Musashi and Monitor
I have been thinking about two ships this past week. One of these ships was the Japanese Super-Battleship Musashi. The Musashi was one of the two largest battleships ever constructed and her wreck was discovered last week where she sank in the Sibuyan Sea. The other ship was the USS Monitor. The tiny Monitor was progenitor of all the great battleships that followed and 153 years ago Monitor helped propel naval architecture and warfare into a new era when she challenged the CSS Virginia at the Battle of Hampton Roads.
The Monitor was one of three experimental designs chosen by the Navy’s Ironclad board to deal with the Virginia. Her design and construction were remarkable, especially for her day. The ship was entirely experimental, nothing like Monitor had ever been built before, but even so it was less than five months from the date she was ordered until she was commissioned and just a few days more than that before she was in action. I cannot imagine any warship ship new design ever breaking that record.
Her designer was John Ericsson, a Swede. Ericsson was the inventor of the screw propeller and designer of the first U.S. Navy Screw Frigate the USS Princeton. Ericsson had be shunned by the Navy after a rifled cannon, which was not of his design or construction exploded aboard Princeton during a gunnery demonstration which killed the Secretary of the Navy and others. Ericcson was not planning to submit a design but was persuaded to and his design, the Monitor was one of the three designs selected.
The Officers of Monitor
The Monitor was like nothing ever seen on the ocean. Described by some as a “cheese box on a raft” the small ship had all of her machinery located below the waterline on a completely iron hull that only drew 11 feet of water. She was 179 feet long, had a beam of 41 and a half feet and displaced 987 tons. Her single vibrating lever steam engine powered by two boilers produced 340 horsepower and drove her at a top speed of six knots.
Her hull was protected by armor plate, but the most notable and innovative feature was a heavily armored revolving turret with eight inches of armor, mounted two massive 11 inch Dahlgren smoothbore guns which “could fire a 170-pound shot or 136-pound shell in any direction except straight ahead, where the pilot house sheathed in nine inches of armor was located.” Future ships remedied this defect. Ericcson’s ship was mocked around the navy and by naval designers, but he and it would prove them wrong. The Monitor’s most notable features, full steam propulsion, heavy armor and the revolving turret mounting heavy caliber guns would set the standard to which future battleships would be constructed.
The Battle of Hampton Roads
Monitor had a brief service life, she fought the Virginia, took part in actions along the James River and sank in a storm off Cape Hatteras North Carolina on December 31st 1861. The British Royal Navy designed an improved monitor with higher freeboard and finally an ocean going turret ship, the HMS Devastation.
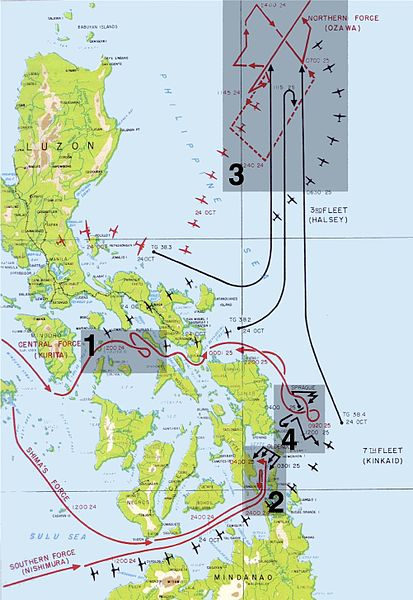
Soon, the navies of the world began to build battleships and in 1906 the Royal Navy built the HMS Dreadnought which like Monitor revolutionized warship construction and naval warfare. Navies around the world began building ever larger, faster and more powerful Dreadnoughts culminating the designs of the late 1930s, the German Bismarck class, the American Iowa class, the British Vanguard, and the Japanese Yamato Class. It is the last ships, the Yamato and her sister Musashi that I want to discuss here, not that the others are not interesting or important, but because of the almost mythic status that these ships maintain in the annals of naval history, as well as their tragic end.
Emperor Hirohito on Musashi in 1943
The Yamato and Musashi were the largest and most heavily armed battleships ever built. Shrouded in secrecy by the Imperial Japanese Navy and Government the ships were designed to offset projected American numerical superiority. Their names were symbolic of Japan’s history. Yamato was named after Yamato Province, the ancestral home of the Yamato People, the dominant native ethnic group in Japan. Musashi was named after Musashi Province in which lays Tokyo Prefecture. A third ship of the class, Shinano, was named after Shinano Province in central Japan which was the home of the prestigious Taketa Shingen family during the Senguku period.
The Conning Tower and Bridge of Musashi
The secrecy surrounding their design and construction was unprecedented. Those charged with their design and construction were thoroughly checked out by Japan’s secret police and sworn to an oath of secrecy. The oath sworn by builders of Musashi at the Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Nagasaki Shipyard were sworn to the oath shown below:
I am aware that all work involving the construction of the No. 2 Battleship is vital to national security. I will make utmost effort to maintain the secrecy of the project, and swear that I will leak no information relating to the said battleship, even to relatives and close friends. In the event I violate this oath, I will submit to the punishment determined by the company and the Navy.
Security measures around the shipyards where Yamato and Musashi were constructed were immense. At Nagasaki where there was a large foreign business and missionary population where the shipyard was visible from most of the city at hemp screen of 75,000 square meters was constructed to shield the ship from prying eyes and spies.
Musashi under Construction
When actual preparations for construction were taken in 1937 secret police swept the areas of foreign, especially Chinese workers. Security was increased inside and outside the shipyard, all blueprints accounted for and placed under strict guard while all shipyard workers were photographed with any having knowledge of the plans or supervising the construction sworn to the secrecy oath.
When a top secret blueprint went missing in 1938 at Nagasaki an intense investigation that included the torture of numerous suspects and the jailing of a blueprinter who accidentally swept the document into the trash was sentenced to 3 years in prison.
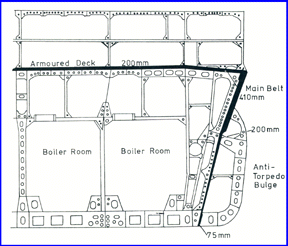
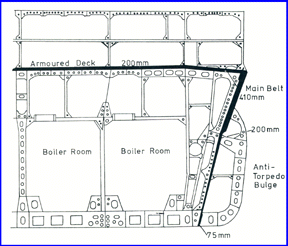
Armor and Protection of Yamato Class
Few pictures exist of the ships and Japanese Naval Officers destroyed many of the records of the ships design and construction just prior to the end of the Second World War. Throughout their existence they were a mystery to the American Navy. During the war the U.S. Navy estimated them to carry nine 16” guns and displace between 40,000-57,000 tons. Even the highly regarded Jane’s Fighting Ships listed them at just 45,000 tons.
Yamato and Musashi together in 1943
Preliminary design work began in 1934 and progressed rapidly following Japan’s withdraw from the League of Nations and renunciation of the Washington and London Naval Treaties and withdraw from the 1936 naval talks in London. The early designs varied in the caliber of guns, size and armor, propulsion systems and endurance. Gun calibers ranged from 16” to 18.1” and a combined diesel-turbine system was considered but rejected in favor of traditional steam turbines.
The final design was for a class of five ships. Each would displace 64,000 tons standard displacement and 72,000 tons at full load. They were 862 feet long with a beam of 127 feet. They were so large that the docks they were built needed to be expanded and special extra-large launch platforms had to be built. At Nagasaki the dock at to be expanded by cutting into the hill adjacent to it.
They were armed with nine 18.1 inch guns in triple turrets which could fire a projectile weighing over a ton. The secondary armament consisted of 12 6.1 inch guns mounted in triple turrets formerly mounted on the Mogami Class cruisers when those ships were equipped with 8” guns. Anti-aircraft defense included twelve 5” guns and twenty-four 25mm anti-aircraft guns. During the war two of the 6.1 inch turrets were removed and replaced with twelve more 5” guns and the 25mm battery was raised to 162 guns. Fire control systems were designed in such a way that the ships could engage multiple surface targets at the same time.
The ships were protected by a massive armored belt ranging from 16 inches to 8 inches with 26 inch armor on the face plates of the main gun turrets. The armor was advanced with excellent sloping but had a flaw where the upper and lower belts connected just below the waterline which exposed them to damage from torpedoes.
Yamato and Musashi viewed beside Battleship Nagato (foreground) just before the Battle of Leyte Gulf
They were powered by 12 Kampon boilers which powered 4 steam turbines and four three bladed propellers. These developed 150,000 shp and could drive the ship at a top speed of 27 knots.
Construction of Yamato began on November 4th 1937 at Kure Naval Shipyard. Musashi on March 28th 1938. Traditionally such events were large public ceremonies but these were limited to just a few Naval Staff and Shipyard executives. Yamato was launched on August 8th 1940 and commissioned on December 16th 1941, just 9 days after Pearl Harbor. Musashi was launched on November 8th 1940 and commissioned on August 5th 1942 just two days before the U.S. Marines invaded Guadalcanal and two months after the disaster at the Battle of Midway.
Yamato served as Admiral Yamamoto’s flagship at Midway where she saw no action. The next two years she was and Musashi alternated as fleet flagship and conducted operations with Battleship Division One in operations between Mainland Japan and the major Japanese base at Truk. On December 25th 1943 while escorting a convoy she was torpedoed by the submarine USS Skate and suffered heavy damage which flooded a magazine. On March 29th while underway Musashi was struck near the bow by a torpedo from the USS Tunny.
Musashi under attack at the Battle of Sibuyan Sea
Both ships participated in the Battle of the Philippine Sea and were part of Vice Admiral Takeo Kurita’s Central Force in the Battle of Leyte Gulf. Musashi was sunk by U.S. Navy Carrier aircraft from the Third Fleet on October 24th 1944 during the Battle of the Sibuyan Sea. Hit by 17 bombs and 19 torpedoes she sank with the loss of nearly 1100 of her crew of almost 2400 men. The survivors were rescued by destroyers and disembarked at Corregidor. Some were sent by troop transport to Japan but one of the ships was torpedoed and sunk leaving her survivors adrift for 19 hours before rescue. Those who reached Japan were isolated from the population while about half of the survivors remained in the Philippines where 117 of 146 of those assigned to the defense of Manila were killed in action.
Yamato or Musashi under air Attack
Yamato saw action in the surface engagement on October 25th against the Escort Carriers and Destroyers of Taffy-3 during the Battle off Samar. Her guns helped sink the Escort Carrier USS Gambier Bay but was forced away from the action by torpedo attacks from the valiant destroyers of Taffy-3.
Yamato under Attack April 7th 1945
By April 1944 Japan’s Navy was decimated and U.S. Naval Forces were raiding Mainland Japan. When the United States landed on Okinawa the Japanese Navy and air force launched wave after wave of Kamikaze attacks on the ships in the waters around the island. Yamato, along with Light Cruiser Yahagi and eight destroyers were designated the Surface Special Attack Force and loaded with a full load of ammunition but only enough fuel for a one way trip got underway on April 6th. The mission was for Yamato to reach Okinawa, beach herself and serve as an “unsinkable” gun battery until she was destroyed. The force was spotted by U.S. Navy flying boats hours after their departure and on April 7th over 400 aircraft launched from Task Groups 58.1 and 58.3. The first wave began its attack at 1230 and by 1400 the ship was mortally wounded. Stuck by at least 8 torpedoes and 11 bombs she was dead in the water and began to capsize at 1405. At 1420 she turned turtle and at 1423 exploded when her forward blew up sending up a mushroom cloud nearly 20,000 feet. Under 300 of her crew of nearly 2400 were rescued.
The End: Yamato Explodes
What had begun with the tiny “cheese box on a raft” had culminated in two of the largest warships ever built, designed when naval experts planned for a war where the battleship would rule and aircraft carriers play a supporting role. Instead both never faced enemy battleships in combat and both were destroyed by the weapon that the battleship admirals had discounted. It is somewhat fitting that each was commissioned shortly after the triumphs of Japanese and American Naval air power at Pearl Harbor and Midway. However they have attained an almost mythic status in naval lore and are symbols to many Japanese of the sacrifice and futility of the war. Both of the cities where the ships were constructed were destroyed by Atomic bombs. They are tragic reminders of the cost of war in human lives, suffering, economic cost and destruction.
Musashi’s wreck was discovered by Microsoft co-founder Paul Allen. He posted the first picture of the ship taken in over seventy years, showing the Chrysanthemum seal on her bow to Twitter. As a devotee of these great ships I was amazed to see this.
In a sense their poetic names and the myth ascribed to them are a tragic requiem to the Japanese Empire and the cost of war. They and their brave sailors were sacrificed when the war was already for all intents and purposes lost. They, especially the Yamato were sacrificed for no military purpose save a convoluted sense of honor. Let us pray that it never happens again.
Peace
Padre Steve+






















































































































 TBF Avenger dropping its “fish” 19 would hit Musashi
TBF Avenger dropping its “fish” 19 would hit Musashi