Christmastide is a joyous time for many, but in the course of history there have been times that military men have fought and died in hopeless battles far from their families. Thus it is often a time of sorry, especially for those that die alone. Among those who died alone in the Arctic darkness of December 26th 1943 were the officers and crew of the German battlecruiser Scharnhorst.
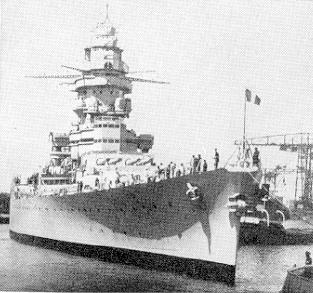
Scharnhorst in port
The Scharnhorst along with her sister ship Gneisenau were the product of the naval architects of Germany who in the early 1930s designed some of the most beautiful as well as deadly warships of the Second World War. Following Germany’s rejection of the provisions of the Treaty of Versailles the Kreigsmarine enacted a building program to enlarge and modernize the German Navy which then was composed of obsolete pre-Dreadnaught battleships and a few modern light cruisers and destroyers. The first major units constructed were actually begun by the predecessor to the Kreigsmarine, the Reichsmarine of the Weimar Republic. These were the Deutschland class Armored Ships, sometimes called “Pocket Battleships” and later reclassified as Heavy Cruisers. These ships were designed to replace the old pre-Dreadnaught battleships and incorporated electric welds to reduce displacement, diesel engines for extended cruise range to enable them to serve as commerce raiders and a battery of six 11” guns. While an advance over anything in the German inventory they were outclassed by the British battle cruisers Hood, Renown and Repulse.
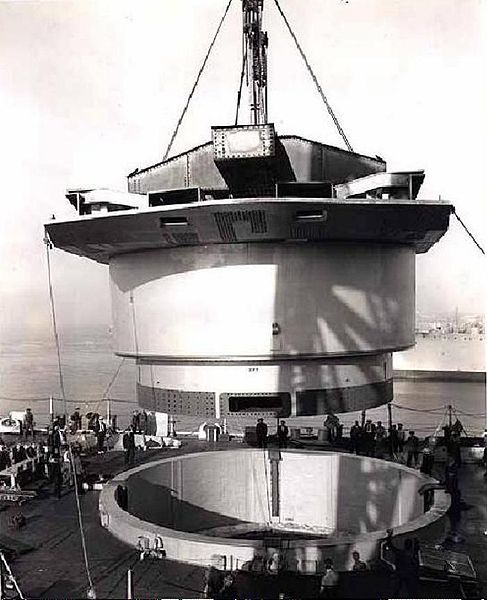
However, the first truly capital ships built by the Kriegsmarine were the Scharnhorst and Gneisenau. Rated as battleships, in reality they were battle cruisers because of their light main battery of 11” guns as opposed to the 14”, 15” or 16” batteries of other nations battleships. Despite this in displacement and armor protection of the ships was comparable to other battleships of the era and their designed speed of 31.5 knots was superior to almost all other battleships of the era including the British King George V Class and the US Navy’s North Carolina class. Only the massive battlecruiser HMS Hood was their superior in speed and firepower.
As built Scharnhorst and Gneisenau displaced 31,000 toms, however at full combat load they both weighed in at nearly 38,000 tons and were 772 feet long. They had an armor belt that was nearly 14 inches thick. Armed with a main battery of nine 11” guns and a secondary armament of twelve 5.9 inch guns they also mounted a powerful for the time anti- aircraft battery of fourteen 4.1 inch guns, 16 37mm and 16 20mm anti-aircraft cannons. Additionally they mounted six 21” torpedo tubes and carried three Arado 196 A3 scout planes. The main battery was eventually to be replaced by six 15” guns but this never occurred although Gneisenau was taken in hand to mount the new weapons but the conversion was never completed.
Scharnhorst firing at HMS Glorious
Laid down on 15 June 1935 and launched 3 October 1936 Scharnhorst was commissioned 7 January 1939. Her sister Gneisenau was laid down 6 May 1935, launched 8 December 1936 and commissioned 21 May 1938. Upon the commencement of the Second World War the two sisters began a reign of destruction on British shipping. In November they sank the Armed Merchant Cruiser HMS Rawalpindi During Operation Weserübung the pair surprised sank the aircraft carrier HMS Glorious and her two escorting destroyers, the only time a Fleet carrier was caught and sunk by battleships during the war. From January to March 1941 they conducted Operation Berlin against British merchant shipping in the North Atlantic sinking 22 ships before returning to base.
Scharnhorst and Gneisenau during Operation Cerebus
While in the port of Brest Gneisenau was bombed and torpedoed requiring extensive repairs. Due to the exposed location of the port the German high command decided to return the ships to Germany along with the Heavy Cruiser Prinz Eugen. The operation was called Operation Cerberus and it took place from 11-13 February 1942. The ships made a dash up the English Channel which was unsuccessfully contested by the British Royal Air Force and Royal Navy. However, both Scharnhorst and Gneisenau were damaged by mines and needed subsequent repairs. While undergoing repairs in Kiel Gneisenau was further damaged by the Royal Air Force requiring repairs in or to steam to the port of Gotenhafen for repair and conversion. Although some work was completed she was decommissioned and sunk as a blockship on 23 March 1945. Following the war she was raised by the Poles and scrapped.
Scharnhorst was repaired following Operation Cerberes and in March 1943 was transferred to Norway where along with Tirpitz, Admiral Scheer, Lutzow (the former Deutschland), Admiral Hipper and Prinz Eugen she became part of a “fleet in being” poised to strike the Allied convoys bound for Russia.
Admiral Bruce Fraser
The German surface ships were a potent force that if the circumstances allowed could devastate the Russia bound convoys and the Commander of the British Home Fleet, Admiral Bruce Fraser was determined to entrap and destroy any of these ships that threatened any convoy. As such in December 1943 Fraser formed a task group built around the HMS Duke of York to be ready to pounce on any German raider that threatened the convoys. His intent was to catch any of these ships, especially Scharnhorst and trap them between the convoys and their base, in conduction with a second task group centered around the cruisers HMS Belfast, HMS Norfolk, and HMS Sheffield, Known as Force One, and destroy the German battleship.
The key to British the British operation was Enigma the German code machine and cipher system which they had acquired from captured U-Boats, and which British code-breakers had mastered. The Germans decided to send Scharnhorst and five destroyers to locate and destroy convoy JW-55B which had been spotted by Luftwaffe reconnaissance aircraft. Because of Enigma Fraser knew that Scharnhorst would attempt to intercept the convoy and put his plan in motion.
Scharnhorst and her escorts set sail on Christmas Day 1943 under the command of Rear Admiral Erich Bey to conduct Operation Ostfront. Since Fraser knew that the Germans were coming he had the convoy to temporarily reverse course which caused the Germans to miss the convoy. When he did not find the convoy in the expected location Bey detached his destroyers to expand the search area, leaving Scharnhorst alone to face the enemy.
Rear Admiral Erich Bey
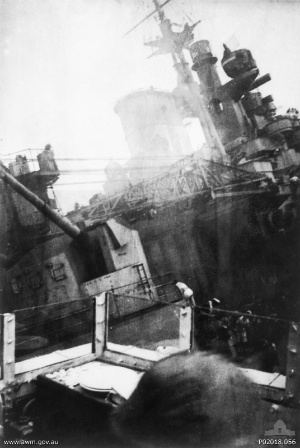
At about 0900 on December 26th 1943 the cruisers of Force One discovered Scharnhorst and the Battle of North Cape was on. Though little damage was suffered in the first engagement, the radar of Scharnhorst was knocked out, leaving her not only without air support or escort, but blind.
HMS Duke of York firing at Scharnhorst
Scharnhorst attempted to flee but Fraser’s Duke of York and her four escorting destroyers destroyers intercepted her. Without radar in the blinding snow squalls Scharnhorst was surprised. Duke of York’s first radar direct salvos knocked out her forward main battery but the German ship appeared to be making a getaway when a shell from Duke of York hit her number one boiler room and reduced her speed to barely ten knots. Although the German engineers and damage control teams made some repairs and were able to bring her speed back up to 22 knots, the British ships rapidly made up the distance enabling the British destroyers to launch torpedo attacks.
Knowing the ship was doomed Admiral Bey dispatched a message to the high command of the Kriegsmarine: “We will fight on until the last shell is fired.”
While she still attempted to fight off her attackers and escape she was struck by torpedoes from several destroyers as well as was pummeled by the at at distance of under 10,000 yards by Duke of York’s 14″ shells, as well as the 6″ shells of HMS Belfast and HMS Jamaica. Savaged by hits and incapable of further resistance the German ship capsized and sank at 1945 hours with the loss of all but 36 of her 1968 man crew. Her wreck was discovered 3 October 2000 some 70 miles north of North Cape Norway.
Survivors of Scharnhorst
Admiral Fraser praised the gallantry of the German ship to his officers later that night saying: “Gentlemen, the battle against Scharnhorst has ended in victory for us. I hope that if any of you are ever called upon to lead a ship into action against an opponent many times superior, you will command your ship as gallantly as Scharnhorst was commanded today”
After the battle Grand Admiral Erich Raeder who had authorized the sortie was relieved as commander in chief of the navy and was replaced by Grand Admiral Karl Donitz who commanded the U-Boat forces. Hitler was furious and ended most surface naval operations.
Memorial to Scharnhorst and her crew at Kiel
I have written many times about the tragedy of war, on land and at sea. Having served in combat zones on land and having been shot at by the enemy, as well as having served at sea on a cruiser I have a sense of what these men must have gone through on that final day of their lives. Though I am a realist and know that such tragedies will likely occur again, I do pray for the day that war will be no more and that those who serve in harm’s way will never have to again.
Peace
Padre Steve+