by the huge popularity of Harriett Beecher Stowe’s 1852 novel Uncle Tom’s Cabin “a vivid, highly imaginative, best-selling, and altogether damning indictment of slavery” [11] the abolitionist movement gained steam and power and “raised a counterindignation among Southerners because they thought Mrs. Stowe’s portrait untrue…” [12] The images in Stowe’s book “were irredeemably hostile: from now on the Southern stereotype was something akin to Simon Legree.” [13]
The leaders of the Abolitionist movement who had fought hard against acts the Fugitive Slave Act and the Dred Scott decision were now beginning to be joined by a Northern population that was becoming less tolerant of slavery and the status quo. With the formation of the Republican Party in 1854, a party founded on opposition to the expansion of slavery in the territories found a formidable political voice and became part of a broad coalition of varied interests groups whose aspirations had been blocked by pro-slavery Democrats. These included “agrarians demanding free-homestead legislation, Western merchants desiring river and harbor improvements at federal expense, Pennsylvania ironmasters and New England textile merchants in quest of higher tariffs.” They also made headway in gaining the support of immigrants, “especially among the liberal, vocal, fiercely anti-slavery Germans who had recently fled the Revolution of 1848.” [14] One of those German immigrants, Carl Schurz observed that “the slavery question” was “not a mere occasional quarrel between two sections of the country, divided by a geographic line” but “a great struggle between two antagonistic systems of social organization.” [15]
In light of the threat posed to slavery by the emerging abolitionist movement forced slaveholders to shift their defense of slavery from it being simply a necessary evil. Like in the North where theology was at the heart of many abolitionist arguments, in the South theology was used to enshrine and defend the institution of slavery. The religiously based counter argument was led by the former Governor of South Carolina, John Henry Hammond. Hammond’s arguments included biblical justification of blacks being biologically inferior to whites and slavery being supported in the Old Testament where the “Hebrews often practiced slavery” and in the New testament where “Christ never denounced servitude.” [16] Hammond warned:
“Without white masters’ paternalistic protection, biologically inferior blacks, loving sleep above all and “sensual excitements of all kinds when awake” would first snooze, then wander, then plunder, then murder, then be exterminated and reenslaved.” [17]
Others in the South, including politicians, pundits and preachers “were preaching “that slavery was an institution sanction by God, and that even blacks profited from it, for they had been snatched out of pagan and uncivilized Africa and been given the advantages of the gospel.” [18]
Slave owners frequently expressed hostility to independent black churches and conducted violence against them, and “attacks on clandestine prayer meetings were not arbitrary. They reflected the assumption (as one Mississippi slave put it) “that when colored people were praying [by themselves] it was against them.” [19] But some Southern blacks accepted the basic tenets do slave owner-planter sponsored Christianity. Douglass wrote “many good, religious colored people who were under the delusion that God required them to submit to slavery and wear their chains with weakness and humility.” [20]
The political and cultural rift began to affect entire church denominations, beginning with the Methodists who in “1844 the Methodist General Conference condemned the bishop of Georgia for holding slaves, the church split and the following year saw the birth of the Methodist Episcopal Church.” The Baptists were next, when the Foreign Mission Board “refused to commission a candidate who had been recommended by the Georgia Baptist Convention, on the ground that he owned slaves” [21] resulting in the formation of the Southern Baptist Convention. Finally in 1861, “reflecting the division of the nation, the Southern presbyteries withdrew from the Presbyterian Church and founded their own denomination.” [22] Sadly, the denominational rifts persisted until well into the twentieth century. The Presbyterians and Methodists both eventually reunited but the Baptists did no. The Southern Baptist Convention is now the largest Protestant denomination in the United States and many of its preachers active in often divisive conservative social and political causes. The denomination that it split from, the American Baptist Convention, though much smaller remains a diverse collection of conservative and progressive local churches. Some of these are still in the forefront of the modern civil rights movement, including voting rights, women’s rights and LGBT issues, all of which find some degree of opposition in the Southern Baptist Convention.
As the 1850s wore on the divisions over slavery became deeper and voices of moderation retreated. The trigger for the for the worsening of the division was the political battle regarding the expansion of slavery, even the status of free blacks in the north who were previously slaves, over whom their owners asserted their ownership. Southerners considered the network to help fugitive slaves escape to non-slave states, called the Underground Railroad “an affront to the slaveholders pride” and “anyone who helped a man or woman escape bondage was simply a thief” who had robbed them of their property and livelihood, as an “adult field hand could cost as much as $2000, the equivalent of a substantial house.” [23]
Dred Scott
In 1856 the Supreme Court, dominated by southern Democrats ruled in favor of southern views in the Dred Scott decision one pillar of which gave slavery the right to expand by denying to Congress the power to prohibit slavery in Federal territories. The decision in the case, the majority opinion which was written by Chief Justice Roger Taney was chilling, not only in its views of race, but the fact that blacks were perpetually property without the rights of citizens. Taney wrote:
“Can a negro, whose ancestors were imported into this country, sold as slaves, become a member of the political community formed and brought into existence by the Constitution of the United States, and as such become entitled to all the rights, and privileges, and immunities, guaranteed by that instrument to the citizen?…It is absolutely certain that the African race were not included under the name of citizens of a state…and that they were not included, and were not intended to be included, under the word “citizens” in the Constitution, and therefore claim none of the rights and privileges which that instrument provides for and secures to citizens of the United States. On the contrary, they were at that time considered as a subordinate and inferior class of beings, who had been subjugated by the dominant race, and, whether emancipated or not, yet remain subject to their authority, and had no rights or privileges but those who held the power and the Government might choose to grant them” [24]
The effect of the ruling on individuals and the states was far reaching. “No territorial government in any federally administered territory had the authority to alter the status of a white citizen’s property, much less to take that property out of a citizen’s hands, without due process of law or as punishment for some crime.” [25] Free slaves were no longer safe, even in Free States from the possibility of being returned to slavery, because they were property.
But the decision had been influenced by President-Elect James Buchanan’s secret intervention in the Supreme Court deliberations two weeks before his inauguration. Buchanan hoped by working with the Justices that he save the Union from breaking apart by appeasing slave owners and catering to their agenda. The president-elect wanted to know not only when, but if the Court would save the new administration and the Union from the issue of slavery in the territories. Would the judges thankfully declare the explosive subject out of bounds, for everyone who exerted federal power? The shattering question need never bother President Buchanan.” [26]In his inaugural address he attempted to camouflage his intervention and “declared that the Court’s decision, whatever it turned out to be, would settle the slavery issue forever.” [27]
This ignited a firestorm in the north where Republicans now led by Abraham Lincoln decried the decision and southerners basked in their judicial victory. Northerners quite rightly feared that an activist court would rule to deny their states the right to forbid slavery. As early as 1854 Lincoln posed the idea that the Declaration of Independence was “the standard maxim of free society …constantly spreading and deepening its influence,” ultimately applicable “to peoples of all colors everywhere.” [28]
But after the Dred Scott decision Lincoln warned that the Declaration was being cheapened and diluted “to aid in making the bondage of the Negro universal and eternal….All the powers of the earth seem rapidly combining against him. Mammon is after him; ambition follows, and philosophy follows, and the theology of the day is fast joining the cry. They have him in his prison house;…One after another they have closed the heavy doors upon him…and they stand musing as to what invention, in all the dominions of mind and matter, can be produced the impossibility of his escape more complete than it is.” [29]
In response to the decision the advocates of the expansion of slavery not only insisted on its westward expansion in Federal territories but to Panama, Nicaragua and Cuba as well. In 1857 Jefferson Davis further provoked northern ire when he insisted that “African Slavery as it exists in the United States is a moral, a social, and a political blessing.” [30]
Jefferson Buford
Southern leaders poured political, human and economic capital into the struggle for the imposition of slavery on the Kansas Territory. Victory in Kansas meant “two new U.S. Senators for the South. If a free labor Kansas triumphed, however, the North would gain four senators: Kansas’s immediately and Missouri’s soon.” [31] Rich Southerners recruited poor whites to fight their battles to promote the institution of slavery. Jefferson Buford of Alabama recruited hundreds of non-slaveholding whites to move to Kansas. Buford claimed to defend “the supremacy of the white race” he called Kansas “our great outpost” and warned that “a people who would not defend their outposts had already succumbed to the invader.” [32] To this end he and 415 volunteers went to Kansas, where they gained renown and infamy as members of “Buford’s Cavalry.” The day they left Montgomery they were given a sendoff. Each received a Bible, and the “holy soldiers elected Buford as their general. Then they paraded onto the steamship Messenger, waving banners conveying Buford’s twin messages: “The Supremacy of the White Race” and “Kansas the Outpost.” [33] His effort ultimately failed but he had proved that “Southern poor men would kill Yankees to keep blacks ground under.” [34]
The issue in Kansas was bloody and full of political intrigue over the Lecompton Constitution which allowed slavery, but which had been rejected by a sizable majority of Kansas residents, so much so that Kansas would not be admitted to the Union until after the secession of the Deep South. But the issue so galvanized the North that for the first time a coalition of “Republicans and anti-Lecompton Douglas Democrats, Congress had barely turned back a gigantic Slave Power Conspiracy to bend white men’s majoritarianism to slavemaster’s dictatorial needs, first in Kansas, then in Congress.” [35]
Taking advantage of the judicial ruling Davis and his supporters in Congress began to bring about legislation not just to ensure that Congress could not “exclude slavery” but to protect it in all places and all times. They sought a statute that would explicitly guarantee “that slave owners and their property would be unmolested in all Federal territories.” This was commonly known in the south as the doctrine of positive protection, designed to “prevent a free-soil majority in a territory from taking hostile action against a slave holding minority in their midst.” [36]
Other extremists in the Deep South had been long clamoring for the reopening of the African slave trade. In 1856 a delegate at the 1856 commercial convention insisted that “we are entitled to demand the opening of this trade from an industrial, political, and constitutional consideration….With cheap negroes we could set hostile legislation at defiance. The slave population after supplying the states would overflow to the territories, and nothing could control its natural expansion.” [37] and in 1858 the “Southern Commercial Convention…”declared that “all laws, State and Federal, prohibiting the African slave trade, out to be repealed.” [38] The extremists knowing that such legislation would not pass in Congress then pushed harder; instead of words they took action.
In 1858 there took place two incidents that brought this to the fore of political debate. The schooner Wanderer owned by Charles Lamar successfully delivered a cargo of four hundred slaves to Jekyll Island, earning him “a large profit.” [39] Then the USS Dolphin captured “the slaver Echo off Cuba and brought 314 Africans to the Charleston federal jail.” [40] The case was brought to a grand jury who had first indicted Lamar were so vilified that “they published a bizarre recantation of their action and advocated the repeal of the 1807 law prohibiting the slave trade. “Longer to yield to a sickly sentiment of pretended philanthropy and diseased mental aberration of “higher law” fanatics…” [41] Thus in both cases juries and judges refused to indict or convict those responsible.
There arose in the 1850s a second extremist movement in the Deep South, this to re-enslave free blacks. This effort was not limited to fanatics, but entered the Southern political mainstream, to the point that numerous state legislatures were nearly captured by majorities favoring such action. [42] That movement which had appeared out of nowhere soon fizzled, as did the bid to reopen the slave trade, but these “frustrations left extremists the more on the hunt for a final solution” [43] which would ultimately be found in secession.
Abraham Lincoln
Previously a man of moderation Lincoln laid out his views in the starkest terms in his House Divided speech given on June 16th 1858. Lincoln understood, possibly with more clarity than others of his time that the divide over slavery was deep and that the country could not continue to exist while two separate systems contended with one another. The Union Lincoln “would fight to preserve was not a bundle of compromises that secured the vital interests of both slave states and free, …but rather, the nation- the single, united, free people- Jefferson and his fellow Revolutionaries supposedly had conceived and whose fundamental principles were now being compromised.” [44] He was to the point and said in clear terms what few had ever said before and which even some in his own Republican Party did not want to use because they felt it was too divisive:
“If we could first know where we are and whither we are tending, we could better judge what to do and how to do it. We are now far into the fifth year since a policy was initiated with the avowed object and confident promise of putting an end to slavery agitation. Under the operation of that policy, that agitation has not only not ceased but has constantly augmented. In my opinion, it will not cease until a crisis shall have been reached and passed. “A house divided against itself cannot stand.” I believe this government cannot endure, permanently, half slave and half free. I do not expect the Union to be dissolved; I do not expect the house to fall; but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing, or all the other. Either the opponents of slavery will arrest the further spread of it and place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in the course of ultimate extinction, or its advocates will push it forward till it shall become alike lawful in all the states, old as well as new, North as well as South.” [45]
Part of the divide was rooted in how each side understood the Constitution. For the South it was a compact among the various states, or rather “only a league of quasi independent states that could be terminated at will” [46] and in their interpretation States Rights was central. In fact “so long as Southerners continued to believe that northern anti-slavery attacks constituted a real and present danger to Southern life and property, then disunion could not be ruled out as an ugly last resort.” [47]
But such was not the view in the North, “for devout Unionists, the Constitution had been framed by the people rather than created as a compact among the states. It formed a government, as President Andrew Jackson insisted of the early 1830s, “in which all the people are represented, which operates directly on the people individually, not upon the States.” [48] Lincoln like many in the North understood the Union that “had a transcendent, mystical quality as the object of their patriotic devotion and civil religion.” [49] His beliefs can be seen in the Gettysburg Address where he began his speech with the words “Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent, a new nation, conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal…” To Lincoln and others the word disunion “evoked a chilling scenario within which the Founders’ carefully constructed representative government failed, triggering “a nightmare, a tragic cataclysm” that would subject Americans to the kind of fear and misery that seemed to pervade the rest of the world.” [50]
Even in the South there was a desire for the Union and a fear over its dissolution, even among those officers like Robert E. Lee who would resign his commission and take up arms against the Union in defense of his native state. Lee wrote to his son Custis in January 1861, “I can anticipate no greater calamity for the country than the dissolution of the Union…I am willing to sacrifice everything but honor for its preservation…Secession is nothing but revolution.” But he added “A Union that can only be maintained by swords and bayonets has no charms for me….” [51] The difference between Lee and others like him and Abraham Lincoln was how they viewed the Union, views which were fundamentally opposed.
In the North there too existed an element of fanaticism. While “the restraining hand of churches, political parties and familial concerns bounded other antislavery warriors,” [52] and while most abolitionists tried to remain in the mainstream and work through legislation and moral persuasion to halt the expansion of slavery with the ultimate goal of emancipation, there were fanatical abolitionists that were willing to attempt to ignite the spark which would cause the powder keg of raw hatred and emotion to explode. Most prominent among these men was John Brown.
John Brown
Brown was certainly “a religious zealot…but was nevertheless every much the product of his time and place….” [53] Brown was a veteran of the violent battles in Kansas where he had earned the reputation as “the apostle of the sword of Gideon” as he and his men battled pro-slavery settlers. Brown was possessed by the belief that God had appointed him as “God’s warrior against slaveholders.” [54] He despised the peaceful abolitionists and demanded action. “Brave, unshaken by doubt, willing to shed blood unflinchingly and to die for his cause if necessary, Brown was the perfect man to light the tinder of civil war in America, which was what he intended to do.”[55]
Brown’s attempt to seize 10,000 muskets at the Federal armory in Harper’s Ferry Virginia in order to ignite a slave revolt was frustrated and Brown captured, by a force of U.S. Marines led by Colonel Robert E. Lee and Lieutenant J.E.B. Stuart. Brown was tried and hung, but his raid “effectively severed the country into two opposing parts, making it clear to moderates there who were searching for compromise, that northerner’s tolerance for slavery was wearing thin.” [56]
It now did not matter that Brown was captured, tried, convicted and executed for his raid on Harper’s Ferry. He was to be sure was “a half-pathetic, half-mad failure, his raid a crazy, senseless exploit to which only his quiet eloquence during trial and execution lent dignity” [57] but his act was the watershed from which the two sides would not be able to recover, the population on both sides having gone too far down the road to disunion to turn back.
Brown had tremendous support among the New England elites, the “names of Howe, Parker, Emerson and Thoreau among his supporters.” [58] To many abolitionists he had become a martyr, “but to Frederick Douglass and the negroes of Chatham, Ontario, nearly every one of whom had learned something from personal experience on how to gain freedom, Brown was a man of words trying to be a man of deeds, and they would not follow him. They understood him, as Thoreau and Emerson and Parker never did.”
But to Southerners Brown was the symbol of an existential threat to their way of life. In the North there was a nearly religious wave of sympathy for Brown, and the “spectacle of devout Yankee women actually praying for John Brown, not as a sinner but as saint, of respectable thinkers like Thoreau and Emerson and Longfellow glorifying his martyrdom in Biblical language” [59] horrified Southerners, and drove pro-Union Southern moderates into the secession camp.
The crisis continued to fester and when Lincoln was elected to the Presidency in November 1860 with no southern states voting Republican the long festering volcano erupted. It did not take long before southern states began to secede from the Union. South Carolina was first, followed by Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana and Texas. Many of the declarations of causes for secession made it clear that slavery was the root cause. The declaration of South Carolina is typical of these and is instructive of the basic root cause of the war:
“all the States north of that line have united in the election of a man to the high office of President of the United States, whose opinions and purposes are hostile to slavery. He is to be entrusted with the administration of the common Government, because he has declared that that “Government cannot endure permanently half slave, half free,” and that the public mind must rest in the belief that slavery is in the course of ultimate extinction.”[60]
Throughout the war slavery loomed large. In his First Inaugural Address Lincoln noted: “One section of our country believes slavery is right and ought to be extended, while the other believes it is wrong and ought not to be extended. This is the only substantial dispute.”[61] Of course he was right, and his southern opponents agreed.
Alexander Stephens
Alexander Stephens the Vice President of the Confederacy noted in his Cornerstone Speech of March 21st 1861 that: “Our new government is founded upon exactly the opposite idea; its foundations are laid, its corner- stone rests upon the great truth, that the negro is not equal to the white man; that slavery — subordination to the superior race — is his natural and normal condition. [Applause.] This, our new government, is the first, in the history of the world, based upon this great physical, philosophical, and moral truth.”[62]
Thus the American ideological war was born, as J.F.C. Fuller wrote:
“At length on 12th April, the tension could no longer bear the strain. Contrary to instructions, in the morning twilight, and when none could see clearly what the historic day portended, the Confederates in Charleston bombarded Fort Sumter, and the thunder of their guns announced that the argument of a generation should be decided by the ordeal of war. A war, not between two antagonistic political parties, but a struggle to the death between two societies, each championing a different civilization…”[63]
After the bloody battle of Antietam, Lincoln published the emancipation proclamation in which he proclaimed the emancipation of slaves located in the Rebel states, and that proclamation had more than a social and domestic political effect, it ensured that Britain would not intervene.
In his Second Inaugural Address Lincoln discussed the issue of slavery as being the cause of the war:
“One-eighth of the whole population were colored slaves, not distributed generally over the Union, but localized in the southern part of it. These slaves constituted a peculiar and powerful interest. All knew that this interest was somehow the cause of the war. To strengthen, perpetuate, and extend this interest was the object for which the insurgents would rend the Union even by war, while the Government claimed no right to do more than to restrict the territorial enlargement of it. Neither party expected for the war the magnitude or the duration which it has already attained. Neither anticipated that the cause of the conflict might cease with or even before the conflict itself should cease. Each looked for an easier triumph, and a result less fundamental and astounding. Both read the same Bible and pray to the same God, and each invokes His aid against the other. It may seem strange that any men should dare to ask a just God’s assistance in wringing their bread from the sweat of other men’s faces, but let us judge not, that we be not judged. The prayers of both could not be answered. That of neither has been answered fully. The Almighty has His own purposes. “Woe unto the world because of offenses; for it must needs be that offenses come, but woe to that man by whom the offense cometh.” If we shall suppose that American slavery is one of those offenses which, in the providence of God, must needs come, but which, having continued through His appointed time, He now wills to remove, and that He gives to both North and South this terrible war as the woe due to those by whom the offense came, shall we discern therein any departure from those divine attributes which the believers in a living God always ascribe to Him? Fondly do we hope, fervently do we pray, that this mighty scourge of war may speedily pass away. Yet, if God wills that it continue until all the wealth piled by the bondsman’s two hundred and fifty years of unrequited toil shall be sunk, and until every drop of blood drawn with the lash shall be paid by another drawn with the sword, as was said three thousand years ago, so still it must be said “the judgments of the Lord are true and righteous altogether.”[64]
When Edmund Ruffin pulled the lanyard of the cannon that fired the first shot at Fort Sumter it marked the end of an era and despite Ruffin, Stephens and Davis’ plans gave birth to what Lincoln would describe as “a new birth of freedom.”
When the war ended with the Confederacy defeated and the south in ruins, Ruffin still could not abide the result. In a carefully crafted suicide note he sent to his son the bitter and hate filled old man wrote on June 14th 1865:
“… And now with my latest writing and utterance, and with what will be near my last breath, I here repeat and would willingly proclaim my unmitigated hatred to Yankee rule — to all political, social and business connections with Yankees, and the perfidious, malignant and vile Yankee race.” [65]
Though Ruffin was dead in the coming years the southern states would again find themselves under the governance of former secessionists who were unabashed white supremacists. By 1877 many southerners we taking as much pride in the “Lost Cause” as Northerners took in Appomattox.[66] This led to nearly a hundred more years of effective second class citizenship for now free blacks who were often deprived of the vote and forced into “separate but equal” public and private facilities, schools and recreational activities. The Ku Klux Klan and other violent organizations harassed, intimidated, persecuted and used violence against blacks. Lynching was common and even churches were not safe. It would not be until the Civil Rights movement of the 1950s and 1960s that blacks would finally begin to gain the same rights enjoyed by whites in most of the south.
Ruffin outlived Lincoln who was killed by the assassin John Wilkes Booth on April 14th 1864. However the difference between the two men was marked. In his Second Inaugural Address Lincoln spoke in a different manner than Ruffin. He concluded that address with these thoughts:
“With malice toward none, with charity for all, with firmness in the right as God gives us to see the right, let us strive on to finish the work we are in, to bind up the nation’s wounds, to care for him who shall have borne the battle and for his widow and his orphan, to do all which may achieve and cherish a just and lasting peace among ourselves and with all nations.” [67]
Though the issues have changed since the time of slavery, there is a common denominator between the Tea Party movement, much of the modern conservative politically minded Dominionist Christianity and the conservative economic elites that back them. The Tea Party leaders, the well-off politically minded preachers, and their economic benefactors use fear of change, fear of race and fear of “the other” to motivate middle class and poor whites and others to vote for their causes and be their foot soldiers just as Jefferson Buford did in 1856. They set their liberty, social and economic position above others. Some in the Tea Party use religion to justify discrimination, and in many places use it as the basis to limit the rights of minorities, women and gays much as the Southern Plantation oligarchs used slavery to control African American slaves, poor whites and blacks who had escaped slavery. In some states Tea Party operatives attempt to use the legislative and judicial branches of government to ensure that they as a minority overrule the will of the majority. They use the same language, often punctuated with exhortations to revolt and violence as did their predecessors in the ante-bellum South.
This may sound harsh to some, especially for honest decent and caring people who have been taken up in the political crusade of the Tea Party and politically minded preachers. Unfortunately the parallels are all too real to dismiss them.
Peace
Padre Steve+
Notes
[1] Fuller, J.F.C. Decisive Battles of the U.S.A. 1776-1918 University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln 2007 copyright 1942 The Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals p.174
[2] Potter, David M. The Impending Crisis: America before the Civil War 1848-1861 completed and edited by Don E. Fehrenbacher Harper Collins Publishers, New York 1976 pp.457-458
[3] Ruffin, Edmund The Political Economy of Slavery in McKitrick, Eric L. ed. Slavery Defended: The Views of the Old South. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall/Spectrum Books, 1963.Retrieved from http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/americanexperience/features/primary-resources/lincolns-political-economy/ 24 March 2014
[4] Jefferson, Thomas Letter to John Holmes dated April 22nd 1824 retrieved from www.loc.gov/exhibits/jefferson/159.html 24 March 2014
[5] U.S. Grant, Personal Memoirs of U.S. Grant New York 1885 pp.243-245
[6] Freehling, William W. The Road to Disunion Volume One: Secessionists at Bay Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York 1990 p.289
[7] Egnal, Marc Clash of Extremes: The Economic Origins of the Civil War Hill and Wang a division of Farrar, Straus and Giroux New York 2009 pp.125-126
[8] Ibid. Egnal Clash of Extremes p.125
[9] Ibid. Freehling The Road to Disunion Volume One p.12
[10] Guelzo, Allen C. Fateful Lightening: A New History of the Civil War Era and Reconstruction Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York 2012 p.91
[11] Ibid. Catton Two Roads to Sumter p.94
[12] Ibid. Catton Two Roads to Sumter p.94
[13] Ibid. Catton Two Roads to Sumter p.94
[14] Catton, William and Bruce, Two Roads to Sumter: Abraham Lincoln, Jefferson Davis and the March to Civil War McGraw Hill Book Company New York 1963, Phoenix Press edition London p.123
[15] Levine, Bruce Half Slave and Half Free: The Roots of the Civil War Revised Edition, Hill and Wang, a division of Farrar, Strauss and Giroux, New York 1992 and 1995 p.15
[16] Ibid. Freehling The Road to Disunion Volume One p.29
[17] Ibid. Freehling The Road to Disunion Volume One p.29
[18] Gonzalez, Justo L. The History of Christianity Volume 2: The Reformation to the Present Day Harper and Row Publishers San Francisco 1985 p.251
[19] Ibid. Levine Half Slave and Half Free p.116
[20] Ibid. Levine Half Slave and Half Free p.116
[21] Ibid. Gonzalez The History of Christianity Volume 2 p.251
[22] Ibid. Gonzalez The History of Christianity Volume 2 p.251
[23] Goodheart, Adam. Moses’ Last Exodus in The New York Times: Disunion, 106 Articles from the New York Times Opinionator: Modern Historians Revist and Reconsider the Civil War from Lincoln’s Election to the Emancipation Proclamation Edited by Ted Widmer, Black Dog and Leventhal Publishers, New York 2013 p.15
[24] Guelzo Fateful Lightening p.91
[25] Ibid. Guelzo Fateful Lightening pp.91-92
[26] Freeling, William. The Road to Disunion Volume II: Secessionists Triumphant 1854-1861 Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York 2007 p.115
[27] Ibid. Freeling, The Road to Disunion Volume II: Secessionists Triumphant 1854-1861 p.109
[28] Ibid. Catton Two Roads to Sumter p.139
[29] Ibid. Catton Two Roads to Sumter p.139
[30] Ibid.Catton Two Roads to Sumter p.142
[31] Ibid. Freeling, The Road to Disunion Volume II: Secessionists Triumphant 1854-1861 p.124
[32] Ibid. Freeling, The Road to Disunion Volume II: Secessionists Triumphant 1854-1861 p.125
[33] Ibid. Freeling, The Road to Disunion Volume II: Secessionists Triumphant 1854-1861 p.126
[34] Ibid. Freeling, The Road to Disunion Volume II: Secessionists Triumphant 1854-1861 p.126
[35] Ibid. Freeling, The Road to Disunion Volume II: Secessionists Triumphant 1854-1861 p.142
[36] Ibid. Catton Two Roads to Sumter p.142
[37] McPherson, James. The Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York 1988 p.102
[38] Ibid Freeling, The Road to Disunion Volume II: Secessionists Triumphant 1854-1861 p.183
[39] Ibid. McPherson The Battle Cry of Freedom p.103
[40] Ibid. Freeling The Road to Disunion Volume II p.183
[41] Ibid. McPherson The Battle Cry of Freedom p.103
[42] Ibid. Freeling The Road to Disunion Volume II p.185
[43] Ibid. Freeling The Road to Disunion Volume II p.185
[44] Gallagher, Gary The Union War Harvard University Press, Cambridge MA and London, 2011 p.47
[45] Lincoln, Abraham A House Divided given at the Illinois Republican Convention, June 16th 1858, retrieved from www.pbs.org/wgbh/ala/part4/4h2934.html 24 March 2014
[46] Ibid. Guelzo Fateful Lightening p.55
[47] Ibid. Guelzo Fateful Lightening p.55
[48] Ibid. Gallagher The Union War p.46
[49] Ibid Gallagher The Union War p.47
[50] Ibid Gallagher The Union War p.47
[51] Korda, Michael. Clouds of Glory: The Life and Legend of Robert E. Lee Harper Collins Publishers, New York 2014 p.221
[52] Ibid. Freeling The Road to Disunion Volume II p.207
[53] Ibid. Levine Half Slave and Half Free p.197
[54] Ibid. Freeling The Road to Disunion Volume II p.207
[55] Ibid. Korda, Clouds of Glory p.xviii
[56] Ibid. Korda Clouds of Glory p.xxxix
[57] Ibid. Catton Two Roads to Sumter p.187
[58] Ibid. Potter The Impending Crisis p.381
[59] Ibid. Catton Two Roads to Sumter p.187
[60] __________ Declaration of the Immediate Causes Which Induce and Justify the Secession of South Carolina from the Federal Union. Retrieved from The Avalon Project, Yale School of Law http://avalon.law.yale.edu/19th_century/csa_scarsec.asp 24 March 2014
[61] Lincoln, Abraham First Inaugural Address March 4th 1861 retrieved from www.bartleby.com/124/pres31.html 24 March 2014
[62] Cleveland, Henry Alexander H. Stevens, in Public and Private: With Letters and Speeches, before, during and since the War, Philadelphia 1886 pp.717-729 retrieved from http://civilwarcauses.org/corner.htm 24 March 2014
[63] Ibid. Fuller . The Conduct of War 1789-1961 p.98
[64] Lincoln, Abraham Second Inaugural Address March 4th 1865 retrieved from www.bartleby.com/124/pres32.html 24 March 2014
[65] Edmund Ruffin (1794-1865). Diary entry, June 18, 1865. Manuscript Division, Library of Congress Retrieved from http://blogs.loc.gov/civil-war-voices/about/edmund-ruffin/ 24 March 2014
[66] Millet Allen R and Maslowski, Peter. For the Common Defense: A Military History of the United States of America The Free Press, a division of McMillan Publishers, New York 1984 p.230
[67] Ibid. Lincoln Second Inaugural Address




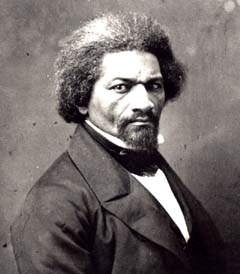























The Dangers of the Expanding National Security State: The Drumhead
Lieutenant Worf: “Sir, the Federation does have enemies. We must seek them out.”
Captain Jean-Luc Picard: “Oh, yes. That’s how it starts. But the road from legitimate suspicion to rampant paranoia is very much shorter than we think. Something is wrong here, Mister Worf. I don’t like what we have become.”
Back in 1991 when I was still in seminary I spent every Saturday evening glued to my television set to watch Star Trek the Next Generation. Even today I enjoy watching the human drama that Gene Roddenberry and his cohorts created on the small screen. Of all the Star Trek series my favorites are TNG and Deep Space Nine. Those series often touched on very pertinent social, political, medical, and technological and dare I say national security issues. In fact I have used some Deep Space Nine episodes in my previous posts about the NSA leak situation and the War on Terrorism.
One of the most chilling episodes regarding national security and potential terrorism or sabotage is called “The Drumhead.” In light of the the ever expanding National Security State and the ability of governments, private industry and even individuals to use technology to gather information on almost anyone and to abuse that power, The Drumhead is an episode that remains as relevant today, perhaps even more so, than when it first aired in 1991.
The episode is about an investigation that takes place on the Enterprise following an explosion in its engineering spaces. Suspicion centers on a Klingon exchange officer. However, the investigator, the retired Starfleet Judge Advocate General, Nora Satie and her Betazed assistant soon casts a wide net which eventually brings charges against a crew member and eventually Captain Picard.
At first Admiral Satie’s investigation seems reasonable. After all the Federation faced danger from the Romulans, who were always trying to use Klingons unhappy with the Federsation-Klingon peace treaty, to further their interests. The initial situation raised the possibility that the Enterprise, was sabotaged and that the Klingons or others might be involved. Thus as Sati began her investigation she was welcomed by the Captain as well as the Security Chief, Lieutenant Worf, the only Klingon serving as a Starfleet officer. Satie, assisted by Enterprise security officers then discovered how the Klingon scientist smuggled classified information off the Enterprise.
The Chief Engineer of the Enterprise, Lieutenant Commander LeForge determined in his investigation that the explosion thought to be “sabotage” was caused by a flaw in a recently replaced dilithium chamber. Although she was convinced that the Klingon was not the saboteur Satie believed that another saboteur was aboard the Enterprise. Satie and her assistant uncovered a piece of information that a crewman lied about his family background on his enlistment contract. They then used it to connect the crewman to to the Klingon spy by supplying false information about the explosion in an attempt to get the crewman to admit guilt.
As the investigation widened Picard discussed it with Lieutenant Worf. I find this dialogue to be quite relevant to today thirteen years into the war on terror and about the same amount of time since the Patriot Act was passed.
Lieutenant Worf: “Sir, the Federation does have enemies. We must seek them out.”
Captain Jean-Luc Picard: “Oh, yes. That’s how it starts. But the road from legitimate suspicion to rampant paranoia is very much shorter than we think. Something is wrong here, Mister Worf. I don’t like what we have become.”
When Picard objected to the grilling of the crewman, Admiral Satie and her chief assistant began an investigation of Picard. As she informed him that he was now a subject of the investigation, the normally calm Picard erupted, telling Sati; “Admiral! What you’re doing here is unethical; it’s immoral. I’ll fight it.” Admiral Sati then laid down the gauntlet, and told Picard, “Do what you must, Captain. And so will I.”
Admiral Satie called on the Director of Starfleet Security, Admiral Henry, to watch her interrogate Picard who she had by now labeled a traitor.
Picard forced to testify at an open hearing where Sati began to attack him. However, the tables are turned during Picard’s testimony. The dialogue is riveting as Sati attempts to use anything that she can to prove Picard a traitor the the Federation.
Admiral Satie: Tell me, Captain, have you completely recovered from your experience with the Borg?
Captain Jean-Luc Picard: Yes, I have completely recovered.
Admiral Satie: It must have been awful for you… actually becoming one of them. Being forced to use your vast knowledge of Starfleet operations to aid the Borg. Just how many of our ships were lost? Thirty-nine? And a loss of life, I believe, measured at nearly 11,000. One wonders how you can sleep at night, having caused so much destruction. I question your actions, Captain; I question your choices, I question your loyalty!
Capt. Picard: You know there are some words I’ve known since I was a schoolboy: “With the first link, the chain is forged. The first speech censured, the first thought forbidden, the first freedom denied, chains us all irrevocably.” Those words were uttered by Judge Aaron Satie, as wisdom and warning. The first time any man’s freedom is trodden on, we’re all damaged. I fear that today…
Admiral Satie: [stands up in anger and interrupts Picard] How dare you! You who consort with Romulans, invoke my father’s name to support your traitorous arguments! It is an offense to everything I hold dear! And to hear those words used to subvert the United Federation of Planets. My father was a great man! His name stands for integrity and principle. You dirty his name when you speak it! He loved the Federation. But you, Captain, corrupt it. You undermine our very way of life. I will expose you for what you are. I’ve brought down bigger men than you, Picard! [Admiral Henry gets up and leaves the room]
With Sati obviously unhinged, Admiral Henry ends the investigation and sends Admiral Satie home.
Of course this is fiction but the mindset and attitude of Admiral Satie seems to have been embraced by some in our government and security agencies, including the TSA and the NSA. But the talk is out there, former Senator and Secretary of Defense William J. Cohen said: “Terrorism is escalating to the point that Americans soon may have to choose between civil liberties and more intrusive means of protection.”
Well the choice has been made and I don’t think that there is any going back despite the posturing of politicians on both sides of the political divide. The fact is that polls show that the majority of Americans are willing to sacrifice freedoms for security.
Sati had become so consumed with “defending liberty” that she was willing to trample the rights of anyone that she suspected of disloyalty to the Federation.
Sati’s questioning of Picard by is fascinating and thought provoking, because there are people that think and act just her fictional character. People who believe, that they too are defending “freedom.”
Frederick Douglass once said: “Find out just what the people will submit to and you have found out the exact amount of injustice and wrong which will be imposed upon them; and these will continue until they are resisted with either words or blows, or with both. The limits of tyrants are prescribed by the endurance of those whom they oppress.”
The balance has to be found in this effort; right now the pendulum is so far to the security side that it seems freedom is no longer even a concern at least for the vast majority of the population and our political leadership, and not just the Executive Branch, the Congress seems to love making new laws that further limit freedom, local governments have militarized their police forces and the courts don’t seem to mind. Unless we undertake a real debate in the issue it is very likely that it will fade away and the national security state that we have become will grow even stronger with the inevitable loss of even more civil liberties.
One only has to look at what politicians on both sides of the political chasm have said about “protecting the homeland” to realize that this is only the beginning and that if we do not have a spirited public debate that we risk our Constitutional liberties under the 4th Amendment as well as potentially the 1st Amendment. Prosecuting actual wrongdoers is one thing, but prominent legislators on important committees dealing with national security suggest prosecuting reporters for doing their job, something that would be a crushing blow to freedom of speech and freedom of the press. The fact that some suggest this shows how just how close we are to surrendering even more freedom in the name of security.
The last scene of The Drumhead is enlightening. Lieutenant Worf, who had so eagerly embraced the investigation, goes to Picard to let him know that Admiral Satie and Admiral Henry have left the Enterprise. Worf is apologetic about his rather overzealous role in the investigation. He tells Picard about Sati: “after yesterday, people will not be so ready to trust her.” Picard replies “Maybe. But she, or someone like her, will always be with us, waiting for the right climate in which to flourish, spreading fear in the name of righteousness. Vigilance, Mister Worf – that is the price we have to continually pay.”
Eternal vigilance in the face of both terrors from abroad and self imposed tyranny designed to protect us from the terrorists. Yes James Madison, was absolutely right when he said “The means of defense against foreign danger historically have become the instruments of tyranny at home.” However I fear that those that warn of such dangers will themselves be labeled the enemy.
Henry Steele Commager said “Men in authority will always think that criticism of their policies is dangerous. They will always equate their policies with patriotism, and find criticism subversive.” This, my friends is the reality that we live in and the danger that we face.
Peace
Padre Steve+
Share this:
Leave a comment
Filed under civil rights, ethics, laws and legislation, national security, political commentary
Tagged as 1st ammendment, 4th amendment, 9-11 2001, admiral satie, attack on benghazi us consulate, Boston marathon bombing, captain jean luc picard, civil liberties, frederick douglass, global war on terrorism, henry steele commager, james madison, lcdr leforge, lieutenant worf, national security state, nsa leaks, Patriot Act of 2001, representativ peter king, star trek the next generation, the drumhead, tsa