 Instruments of Death SBD Dauntless Dive Bombers at Midway
Instruments of Death SBD Dauntless Dive Bombers at Midway
Six months after Pearl Harbor the United States Navy met the Imperial Japanese Navy in battle on the seas and in the airspace around Midway Island. It was a battle between a fleet that had known nothing but victory in the months after Pearl Harbor, sweeping across the Pacific and the Indian Oceans and decimating Allied Naval forces that stood in their way, the HMS Prince of Wales and HMS Repulse off of Singapore, a force of Royal Navy cruisers and the Aircraft Carrier HMS Hermes in the Indian Ocean, the bulk of the US Asiatic Fleet in the waters around the Philippines and the Dutch East Indies culminating in the Battle of the Java Sea where the bulk of the American, British, Dutch and Australian naval forces engaged were annihilated. In only one place had a Japanese Naval task force been prevented from its goal and that was at the Battle of the Coral Sea where Task Force 11 and Task Force 17 centered on the Carriers USS Lexington and USS Yorktown prevented a Japanese invasion force from taking Port Moresby sinking the light carrier Shoho, damaging the modern carrier Shokaku and decimating the air groups of the Japanese task force.
In May US Navy code breakers discovered the next move of the Imperial Navy an attack on Midway Island and the Aleutian islands. Since the occupation of Midway by Japanese forces would give them an operational base less than 1000 miles from Pearl Harbor Admiral Chester Nimitz committed the bulk of his naval power, the carriers USS Enterprise CV-6, USS Yorktown CV-5 and USS Hornet CV-8 and their 8 escorting cruisers and 15 destroyers, a total of 26 ships with 233 aircraft embarked to defend Midway along with a force of 5 cruisers and 4 destroyers to cover the Aleutians. Midway had a mixed Marine, Navy and Army air group of 115 aircraft which included many obsolete aircraft, 32 PBY Catalina Flying Boats, of which the 83 fighters, dive bombers, torpedo planes and Army Air Force bombers piloted by a host of inexperienced pilots.
The Japanese sent a force of 7 battleships, 7 carriers including the elite First Carrier Striking Group composed of the Pearl Harbor attackers Akagi, Kaga, Soryu and Hiryu and their highly trained and combat experienced air groups composed of 273 aircraft along with 14 cruisers and 39 destroyers assigned to take Midway and destroy the US Navy when it came out to fight as well as a force of 4 battleships, 12 destroyers assigned screen to the Aleutian invasion force which was accompanied by 2 carriers 6 cruisers and 10 destroyers. The other carriers embarked a further 114 aircraft. A factor which aided the Americans was the distance between the Japanese Task forces which were scattered over thousands of square miles of the Northern Pacific Ocean from which they could not rapidly come to the assistance of any other group.
With the foreknowledge provided by the code breakers the US forces hurried to an intercept position northeast of Midway eluding the Japanese submarine scout line which the Japanese Commander Admiral Yamamoto presumed would find them when they sailed to respond to the Japanese attack on Midway. Task Force 16 with the Enterprise and Hornet sailed first under the command of Rear Admiral Raymond A Spruance and Task Force 17 under Rear Admiral Frank “Jack” Fletcher with the Yorktown which had been miraculously brought into fighting condition after suffering heavy damage at Coral Sea. Fletcher assumed overall command by virtue of seniority and Admiral Nimitz instructed his commanders to apply the principle of calculated risk when engaging the Japanese as the loss of the US carriers would place the entire Pacific at the mercy of the Japanese Navy.
On June 3rd a PBY Catalina discovered the Japanese invasion force and US long range bombers launched attacks against it causing no damage. The morning of the 4th the Americans adjusted their search patterns in and the Japanese came into range of Midway and commenced their first strike against the island. In response land based aircraft from Midway attacked the Japanese carrier force taking heavy casualties and failing to damage the Japanese task force. The American Carrier task forces launched their strike groups at the Japanese fleet leaving enough aircraft behind of the Combat Air Patrol and Anti-submarine patrol. As the Americans winged toward the Japanese fleet the Japanese were in confused. A scouting report by an aircraft that had been delayed at launch discovered US ships but did not identify a carrier until later into the patrol. This was the Yorktown and TF 17. The Japanese attempted to recover their strike aircraft and prepare for a second strike on the island and then on discovery of the carrier embarked on the task of unloading ground attack ordnance in favor of aerial torpedoes and armor piercing bombs. The hard working Japanese aircrew did not have time to stow the ordnance removed from the aircraft but by 1020 they had the Japanese strike group ready to launch against the US carriers.
 AM6-2 Zeros Mauled the US Torpedo Bombers
AM6-2 Zeros Mauled the US Torpedo Bombers
As the Japanese crews worked the Japanese carriers were engaged in fending off attacks by the US torpedo bomber squadrons, VT-6 from Enterprise, VT-8 from Hornet and VT-3 from Yorktown. The Japanese Combat Air Patrol ripped into the slow, cumbersome and under armed TBD Devastators as they came in low to launch their torpedoes. Torpedo Eight from Hornet under the command of LCDR John C Waldron pressed the attack hard but all 15 of the Devastators were shot down. Only Ensign George Gay’s aircraft was able to launch its torpedo before being shot down and Gay would be the sole survivor of the squadron.
 Hopelessly obsolete 40 of 44 TBD Devastators were lost in action
Hopelessly obsolete 40 of 44 TBD Devastators were lost in action
Torpedo 6 under the command of LCDR Eugene Lindsey suffered heavy casualties losing 10 of 14 aircraft with Lindsey being one of the casualties. The last group of Devastators to attack was Torpedo 3 under the command of LCDR Lem Massey from the Yorktown. These aircraft were also decimated and Massey killed but they had drawn the Japanese Combat Air Patrol down to the deck leaving the task force exposed to the Dive Bombers of the Enterprise and Yorktown.
 TBD Devastator attacking Akagi
TBD Devastator attacking Akagi
There had been confusion among the Americans as to the exact location of the Japanese Carriers, the Bombing 8 and Scouting 8 of Hornet did not find the carriers and had to return for lack of fuel with a number of bombers and their fighter escort having to ditch inn the ocean and wait for rescue. The Enterprise group under LCDR Wade McClusky was perilously low on fuel when the wake of a Japanese destroyer was spotted. McClusky followed it to the Japanese Task Force. The Yorktown’s group under LCDR Max Leslie arrived about the same time. The found the skies empty of Japanese aircraft. Aboard the Japanese ships there was a sense of exhilaration as each succeeding group of attackers was brought down and with their own aircraft ready to launch and deal a fatal blow to the American carrier wondered how big their victory would be.
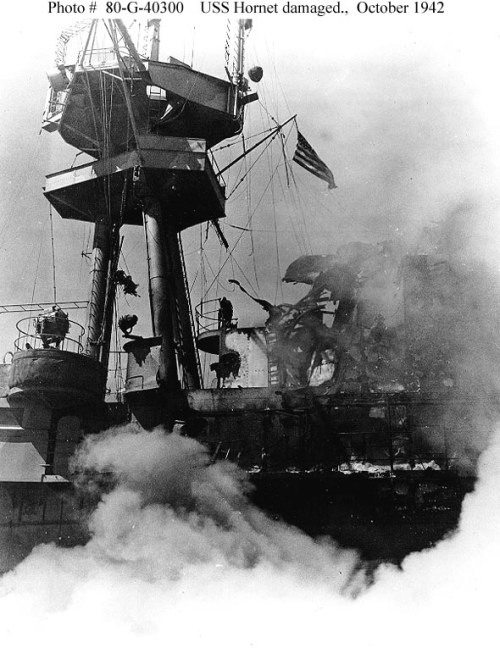
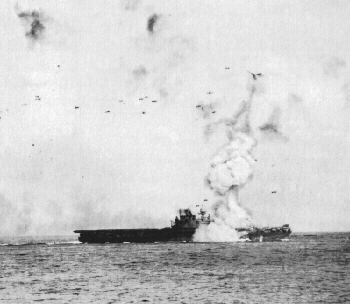
At 1020 the first Zero of the Japanese attack group began rolling down the flight deck of the flagship Akagi, aboard Kaga aircraft were warming up as they were on the Soryu. The unsuspecting Japanese were finally alerted when lookouts screamed “helldivers.” Wade McClusky’s aircraft lined up over the Akagi and Kaga pushing into their dives at 1022. There was a bit of confusion when the bulk of Scouting 6 joined the attack of Bombing 6 on the Kaga. The unprepared carrier was struck by four 1000 pound bombs which exploded on her flight deck and hangar deck igniting the fully fueled and armed aircraft of her strike group and the ordnance littered about the hangar deck. Massive fires and explosions wracked the ship and in minutes the proud ship was reduced to an infernal hell with fires burning uncontrollably. She was abandoned and would sink at 1925 taking 800 of her crew with her. LT Dick Best of Scouting 6 peeled off from the attack on Kaga and shifted to the Japanese flagship Akagi. On board Akagi were two of Japans legendary pilots CDR Mitsuo Fuchida leader of and CDR Minoru Genda the architect of the Pearl Harbor attack and subsequent string of Japanese victories. Both officers were on the sick list and had come up from sick bay to watch as the fleet was attacked. Seeing Kaga burst into flames they stood mesmerized until Akagi’s lookouts screamed out the warning “helldivers” at 1026. Best’s aircraft hit with deadly precision landing tow of their bombs on Akagi’s flight deck creating havoc among the loaded aircraft and starting fires and igniting secondary explosions which turned the ship into a witch’s cauldron. By 1046 Admiral Nagumo and his staff were forced to transfer the flag to the cruiser Nagara as Akagi’s crew tried to bring the flames under control. They would do so into the night until nothing more could be done and abandoned ship at 2000. Admiral Yamamoto ordered her scuttled and at 0500 on June 5th the pride of the Japanese carrier force was scuttled.
VB-3 under LCDR Max Leslie from the Yorktown stuck the Soryu with 17 aircraft, only 13 of which had bombs due to an electronic arming device malfunction on 4 of the aircraft including the squadron leader Leslie. Despite this they dove on the Soryu at 1025 hitting that ship with 3 and maybe as many as 5 bombs. Soryu like her companions burst into flames as the ready aircraft and ordnance exploded about her deck. She was ordered abandoned at 1055 and would sink at 1915 taking 718 of her crew with her.
The remaining Japanese flattop the Hiryu attained the same fate later in the day after engaging in an epic duel with the Yorktown which her aircraft heavily damaged.
It was quite miraculous what happened at Midway in those five pivotal minutes. Authors have entitled books about Midway Incredible Victory and Miracle at Midway and the titles reflect the essence of the battle. A distinctly smaller force defeated a vastly superior fleet in terms of experience, training and equipment and when it appeared that the Japanese Fleet would advance to victory in a span of less than 5 minutes turn what looked like certain defeat into one of the most incredible and even miraculous victories in the history of Naval warfare. In those 5 minutes history was changed in a breathtaking way. While the war would drag on and the Japanese still inflict painful losses and defeats on the US Navy in the waters around Guadalcanal the tide had turned and the Japanese lost the initiative in the Pacific never to regain it. The Japanese government hid the defeat from the Japanese people instead proclaiming a great victory while the American government could not fully publicize the information that led to the ability of the US Navy to be at the right place at the right time and defeat the Imperial Navy.
When one looks at implications of the victory it did a number of things. First it changed the course of the war in the Pacific probably shortening it by a great deal. Secondly it established the aircraft carrier and the fast carrier task force as the dominant force in naval warfare which some would argue it still remains. Finally those five minutes ushered in an era of US Navy dominance of the high seas which at least as of yet has not ended as the successors to the Enterprise, Hornet and Yorktown ply the oceans of the world and the descendants of those valiant carrier air groups ensure air superiority over battlefields around the world.
Peace
Padre Steve+
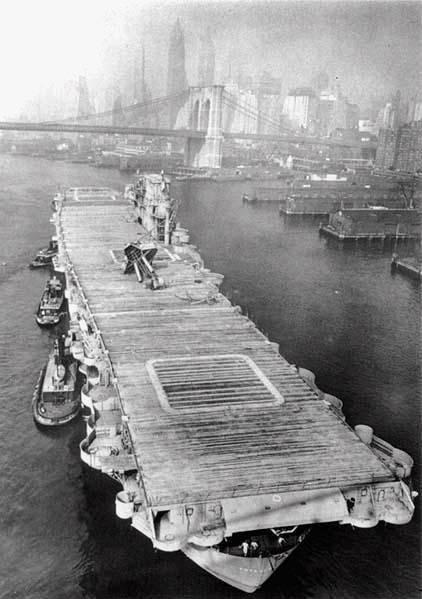
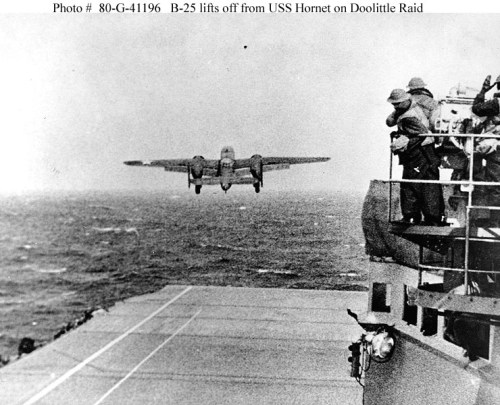
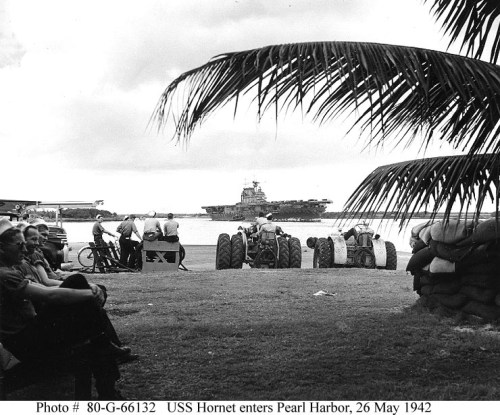
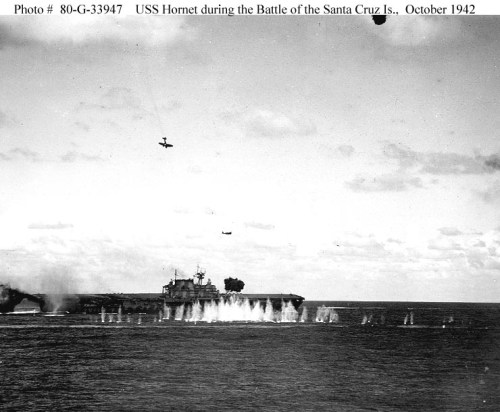





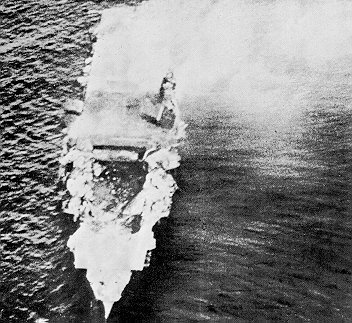















































 Aircraft over Saratoga
Aircraft over Saratoga USS Langley CV-1 The “Covered Wagon”
USS Langley CV-1 The “Covered Wagon”  Langley after conversion to AV-3
Langley after conversion to AV-3 USS Lexington CV-2
USS Lexington CV-2 USS Saratoga CV-3
USS Saratoga CV-3 Lexington Burning and Sinking
Lexington Burning and Sinking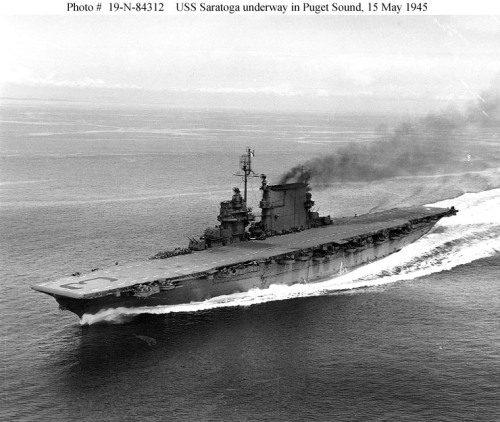 Saratoga 1945
Saratoga 1945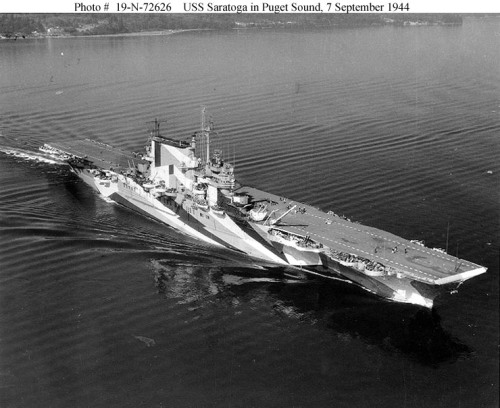 Saratoga September 1943
Saratoga September 1943 Saratoga burning after Kamikaze hits in 1945
Saratoga burning after Kamikaze hits in 1945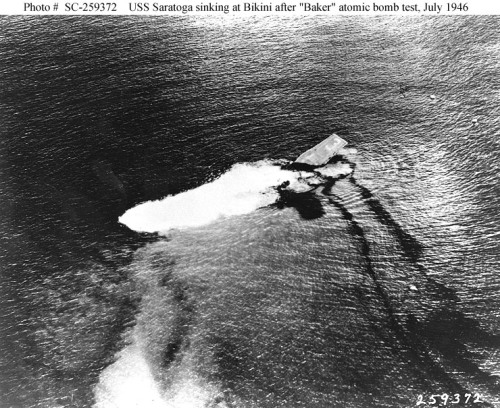 The End of an Era- Saratoga goes down at Bikini
The End of an Era- Saratoga goes down at Bikini SBD Dauntless Dive Bombers at Midway
SBD Dauntless Dive Bombers at Midway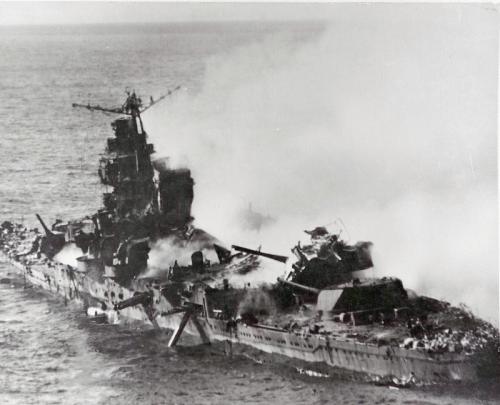
 Randy Johnson
Randy Johnson Senior Chief Hospital Corpsman Pamela Branum
Senior Chief Hospital Corpsman Pamela Branum