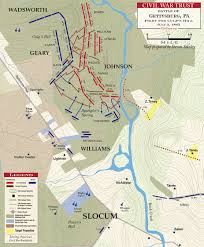
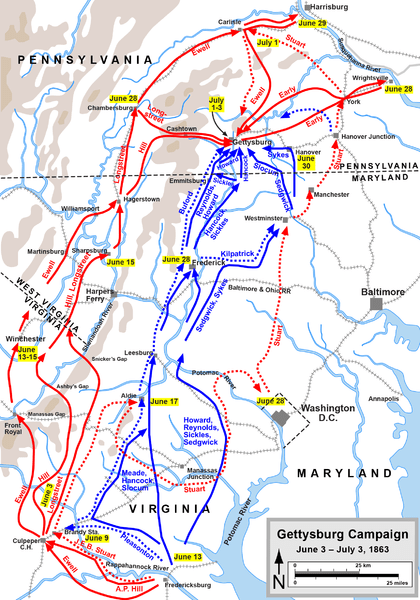
Note: This is a resource for those following my Gettysburg series and for my students that go with me on the Gettysburg Staff Ride. When the armies met at Gettysburg Lee’s Army of Norther Virginia had about 75,000-80,000 effectives, Meade’s Army of the Potomac had about 80,000-85,000 depending on the sources. This meant that they were relatively evenly matched in terms of manpower and that the battle came down to leadership, tactical decisions and strategic factors that were already in play by the time that the armies met at Gettysburg.
As a note of explanation the Confederate forces at the division and brigade level were named after their commander’s, or in some cases previous commanders. Confederate units were allocated to the Army from the various states, thus there is no Confederate “Regulars” as are shown in the Union order of battle. Union Corps were numbered as were the divisions and brigades in each corps. In some cases the brigades or divisions were referred to by the names of their commanders, but this was not consistent. Federal forces consisted of both Regular Army units as well as units allocated by the states. The reader can note the composition of each brigade in both the Union and Confederate armies to see from where the soldiers were recruited from.
So apart from that there is no story to tell tonight. Nothing in the way of commentary. This is simply a resource.
Have a great night.
Peace
Padre Steve+

Army of Northern Virginia – General Robert Edward Lee, Commanding

General Staff: Chief of Staff and Inspector General: Col Robert H. Chilton; Chief of Artillery: BG William N. Pendleton; Medical Director: Dr. Lafayette Guild; Aide de Camp and Asst. Adjutant General: Maj Walter H. Taylor; Aide de Camp and Asst. Military Secretary: Maj Charles Marshall; Aide de Camp and Asst. Inspector General: Maj Charles S. Venable; Aide de Camp: Maj Thomas M. R. Talcott
General Headquarters
Escort: 39th Virginia Cavalry Battalion (companies A & C)
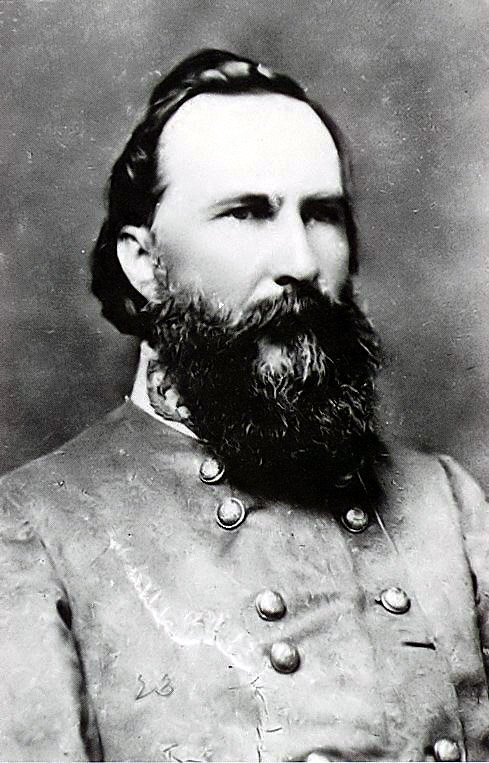

I Corps- Lt. Gen. James Longstreet, Commanding

McLaws’ Division- MG Lafayette McLaws
Kershaw’s Brigade-BG Joseph B. Kershaw
2nd South Carolina, 3rd South Carolina, 7th South Carolina, 8th South Carolina, 15th South Carolina; 3rd South Carolina Battalion
Barksdale’s Brigade- BG William Barksdale (mw); Col Benjamin G. Humphreys
13th Mississippi, 17th Mississippi, 18th Mississippi, 21st Mississippi
Semmes’ Brigade- BG Paul J. Semmes (mw); Col Goode Bryan
10th Georgia, 50th Georgia, 51st Georgia, 53rd Georgia
Wofford’s Brigade- BG William T. Wofford
16th Georgia, 18th Georgia, 24th Georgia, Cobb’s (Georgia) Legion, Phillips’ (Georgia) Legion, 3rd Georgia Sharpshooter Battalion
Cabell’s Artillery Battalion- Col Henry C. Cabell; Maj Samuel P. Hamilton
1st North Carolina Artillery, Battery A, Pulaski (Georgia) Artillery, 1st Richmond Howitzers, Troup (Georgia) Artillery

Pickett’s Division- MG George E. Pickett
Garnett’s Brigade- BG Richard B. Garnett (k); Maj Charles S. Peyton
8th Virginia, 18th Virginia, 19th Virginia, 28th Virginia, 56th Virginia
Kemper’s Brigade- BG James L. Kemper (w&c); Col Joseph Mayo, Jr
1st Virginia, 3rd Virginia, 7th Virginia, 11th Virginia, 24th Virginia
Armistead’s Brigade- BG Lewis A. Armistead (mw&c); Ltc William White (w); Maj Joseph R. Cabell; Col William R. Aylett
9th Virginia, 14th Virginia, 38th Virginia, 53rd Virginia, 57th Virginia
Dearing’s Artillery Battalion- Maj James Dearing; Maj John P. W. Read 
Fauquier (Virginia) Artillery, Hampden (Virginia) Artillery, Richmond Fayette (Virginia) Artillery, Blount’s (Virginia) Battery

Hood’s Division- MG John Bell Hood (w); BG Evander M. Law
Law’s Brigade-BG Evander M. Law; Col James L. Sheffield
4th Alabama, 15th Alabama, 44th Alabama, 47th Alabama, 48th Alabama
Robertson’s Brigade- BG Jerome B. Robertson (w); Ltc Philip A. Work
3rd Arkansas, 1st Texas, 4th Texas, 5th Texas
Anderson’s Brigade- BG George T. Anderson (w); Ltc William Luffman 
7th Georgia, 8th Georgia, 9th Georgia, 11th Georgia, 59th Georgia
Benning’s Brigade- BG Henry L. Benning
2nd Georgia, 15th Georgia, 17th Georgia, 20th Georgia
Henry’s Artillery Battalion- Maj Mathias W. Henry; Maj John C. Haskell
Branch (North Carolina) Battery, Charleston German (South Carolina) Artillery, Palmetto (South Carolina) Light Artillery, Rowan North Carolina Artillery
Artillery Reserve- Col James B. Walton
Alexander’s Artillery Battalion- Col Edward P. Alexander 
Ashland (Virginia) Artillery, Bedford (Virginia) Artillery, Brooks (South Carolina) Artillery, Madison (Louisiana) Light Artillery, Richmond (Virginia) Battery, Bath (Virginia) Battery
Washington (Louisiana) Artillery Battalion- Maj Benjamin F. Eshleman
First Company, Second Company, Third Company, Fourth Company

II Corps- Lt. Gen. Richard S. Ewell Commanding

Early’s Division- MG Jubal A. Early
Hays’ Brigade- BG Harry T. Hays
5th Louisiana, 6th Louisiana, 7th Louisiana, 8th Louisiana, 9th Louisiana
Smith’s Brigade-BG William Smith
31st Virginia, 49th Virginia, 52nd Virginia
Hoke’s Brigade- Col Isaac E. Avery (mw); Col Archibald C. Godwin
6th North Carolina: Maj Samuel McD. Tate, 21st North Carolina: Col William W. Kirkland, Maj James Beall, 57th North Carolina: Col Archibald C. Godwin, Ltc Hamilton C. Jones
Gordon’s Brigade- BG John Brown Gordon
13th Georgia, 26th Georgia, 31st Georgia, 38th Georgia, 60th Georgia, 61st Georgia
Jones’ Artillery Battalion- Ltc Hilary P. Jones
Charlottesville (Virginia) Artillery, Courtney (Virginia) Artillery, Louisiana Guard Artillery, Staunton (Virginia) Artillery
Cavalry 35th Virginia Battalion: Ltc Elijah V. White

Johnson’s Division- MG Edward Johnson
Steuart’s Brigade- BG George H. Steuart
1st Maryland Battalion, 1st North Carolina, 3rd North Carolina, 10th Virginia, 23rd Virginia, 37th Virginia
Stonewall Brigade- BG James A. Walker
2nd Virginia, 4th Virginia, 5th Virginia, 27th Virginia, 33rd Virginia
Nicholls’ Brigade-Col Jesse M. Williams
1st Louisiana, 2nd Louisiana, 10th Louisiana, 14th Louisiana, 15th Louisiana
Jones’ Brigade- BG John M. Jones (w); Ltc Robert H. Dungan
21st Virginia, 25th Virginia, 42nd Virginia, 44th Virginia, 48th Virginia, 50th Virginia
Andrews’ Artillery Battalion- Maj Joseph W. Latimer (mw); Cpt Charles I. Raine
1st Maryland Battery, Alleghany (Virginia) Artillery, Chesapeake (Maryland) Artillery, Lee (Virginia) Battery

Rodes’ Division- MG Robert E. Rodes
Daniel’s Brigade-BG Junius Daniel
32nd North Carolina, 43rd North Carolina, 45th North Carolina, 53rd North Carolina, 2nd North Carolina Battalion
Doles’ Brigade-BG George P. Doles
4th Georgia, 12th Georgia, 21st Georgia, 44th Georgia
Iverson’s Brigade- BG Alfred Iverson, Jr.
5th North Carolina, 12th North Carolina, 20th North Carolina, 23rd North Carolina
Ramseur’s Brigade- BG Stephen D. Ramseur
2nd North Carolina, 4th North Carolina, 14th North Carolina, 30th North Carolina
Rodes’ (old) Brigade- Col Edward A. O’Neal
3rd Alabama, 5th Alabama, 6th Alabama, 12th Alabama, 26th Alabama
Carter’s Artillery Battalion-Ltc Thomas H. Carter
Jefferson Davis (Alabama) Artillery, King William (Virginia) Artillery, Morris (Virginia) Artillery, Orange (Virginia) Artillery
Artillery Reserve- Col J. Thompson Brown
First Virginia Artillery Battalion- Cpt Willis J. Dance
2nd Richmond (Virginia) Howitzers, 3rd Richmond (Virginia) Howitzers, Powhatan (Virginia) Artillery, Rockbridge (Virginia) Artillery, Salem (Virginia) Artillery
Nelson’s Artillery Battalion- Ltc William Nelson
Amherst (Virginia) Artillery, Fluvanna (Virginia) Artillery, Milledge’s Georgia Battery

III Corps- Lt. Gen. Ambrose Powell Hill Commanding

Anderson’s Division- MG Richard H. Anderson
Wilcox’s Brigade- BG Cadmus M. Wilcox
8th Alabama, 9th Alabama, 10th Alabama, 11th Alabama, 14th Alabama
Mahone’s Brigade- BG William Mahone
6th Virginia, 12th Virginia, 16th Virginia, 41st Virginia, 61st Virginia
Wright’s Brigade-BG Ambrose R. Wright; Col William Gibson; BG Ambrose R. Wright
3rd Georgia, 22nd Georgia, 48th Georgia, 2nd Georgia Battalion
Perry’s Brigade- Col David Lang
2nd Florida, 5th Florida, 8th Florida
Posey’s Brigade- BG Carnot Posey (w); Col. Nathaniel Harris
12th Mississippi, 16th Mississippi, 19th Mississippi, 48th Mississippi
Cutt’s Artillery Battalion- Maj John Lane
Company A, Company B, Company C

Heth’s Division- MG Henry Heth (w); BG James J. Pettigrew 
Pettigrew’s Brigade-BG James J. Pettigrew; Col James K. Marshall (k); Maj John T. Jones 
11th North Carolina, 26th North Carolina, 47th North Carolina, 52nd North Carolina
Heth’s (old) Brigade- Col John M. Brockenbrough; Col Robert M. Mayo
40th Virginia, 47th Virginia, 55th Virginia, 22nd Virginia Battalion
Archer’s Brigade- BG James J. Archer (w&c); Col Birkett D. Fry (w&c); Ltc Samuel G. Shepard
13th Alabama, 5th Alabama Battalion, 1st Tennessee (Provisional Army), 7th Tennessee, 14th Tennessee
Davis’ Brigade- BG Joseph R. Davis 
2nd Mississippi, 11th Mississippi, 42nd Mississippi, 55th North Carolina
Garnett’s Artillery Battalion- Ltc John J. Garnett
Donaldsonville (Louisiana) Artillery, Huger (Virginia) Artillery, Lewis (Virginia) Artillery, Norfolk (Virginia) Blues Artillery

Pender’s Division-MG William D. Pender (mw); BG James H. Lane; MG Isaac R. Trimble (w&c); BG James H. Lane
McGowan’s Brigade-Col Abner M. Perrin
1st South Carolina (Provisional Army), 1st South Carolina Rifles, 12th South Carolina, 13th South Carolina, 14th South Carolina
Lane’s Brigade- BG James H. Lane; Col Clark M. Avery
7th North Carolina, 18th North Carolina, 28th North Carolina, 33rd North Carolina, 37th North Carolina
Thomas’ Brigade- BG Edward L. Thomas
14th Georgia, 35th Georgia, 45th Georgia, 49th Georgia
Scales’ Brigade- BG Alfred M. Scales (w); Ltc George T. Gordon; Col William L. J. Lowrance
13th North Carolina, 16th North Carolina, 22nd North Carolina, 34th North Carolina, 38th North Carolina
Poague’s Artillery Battalion- Maj William T. Poague
Albemarle (Virginia) Artillery, Charlotte (North Carolina) Artillery, Madison (Mississippi) Artillery, Brooke’s Virginia Battery
Artillery Reserve- Col Reuben L. Walker
McIntosh’s Artillery Battalion- Maj David G. McIntosh
Danville (Virginia) Artillery, Hardaway (Alabama) Artillery, 2nd Rockbridge (Virginia) Artillery, Johnson’s Virginia Battery
Pegram’s Artillery Battalion- Maj William R. J. Pegram; Cpt Ervin B. Brunson
Crenshaw (Virginia) Battery, Fredericksburg (Virginia) Artillery, Letcher (Virginia) Artillery, Pee Dee (South Carolina) Artillery, Purcell (Virginia) Artillery
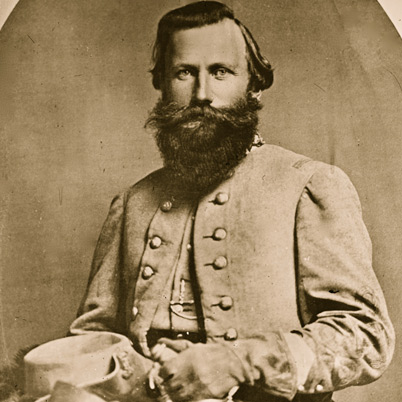

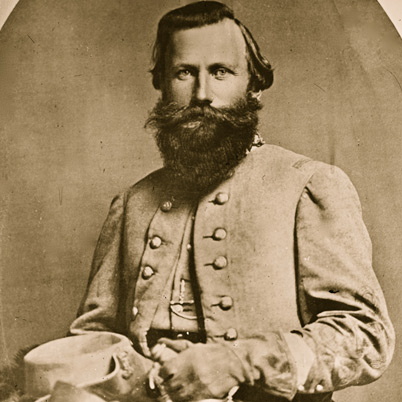
Cavalry Division- Maj. Gen. James Ewell Brown Stuart
Hampton’s Brigade- BG Wade Hampton 
1st North Carolina, 1st South Carolina, 2nd South Carolina, Cobb’s (Georgia) Legion, Jeff Davis (Mississippi) Legion, Phillips (Georgia) Legion
Robertson’s Brigade (not present at Gettysburg) BG Beverly H. Robertson
4th North Carolina, 5th North Carolina
Fitzhugh Lee’s Brigade- BG Fitzhugh Lee
1st Maryland Battalion, 1st Virginia, 2nd Virginia, 3rd Virginia, 4th Virginia, 5th Virginia
Jenkins’ Brigade- BG Albert G. Jenkins (w); Col Milton J. Ferguson
14th Virginia, 16th Virginia, 17th Virginia, 34th Virginia Battn., 36th Virginia Battn., Jackson’s (Virginia) Battery
William H. F. (Rooney) Lee’s Brigade- Col John R. Chambliss, Jr.
2nd North Carolina Cavalry, 9th Virginia, 10th Virginia, 13th Virginia
Jones’ Brigade- BG William E. Jones
6th Virginia, 7th Virginia, 11th Virginia
Stuart’s Horse Artillery- Maj Robert F. Beckham
Breathed’s (Virginia) Battery, Chew’s (Virginia) Battery, Griffin’s (Maryland) Battery Hart’s (South Carolina) Battery, McGregor’s (Virginia) Battery, Moorman’s (Virginia) Battery
Imboden’s Command- BG John D. Imboden
18th Virginia, 62nd Virginia, McNeill’s Company (Virginia), Staunton (Virginia) Battery
Union Order of Battle


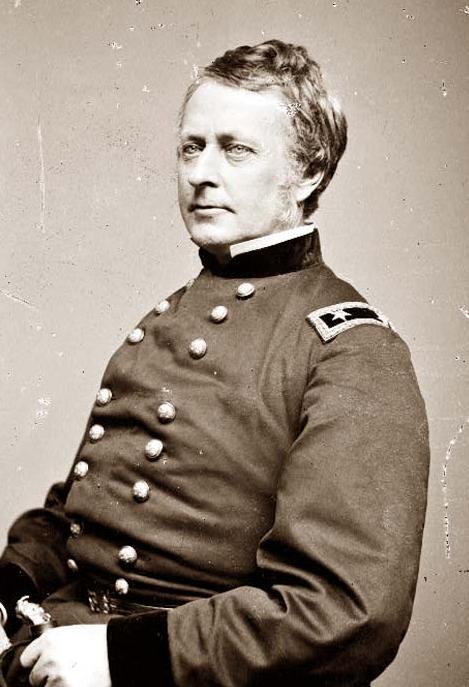
Army of the Potomac – Major General George Gordon Meade, Commanding
General Staff: Chief of Staff: Maj. Gen. Daniel Butterfield, Chief of Artillery: Brig. Gen. Henry J. Hunt, Medical Director: Maj Jonathan Letterman, Chief of Engineers: Brig. Gen. Gouverneur K. Warren, Bureau of Military Information: Col. George H. Sharpe
Command of the Provost Marshal General: Brig. Gen. Marsena R. Patrick
93rd New York: Col. John S. Crocker, 8th United States (8 companies): Capt. Edwin W. H. Read, 2nd Pennsylvania Cavalry: Col. R. Butler Price, 6th Pennsylvania Cavalry (Companies E&I): Capt. James Starr, Regular cavalry
Engineer Brigade: Brig. Gen. Henry W. Benham
15th New York (3 companies): Maj Walter L. Cassin, 50th New York: Col. William H. Pettes, U.S. Battalion: Capt. George H. Mendell

I Corps- Maj. Gen. John F. Reynolds (k)

First Division- Brig. Gen. James S. Wadsworth
1st Brigade (The Iron Brigade)-Brig. Gen. Solomon Meredith (w); Col.. William W. Robinson
19th Indiana, 24th Michigan, 2nd Wisconsin, 6th Wisconsin, 7th Wisconsin
2nd Brigade- Brig. Gen. Lysander Cutler
7th Indiana, 76th New York, 84th New York (14th Militia), 95th New York, 147th New York, 56th Pennsylvania (9 companies)

Second Division- Brig. Gen. John C. Robinson
1st Brigade- Brig. Gen. Gabriel R. Paul (w); Col. Samuel H. Leonard (w); Col. Adrian R. Root (w&c); Col. Richard Coulter (w); Col. Peter Lyle; Col. Richard Coulter
16th Maine, 13th Massachusetts, 94th New York, 104th New York, 107th Pennsylvania
2nd Brigade-Brig. Gen. Henry Baxter
12th Massachusetts, 83rd New York (9th Militia), 97th New York, 11th Pennsylvania, 88th Pennsylvania, 90th Pennsylvania

Third Division- Maj. Gen. Abner Doubleday; Brig. Gen. Thomas A. Rowley; Maj. Gen. Abner Doubleday
1st Brigade- Col. Chapman Biddle; Brig. Gen. Thomas A. Rowley; Col. Chapman Biddle
80th New York (20th Militia), 121st Pennsylvania, 142nd Pennsylvania, 151st Pennsylvania
2nd Brigade-Col. Roy Stone (w); Col. Langhorne Wister (w); Col. Edmund L. Dana
143rd Pennsylvania, 149th Pennsylvania, 150th Pennsylvania
3rd Brigade- Brig. Gen. George J. Stannard (w); Col. Francis V. Randall
13th Vermont, 14th Vermont, 16th Vermont
Artillery Brigade- Col. Charles S. Wainwright
Maine Light, 2nd Battery (B), Maine Light, 5th Battery (E), 1st New York Light, Batteries E&L, 1st Pennsylvania Light, Battery B, 4th United States, Battery B

II Corps- Maj. Gen. Winfield S. Hancock (w); Brig. Gen. John Gibbon; Brig. Gen. William Hays

First Division- Brig. Gen. John C. Caldwell
1st Brigade- Col. Edward E. Cross (mw); Col. H. Boyd McKeen
5th New Hampshire, 61st New York, 81st Pennsylvania , 148th Pennsylvania
2nd Brigade (The Irish Brigade) – Col. Patrick Kelly
28th Massachusetts, 63rd New York (2 companies),69th New York (2 companies), 88th New York (2 companies), 116th Pennsylvania (4 companies)
3rd Brigade-Brig. Gen. Samuel K. Zook (mw); Lt. Col.. Charles G. Freudenberg (w); Col. Richard P. Roberts (k); Lt. Col.. John Fraser
52nd New York, 57th New York, 66th New York, 140th Pennsylvania
4th Brigade- Col. John R. Brooke 
27th Connecticut (2 companies), 2nd Delaware, 64th New York, 53rd Pennsylvania, 145th Pennsylvania (7 companies)

Second Division- Brig. Gen. John Gibbon (w); Brig. Gen. William Harrow
1st Brigade- Brig. Gen. William Harrow; Col. Francis E. Heath
19th Maine, 15th Massachusetts, 1st Minnesota, 82nd New York (2nd Militia)
2nd Brigade- Brig. Gen. Alexander S. Webb 
69th Pennsylvania, 71st Pennsylvania, 72nd Pennsylvania, 106th Pennsylvania
3rd Brigade- Col. Norman J. Hall
19th Massachusetts, 20th Massachusetts, 7th Michigan, 42nd New York, 59th New York (4 companies)
Unattached: Massachusetts Sharpshooters, 1st Company

III Corps- Maj. Gen. Daniel E. Sickles (w); Maj. Gen. David B. Birney

First Division- Maj. Gen. David B. Birney; Brig. Gen. J. H. Hobart Ward 
1st Brigade- Brig. Gen. Charles K. Graham (w&c); Col. Andrew H. Tippin; Col. Henry J. Madill
57th Pennsylvania (8 companies), 63rd Pennsylvania, 68th Pennsylvania, 105th Pennsylvania, 114th Pennsylvania, 141st Pennsylvania
2nd Brigade- Brig. Gen. J. H. Hobart Ward; Col. Hiram Berdan
20th Indiana, 3rd Maine, 4th Maine, 86th New York, 124th New York, 99th Pennsylvania, 1st United States Sharpshooters, 2nd United States Sharpshooters (8 companies)
3rd Brigade- Col. P. Régis de Trobriand
17th Maine, 3rd Michigan, 5th Michigan, 40th New York, 110th Pennsylvania (6 companies)

Second Division- Brig. Gen. Andrew A. Humphreys
1st Brigade- Brig. Gen. Joseph B. Carr 
1st Massachusetts, 11th Massachusetts, 16th Massachusetts, 12th New Hampshire, 11th New Jersey,26th Pennsylvania
2nd Brigade-Col. William R. Brewster
70th New York, 71st New York, 72nd New York, 73rd New York, 74th New York, 120th New York
3rd Brigade-Col. George C. Burling
2nd New Hampshire, 5th New Jersey, 6th New Jersey, 7th New Jersey, 8th New Jersey,115th Pennsylvania
Artillery Brigade-Capt. George E. Randolph (w); Capt. A. Judson Clark
1st New Jersey Light, Battery B, 1st New York Light, Battery D, New York Light, 4th Battery, 1st Rhode Island Light, Battery E, 4th United States, Battery K

V Corps-Maj. Gen. George Sykes

First Division- Brig. Gen. James Barnes 
1st Brigade-Col. William S. Tilton
18th Massachusetts, 22nd Massachusetts, 1st Michigan, 118th Pennsylvania
2nd Brigade-Col. Jacob B. Sweitzer
9th Massachusetts, 32nd Massachusetts, 4th Michigan, 62nd Pennsylvania
3rd Brigade-Col. Strong Vincent (mw); Col. James C. Rice
20th Maine, 16th Michigan, 44th New York, 83rd Pennsylvania

Second Division-Brig. Gen. Romeyn B. Ayres
1st Brigade- Col. Hannibal Day
3rd United States (Cos. B, C, E, G, I and K), 4th United States (Cos. C, F, H and K), 6th United States (Cos. D, F, G, H and I), 12th United States (Cos. A, B, C, D and G, 1st Bn. and Cos. A, C and D, 2nd Bn.), 14th United States (Cos. A, B, D, E, F and G, 1st Bn. and Cos. F and G, 2nd Bn.)
2nd Brigade-Col. Sidney Burbank
2nd United States (Cos. B, C, F, H, I and K), 7th United States (Cos. A, B, E and I), 10th United States (Cos. D, G and H), 11th United States (Cos. B, C, D, E, F and G),17th United States (Cos. A, C, D, G and H, 1st Bn. and Cos. A and B, 2nd Bn.)
3rd Brigade-Brig. Gen. Stephen H. Weed (k); Col. Kenner Garrard
140th New York, 146th New York, 91st Pennsylvania, 155th Pennsylvania
Third Division-Brig. Gen. Samuel W. Crawford
1st Brigade-Col. William McCandless
1st Pennsylvania Reserves (9 companies), 2nd Pennsylvania Reserves, 6th Pennsylvania Reserves,13th Pennsylvania Reserves
2nd Brigade (not present—assigned to Washington defenses)
3rd Brigade-Col. Joseph W. Fisher
5th Pennsylvania Reserves, 9th Pennsylvania Reserves, 10th Pennsylvania Reserves, 11th Pennsylvania Reserves, 12th Pennsylvania Reserves (9 companies)
Artillery Brigade-Capt. Augustus P. Martin
Massachusetts Light, 3rd Battery, 1st New York Light, Battery C, 1st Ohio Light, Battery L, 5th United States, Battery D, 5th United States, Battery I

VI Corps-Maj. Gen. John Sedgwick

First Division-Brig. Gen. Horatio G. Wright
1st Brigade-Brig. Gen. Alfred T. A. Torbert
1st New Jersey, 2nd New Jersey, 3rd New Jersey, 15th New Jersey
2nd Brigade-Brig. Gen. Joseph J. Bartlett; Col. Emory Upton
5th Maine, 121st New York, 95th Pennsylvania, 96th Pennsylvania
3rd Brigade-Brig. Gen. David A. Russell
6th Maine, 49th Pennsylvania (4 companies), 119th Pennsylvania, 5th Wisconsin
Provost Guard: 4th New Jersey (3 companies): Capt. William R. Maxwell

Second Division- Brig. Gen. Albion P. Howe
2nd Brigade-Col. Lewis A. Grant
2nd Vermont, 3rd Vermont, 4th Vermont, 5th Vermont, 6th Vermont
3rd Brigade-Brig. Gen. Thomas H. Neill
7th Maine (6 companies), 33rd New York (detachment), 43rd New York, 49th New York, 77th New York, 61st Pennsylvania

Third Division-Maj. Gen. John Newton; Brig. Gen. Frank Wheaton
1st Brigade-Brig. Gen. Alexander Shaler
65th New York, 67th New York, 122nd New York, 23rd Pennsylvania, 82nd Pennsylvania
2nd Brigade-Col. Henry L. Eustis
7th Massachusetts, 10th Massachusetts, 37th Massachusetts, 2nd Rhode Island.
3rd Brigade-Brig. Gen. Frank Wheaton; Col. David J. Nevin
62nd New York, 93rd Pennsylvania, 98th Pennsylvania,139th Pennsylvania
Artillery Brigade-Col. Charles H. Tompkins
Massachusetts Light, 1st Battery, New York Light, 1st Battery, New York Light, 3rd Battery, 1st Rhode Island Light, Battery C, 1st Rhode Island Light, Battery G, 2nd United States, Battery D, 2nd United States, Battery G, 5th United States, Battery F
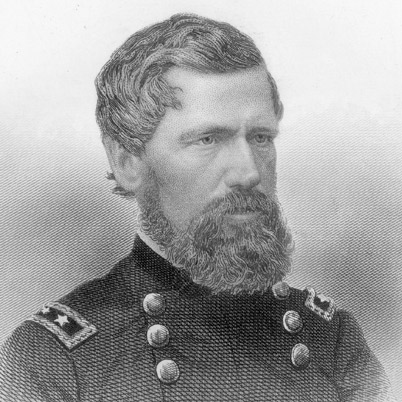

XI Corps-Maj. Gen. Oliver O. Howard; Maj. Gen. Carl Schurz

First Division-Brig. Gen. Francis C. Barlow (w); Brig. Gen. Adelbert Ames
1st Brigade-Col. Leopold von Gilsa
1st New York (9 companies), 54th New York, 68th New York, 153rd Pennsylvania
2nd Brigade-Brig. Gen. Adelbert Ames; Col. Andrew L. Harris
17th Connecticut, 25th Ohio, 75th Ohio, 107th Ohio

Second Division-Brig. Gen. Adolph von Steinwehr
1st Brigade-Col. Charles R. Coster
134th New York, 154th New York, 27th Pennsylvania, 73rd Pennsylvania
2nd Brigade Col. Orland Smith
33rd Massachusetts, 136th New York, 55th Ohio, 73rd Ohio

Third Division-Maj. Gen. Carl Schurz; Brig. Gen. Alexander Schimmelfennig; Maj. Gen. Carl Schurz
1st Brigade-Brig. Gen. Alexander Schimmelfennig; Col. George von Amsberg
82nd Illinois, 45th New York, 157th New York, 61st Ohio, 74th Pennsylvania
2nd Brigade-Col. Wladimir Krzyzanowski
58th New York, 19th New York, 82nd Ohio, 75th Pennsylvania, 26th Wisconsin
Artillery Brigade-Maj Thomas W. Osborn
1st New York Light, Battery I, New York Light, 13th Battery, 1st Ohio Light, Battery I, 1st Ohio Light, Battery K, 4th United States, Battery G

XII Corps-Maj. Gen. Henry W. Slocum; Brig. Gen. Alpheus S. Williams

First Division-Brig. Gen. Alpheus S. Williams; Brig. Gen. Thomas H. Ruger
1st Brigade-Col. Archibald L. McDougall
5th Connecticut, 20th Connecticut, 3rd Maryland, 123rd New York, 145th New York, 46th Pennsylvania
3rd Brigade-Brig. Gen. Thomas H. Ruger; Col. Silas Colgrove
27th Indiana, 2nd Massachusetts, 13th New Jersey, 107th New York, 3rd Wisconsin
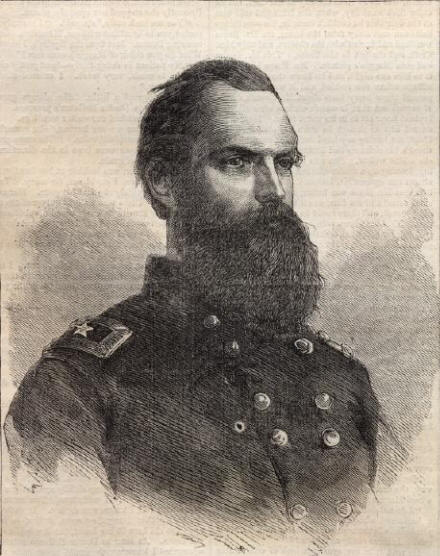

Second Division-Brig. Gen. John W. Geary
1st Brigade-Col. Charles Candy
5th Ohio, 7th Ohio, 29th Ohio, 66th Ohio, 28th Pennsylvania, 147th Pennsylvania (8 companies)
2nd Brigade-Col. George A. Cobham, Jr.; Brig. Gen. Thomas L. Kane
29th Pennsylvania, 109th Pennsylvania, 111th Pennsylvania
3rd Brigade-Brig. Gen. George S. Greene 
60th New York, 78th New York, 102nd New York, 137th New York, 149th New York
Lockwood’s Brigade-Brig. Gen. Henry H. Lockwood
1st Maryland, Potomac Home Brigade, 1st Maryland, Eastern Shore,150th New York
Artillery Brigade-Lt Edward D. Muhlenberg
1st New York Light, Battery M, Pennsylvania Light, Battery E,4th United States, Battery F 5th United States, Battery K
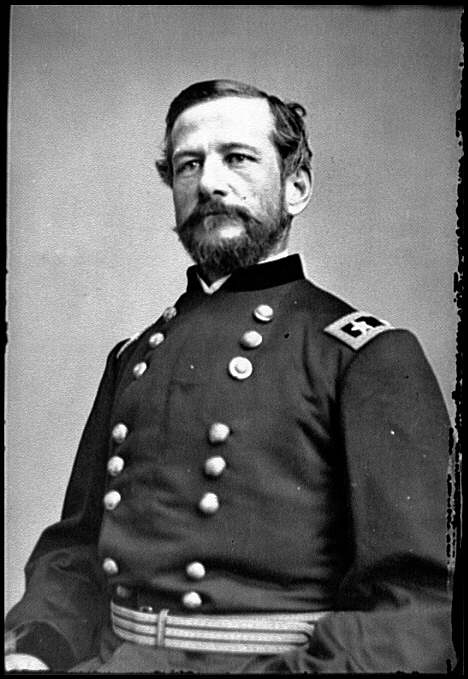

Cavalry Corps -Maj. Gen. Alfred Pleasonton
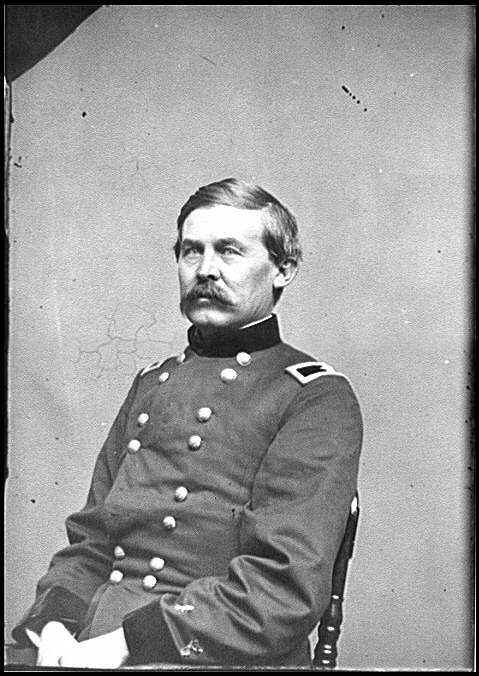

First Division-Brig. Gen. John Buford
1st Brigade-Col. William Gamble
8th Illinois, 12th Illinois (4 cos.) & 3rd Indiana (6 cos.), 8th New York
2nd Brigade-Col. Thomas Devin
6th New York (6 companies), 9th New York, 17th Pennsylvania, 3rd West Virginia, Companies A and C
Reserve Brigade-Brig. Gen. Wesley Merritt
6th Pennsylvania, 1st United States, 2nd United States, 5th United States, 6th United States

Second Division-Brig. Gen. David Gregg
1st Brigade-Col. John B. McIntosh
1st Maryland (11 companies), Purnell (Maryland) Legion, Company A, 1st Massachusetts, 1st New Jersey, 1st Pennsylvania, 3rd Pennsylvania, 3rd Pennsylvania Heavy Artillery, Section, Battery H
3rd Brigade-Col. John I. Gregg
1st Maine (10 companies), 10th New York, 4th Pennsylvania, 16th Pennsylvania

Third Division-Brig. Gen. Judson Kilpatrick
1st Brigade-Brig. Gen. Elon J. Farnsworth (k); Col. Nathaniel P. Richmond
5th New York, 18th Pennsylvania, 1st Vermont, 1st West Virginia (10 companies)
2nd Brigade-Brig. Gen. George A. Custer
1st Michigan, 5th Michigan, 6th Michigan, 7th Michigan: (10 companies)
Horse Artillery
1st Brigade-Capt. James M. Robertson
9th Michigan Battery, 6th New York Battery,2nd United States, Batteries B and L, 2nd United States, Battery M, 4th United States, Battery E
2nd Brigade-Capt. John C. Tidball
1st United States, Batteries E and G, 1st United States, Battery K, 2nd United States, Battery A

Artillery Reserve-Brig. Gen. Robert O. Tyler, Capt. James M. Robertson
1st Regular Brigade-Capt. Dunbar R. Ransom
1st United States, Battery H, 3rd United States, Batteries F and K, 4th United States, Battery C, 5th United States, Battery C
1st Volunteer Brigade-Lt. Col.. Freeman McGilvery
Massachusetts Light, 5th Battery (E), Massachusetts Light, 9th Battery, New York Light, 15th Battery, Pennsylvania Light, Batteries C and F
2nd Volunteer Brigade-Capt. Elijah D. Taft
1st Connecticut Heavy, Battery B, 1st Connecticut Heavy, Battery M, Connecticut Light, 2nd Battery. New York Light, 5th Battery
3rd Volunteer Brigade-Capt. James F. Huntington
New Hampshire Light, 1st Battery, 1st Ohio Light, Battery H, 1st Pennsylvania Light, Batteries F and G, West Virginia Light, Battery C
4th Volunteer Brigade-Capt. Robert H. Fitzhugh
Maine Light, 6th Battery, Maryland Light, Battery A, New Jersey Light, 1st Battery, 1st New York Light, Battery G, 1st New York Light, Battery K
Train Guard: 4th New Jersey Infantry (7 companies)