Elizabeth Cady Stanton
Friends of Padre Steve’s World,
Today and for the next few days I am going back to a part of my Gettysburg and Civil War text dealing with women’s rights. As you might have noticed I frequently write about civil rights and history. This is important to me and I cannot imaging not trying to continually write and educate people about subjects that matter as much now as they did 150 years ago or more. I have spent a lot of time working on this section recently, and will probably do some more in the coming weeks, but I think that you will find it interesting, and still relevant in our society.
Peace
Padre Steve+
Another development, which in large part is related to the abolition movement, was the campaign for women’s rights. The Civil War was also revolutionary because it was instrumental in propelling women into positions in American society that they had never before been allowed. The war Some of this was because many women decided to like those who campaigned for the end of slavery and the rights of African Americans to turn the world upside down. The war allowed the women who served, “in uniform or not, war permitted these women to experiment with a series of role reversals in gender,” [1] and in some cases gender and race. These experiments were the beginning of the struggle for women’s equality and to women serving in the military.
In much of the country and in particular the South women’s rights were the same as granted in English Common Law. Common law held to the more archaic understanding of the Christian Church that women were the property of their husbands, especially in cases of infidelity including during the trial of Dan Sickles for killing Barton Key. But the war “imposed on American society as such social disruption as it did physical destruction. Within that disruption, for one brief and bloody historical moment, an entirely new way of ordering of race and gender within a republican society became possible,” [2] however, in the end it would take another century or more for much of this change to be realized.
Southern culture and law ensured that women had even few rights than the women in the North. In the North women were making some gains in the workplace and in various professions such as teaching and nursing, and as the industrial revolution modernized the workplace and required more skilled workers, particularly in the textile industries, the availability of work for women who wanted to work outside the home increased. Even uneducated Northern women sought work in the growing number of factories and by 1860 “there were more than 270,000 female operatives, the vast majority being employed in Northern textile, shoe, clothing, printing, and publishing establishments. Over 135,000 worked in New England factories and composed 65 percent of the region’s industrial labor.” [3] Educated Northern women, while excluded from most professions, found their way into teaching, nursing, non-ordained religious work, and writing. Some found work in Federal government agencies in Washington DC, including “Clara Barton, a successful teacher who had trouble landing a position because she was a women, found work in the Patent Office, where she briefly made the same salary as her male colleagues.” [4]
But in the South women were continued to be held back. This was in large part due to the understanding that the “household was a spatial unit, defined by the property to which the owner not only held legal title over, but over which he exercised exclusive rights.” [5] As such Southern men had nearly unlimited rights and power over what occurred on his property, for “in societies in which landed property comprised the chief means of subsistence…legal title to the land had historically incorporated claims over the persons and labor of those who were dependents on it.” [6] In the South, as opposed to the North comparatively few women entered the Southern labor market, in large part because of the region’s emphasis on agriculture, dependence on slave labor, and a culture that frowned on women working outside the home. 1860 when Northern women were becoming a force to be reckoned with in the labor market, “only 12,000 women worked in factories, 10 percent of the regions wage earners.” [7] The lack of trained and experienced women workers would be a crippling impediment to the Confederate War effort.
For Southern men the stakes of ensuring slavery’s continuation and expansion were high, the culture of the South ante-bellum South was deeply patriarchal and “The possibility that the black man might be empowered like any other was such a threat to the southern social hierarchy that some white southerners were inclined to fear not only for their position as slaveowners but for the entire basis of their claim to patriarchal power. They feared for their power not only over their slaves but over their women as well.” [8]
William Lloyd Garrison and the leaders of the abolitionist movement came into contact with two southern women who had converted to the abolitionist cause; South Carolina cotton heiresses, Sarah and Angelina Grimke. The two women were passionate as well as eloquent and became popular lecturers on the abolitionist speaking circuit. Angelina Grimke was a powerful speaker linked to abolition and women’s rights, she made herself unwelcome in her native Charleston South Carolina “with the publication of An Appeal to the Christian Women of the South. She urged Southern women, many of whom opposed slavery, to speak out, and despite her failure to reach the audience to which she spoke, hers is one of the most significant abolitionist writings.” [9] She proclaimed:
“We cannot push Abolitionism forward with all our might until we take up the stumbling block out of the road…. If we surrender the right to speak in public this year, we must surrender the right to petition next year, and the right to write the year after, and so on. What then can the woman do for the slave, when she herself is under the feet of man and shamed into silence?” [10]
Her sister Sarah was also active in writing, but she focused her attention not just on abolition, but “on the inferior status of both woman and the Negro in The Equality of the Sexes and the Condition of Women.” [11] The Grimke sisters and other women like them brought Garrison and others in the abolitionist movement into contact with the early leaders of the new women’s rights movement. The leaders of the movement, Elizabeth Cady Stanton, Abby Kelley, and Lydia Maria Child were outspoken in their belief that “a campaign to emancipate slaves could not avert its eyes from the need to emancipate American women from social conventions and legal restraints that prevented them, like the slave, from owning property and voting, and kept them altogether subservient to the interests of white males.” [12]
The principals involved in the abolitionist and the women’s movements, those of freedom, emancipation and equality eventually forged a bond between them, and have provided inspiration to others in their quest for political and social equality. For William Lloyd Garrison “the woman question clearly demonstrated how the logic of reform united all good causes and carried them to new ground. If in their endeavors to break the chains of slavery women discovered, as Abby Kelley put it, that “we were manacled ourselves,” the abolitionist principle required a defense of equal rights without regard to race or sex.” [13]
While women and blacks were “being brought together in a dual crusade, often behind the same leaders,” [14] that did not mean that both parties were given equal consideration, even among the supporters of abolition and women’s rights. All to often, women found that their rights were not considered as important by the political leadership fighting for the rights of black men. Few in Congress “responded sympathetically to feminists’ demands. Reconstruction they insisted, was the “Negro’s hour,” [15] a view shared by Frederick Douglass. Though the economic situation of women began to improve, especially through women being admitted to the Civil Service, much else remained unchanged, women were still second class citizens without the right to vote, with few legal rights, and few opportunities to move up in society apart from her husband.
But change was beginning to occur as women began to have more educational opportunities in the post-war years, and began to find employment opportunities with the expansion of industry. Women’s suffrage was not included in the Fifteenth Amendment, which caused a split between women’s groups and their long-time abolitionist allies who told them “If put on the same level and urged in the same connection, neither will soon be accomplished.” [16] Even so in some territories women were granted the right to vote in territorial elections, “women were given the vote in Wyoming Territory in 1869. However, Wyoming’s admission as a state twenty years later came only after a heated debate on the women’s suffrage article in the state constitution.” [17]
In the 1800s women in the United States found themselves bound by two major factors, law and culture. English common law and early in the life of the Republic it was determined by John Adams that women should be exclude from political life as they were “unsuited by nature for the businesses of life or the hardy enterprises of war, they had nothing of value to offer the state.” [18] Women had no claim to property, wages, or even their children. Thomas Jefferson had “defined the essence of liberty as independence, which required ownership of productive property. A man dependent on others for a living could never truly be free, nor could a dependent class constitute the basis of republican government. Women, children, and slaves were dependent; that defined them out of the polity of republican freedmen.” [19] This understanding of the rights and citizenship of women persisted as the official law of the nation throughout the ante-bellum era, through and after the Civil War, and up until the passage and ratification of the Nineteenth Amendment.
As such, single women had few rights while married women had even fewer as, married women could not “own property in her own right, make contracts or otherwise conduct business of her own. She was supposed to be modest and submissive. The married woman, in fact, was for all intents and purposes the chattel of her husband.” [20] The reality was stark for women, but especially married women for as one historian noted: “marriage very nearly meant the legal annihilation of a woman…once a woman was married all property and property rights were transferred to her husband, and she was permitted to own nothing in her own name. Married women could not make contracts, could not sue, could not buy or sell, except over their husband’s signatures.” [21] Adult white women were citizens in a constitutional sense, but in the North and South alike their terms “of their citizenship had always been set by the perceived necessities of marriage and its gender asymmetries between man and woman, husband and wife.” [22]
The role of culture and religion was another major constraint on women’s rights during the ante-bellum period and much of this centered on Victorian social and cultural ideals which brought about what can be safely called a “a cult of true womanhood” which “dictated that women always appear demure, submissive, pious, and concerned with the home and family.” [23] In the Victorian ideal, it was the man whose sphere of life was in worldly pursuits, while women were limited to the task of bearing and raising children and maintaining the traditional private domain of hearth and home. This understanding of separate spheres was supported was often supported by the churches, especially those the conservative and evangelical variety.
While this was true in the North it was especially prevalent in the South and promoted by southern evangelical churches. The “explicit goal of southern evangelicalism was to keep the religious role of white women within narrow and carefully policed bounds. Evangelical Southerners clearly designated men as society’s (and women’s) rightful rulers and ultimate authorities. They were, in the 1830 words of Southern writer Virginia Carey, “the anointed lords of creation”; St. Paul’s injunction that wives “submit yourself to your own husbands as to the Lord” provided the text for many a Sunday sermon.” [24]
In matters of sexual behavior there was a pronounced double standard between men and women. If a man was an adulterer it was frowned upon, but not necessarily a condition that would invoke the scorn of the community unless an aggrieved husband took the law into his own hands and killed the adulterer, in which case the murderer could easily be forgiven. However, for the married adulteress, the social damnation was all too real, even from other women, who often believed that there was no excuse for such behavior and that the adulteress “deserved the most stringent fate for her violation of the dictates of virtue.” [25]
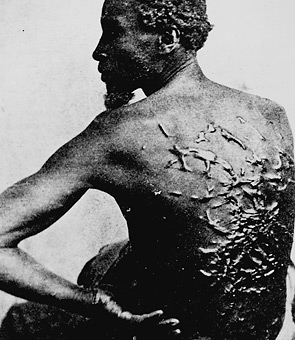
A married woman’s position was as close to being a slave as could be, and only the plight of black female slaves was worse, for they were simply chattel. The few free black women mainly stayed unmarried “in order to maintain what few property rights they were entitled to.” [26] As they also did over blacks, white men ruled over women in all spheres of life. While the eventual emancipation of blacks provided more rights for black men, those did not help many black women as Sojourner Truth, a pioneering African-American abolitionist who spent forty-years as a slave said toward the end of her long life:
“There is a great stir about colored men getting their rights, but not one word about colored women; and if colored men get their rights, and not colored women theirs, you see colored men will be master over the women, and it will be just as bad as it was before. So I am for keeping the thing going while things are still stirring because if we wait till it is still, it will take a great while to get it going again….I suppose I am the only colored woman that goes on to speak for the rights of the colored women. I want to keep the thing stirring, now that the ice is cracked…” [27]
Elizabeth Cady Stanton was among the most vocal of women’s rights advocates. She was the daughter of a leading Federalist lawyer, who served a term in the House of Representatives and on the New York Supreme Court. Her father planted in her the desire to learn, a love for law, and a passion for civil rights which she was able to pursue. Unlike many women of her day, Stanton was able to graduate from the Johnstown Academy and the Troy Female Academy in Troy, New York, before she was married to Henry Brewster Stanton, a journalist, anti-slavery orator and attorney, with who she had seven children.
Stanton believed that a woman’s place in the home was ultimately destructive and “reflected her subordinate position in society and confined her to domestic duties that served to “destroy her confidence in her own powers, lessen her self respect, and to make her willing to lead a dependent and abject life.” [28] Stanton noted how the condition of women of her day was “more fully identified with the slave than man possibly can be… For while the man is born to do whatever he can, for the woman and the negro the is no such privilege.” [29] It was a key observation and something even today, a state that some politicians, pundits and preachers would like to return women.
Since nearly all of the most “outspoken feminists had been schooled in abolitionist movement” they were “suspect in the South, where society was conservative, patriarchal, and insistence that ladies live in a kind of earthly limbo.” [30] Such women posed a threat to the pillars of Southern society. Since the South was now fighting tooth and nail against the abolitionist movement, anything closely connected with that movement, including the women who advocated abolition and women’s rights were shunned and their message rejected and inflammatory and revolutionary. It was not until the crisis caused by the Civil war that Southern women began to seize “the opportunity to lay claim to an increased reciprocity in gender relations.” [31]
But even with the abolition movement there was opposition the women’s rights, the 1839 meeting of the American Anti-Slavery Society witnessed a debate over including women in the membership. Conservative Evangelicals recoiled in disgust, and when the convention voted to allow women into the membership Lewis Tappan “got up a starchy “protest” which condemned the “repugnant” admission of women as an ‘expression of local and sectarian feelings…well suited to the unnecessary reproach and embarrassment to the cause of the enslaved as [it] is at variance with the general usage and sentiments of this and other nations.” [32] In May of 1840 the American Anti-Slavery Society split among religious lines when leading evangelicals led by the Tappan brothers withdrew from it.
But that neither stopped Garrison from working with women, nor kept Frederick Douglass from embracing them as part of the abolitionist movement. From this rather inauspicious beginning, the women’s rights movement began to infiltrate society, especially in the field of education. In 1848 at Seneca New York there was a convention that launched the modern women’s rights movement. Led by Stanton and Elizabeth Mott the delegates published a “Declaration of Sentiments, modeled on the Declaration of Independence, proclaimed “that all men and women are created equal” and deserved their “inalienable rights” include the right to elective franchise.” [33] The declaration was bold and its denunciation of the place of women in society to be considered revolutionary in character. Part read:
“He has never permitted her to exercise her inalienable right to elective franchise. He has compelled her to submit to laws, in the formation of which she had no voice. He has withheld from her rights which are given to the most ignorant and degraded men – both natives and foreigners… He has made her, if married, in the eye of the law, civilly dead. He has taken from her all right to property, even to the wages that she earns…. After depriving her of all her rights as a married woman, if single, and the owner of property, he has taxed her to support a government which recognizes her only when her property can be made profitable to it. He has monopolized nearly all the profitable employments, and from those she is permitted to follow she receives but a scanty remuneration. He closes against her all the avenues to wealth and distinction which he considers honorable to himself. As a teacher of theology, medicine of the law, she is not known… He has created a false public sentiment by giving the world a different code of morals for men and women, by which moral delinquencies which exclude women from society, are not only tolerated, but deemed of little account in man. He has usurped the prerogative of Jehovah alone, claiming his right to assign for her a sphere of action, when that belongs to her conscience and to her God. He has endeavored, in every way that he could, to destroy her confidence in her own powers, lessen her self-respect, and to make her willing to lead an abject and dependent life.” [34]
The declaration also stated, in words which inflamed many men that: “the history of mankind is a history of repeated injuries and usurpations on the part of man toward woman, having in direct object of an absolute tyranny over her.” [35] In the years following this meeting women took up an even more important place in the abolitionist movement, Abby Kelly Foster returned to head the work and recruited many talented women agents including Sallie Holley, Lucy Stone and Susan B. Anthony who “often made five or six appearances a week” in various abolitionist meetings and in 1850-1851 they were joined by the “black evangelist Sojourner Truth, whom Garrison had met and the Northampton colony in 1843 and for whom he had printed an autobiographical narrative.” [36] These women contributed greatly to the abolitionist cause and would in the years to come be among those who continued to fight not only for the rights of blacks, but the rights of women.
The new women’s rights groups continued to work hand in hand with the abolitionist groups but also began a campaign for the rights of women. In the mid-1850s primarily focused on “obtaining state laws guaranteeing women’s right to control their property and wages, to be legal guardians of their children, and to be paid salaries commensurate with their labors, while a few women advocated for more liberal divorce laws so that they could rid themselves of alcoholic, insane, criminal, or brutal husbands.” [37] These efforts secured some modest gains and by 1861 most states had granted women some type of property rights or had changed their laws to follow the community property principle.
While the movement made modest progress regarding property rights for women in some states, they made little progress in terms of elective franchise and better wages and working conditions. During the ante-bellum period, women who lobbied for such rights were met with open opposition and scorn. The press “frequently denounced and ridiculed the “strong-minded women…” [38] Despite such attitudes women did make some significant advancements, particularly in lay aspects of the church, such as Bible societies, moral reform organizations, as well as the abolition and temperance movements, which had gained prominence during the Second Great Awakening.
During the ante-bellum period women made great progress in education. By 1850 the United States was the only country where “girls went to elementary school and achieved literacy in virtually the same proportion as boys.” [39] Likewise a few women entered higher education, particularly at women’s seminaries, which were for all practical purposes boarding schools that produced teachers and writers, as well as the Oberlin College, which was founded by Christian abolitionists and welcomed students of both genders as well as of any racial minority. During the three decades prior to the war women made some specific gains, but more important “was the development to their talents for organization, cooperation, leadership, and self expression. It was a time of beginnings and not fulfillment, a time when most women realized and accepted the fact that they lived in a man’s world, a time when a few dedicated but belligerent visionaries were frustrated in their attempt to remake the social order “overnight.” [40]
However, the war would help bring about many more opportunities for women. In 1850 a follow on conference to the Seneca conference, the National Women’s Rights Convention denied the right of anyone to dictate what women could do with their lives:
“The right of any portion of the species to decide for another portion, of any individual to decide for another Individual what is not their “proper sphere”; that the proper sphere for all human beings is the largest and highest to which they are able to attain; what this is, can not be ascertained without complete Liberty of choice; women therefore, ought to choose for herself what sphere she will fill, what education she will seek, and what employment she will follow, and will not be bound to accept, in submission, the rights, the education, and the place which man thinks proper to allow her.” [41]
To be continued…
Notes
[1] Ibid. Guelzo Fateful Lightning p.395
[2] Ibid. Guelzo Fateful Lightning p.374
[3] Massey, Mary Elizabeth, Women in the Civil War University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln NE 1966 p.5
[4] Roberts, Cokie Capital Dames: The Civil War and the Women of Washington, 1848-1868 Harper Collins Publishers, New York 2015 p.18
[5] McCurry, Stephanie The Politics of Yeoman Households in South Carolina in Divided Houses: Gender and the Civil War Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York 1992 p.23
[6] Ibid. McCurry The Politics of Yeoman Households in South Carolina p.23
[7] Ibid. Massey Women in the Civil War p.5
[8] Whites, Leeann The Civil War as a Crisis in Gender in Major Problems in the Civil War and Reconstruction, 3rd Edition Edited by Michael Perlman and Murrell Taylor Wadsworth Centage Learning, Boston 2011 p.16
[9] Ibid. Massy Women in the Civil War p.15
[10] Ibid. Zinn The Other Civil War p.121
[11] Ibid. Massey Women in the Civil War p. 16
[12] Ibid. Guelzo Fateful Lightening pp.49-50
[13] Mayer, Henry All on Fire: William Lloyd Garrison and the Abolition of Slavery W.W. Norton and Company, New York and London 1998 p.265
[14] Ibid. Massey Women in the Civil War p.16
[15] Ibid. Foner Forever Free p.124
[16] Ibid. Foner Forever Free p.125
[17] Ibid. Massey Women in the Civil War p. 358
[18] Ibid. McCurry Confederate Reckoning p.24
[19] Ibid. McPherson Battle Cry of Freedom p.23
[20] Brant, Nat The Congressman Who Got Away with Murder Syracuse University Press, Syracuse New York 1991 p.67
[21] Ibid. Guelzo Fateful Lightening p.391
[22] Ibid. McCurry Confederate Reckoning p.23
[23] Blanton, DeAnne and Cook, Lauren M. They Fought Like Demons: Women Soldiers in the Civil War Vintage a books, a Division of Random House New York 2002 p.3
[24] Ibid. Levine, Bruce Half Slave and Half Free: The Roots of the Civil War Revised Edition p.114
[25] Ibid. Brant The Congressman Who Got Away with Murder p.141
[26] Ibid. Guelzo Fateful Lightening p.391
[27] Ibid. Zinn The Other Civil War pp.53-54
[28] Ibid. Goldfield America Aflame p.74
[29] Ibid. Guelzo Fateful Lightening p.50
[30] Ibid. Massey Women in the Civil War p. 19
[31] Ibid. Whites The Civil War as a Crisis in Gender p.21
[32] Ibid. Mayer All on Fire p.267
[33] Ibid. McPherson Battle Cry of Freedom p.36
[34] Ibid. Blanton and Cook They Fought Like Demons: Women Soldiers in the Civil War pp.3-4
[35] Ibid. Guelzo Fateful Lightening p.392
[36] Ibid. Mayer All on Fire p.424
[37] Ibid. Massey Women in the Civil War p.21
[38] Ibid. Massey Women in the Civil War pp.21-22
[39] Ibid. McPherson The Battle Cry of Freedom p.36
[40] Ibid. Massey Women in the Civil War p.23
[41] Ibid. Guelzo Fateful Lightning p.392