Note to my friends at Padre Steve’s World: This is another in my articles on Gettysburg that I am preparing for my next “Staff Ride” for the incoming class at the Staff College where I teach. Eventually I will have a page with a tab at the top of this site for my readers to access all of those articles.
The Artillery of the Army of the Potomac at Gettysburg proved that it was the “King of Battle” and a key part of Union commanders and their use of combined arms. The superiority of the Federal artillery at Gettysburg over their Confederate counterparts was not simply due to the numbers of guns employed, it was in the manner that they were employed and the manner that Federal commanders employed the artillery under their command.
This is not to say that the Confederate artillerymen were inferior to their Federal counterparts, Porter Alexander, who commanded First Corps artillery under Longstreet was an excellent artillery commander, although Brigadier General Henry J. Hunt was by far superior to his Confederate Counterpart Brigadier General William Pendleton. The problems lay in equipment, ammunition and their employment by their carious Corps and division commanders.
Hunt and Pendleton were both graduates of the West Point, however Pendleton had left active service in the 1830s to become an Episcopal Priest and had no combat experience. Hunt remained in the Army, served in Mexico and at the beginning of the war was the the chief artillery instructor at West Point. His treatise on the use of artillery Instructions for Field Artillery published by the War Department in 1861 was the primary instruction for all Union artillery units.
 Brigadier General William Pendleton
Brigadier General William Pendleton
Union and Confederate organizations differed. Hunt was instrumental in reorganizing Union artillery organizations. Brigades retained their assigned batteries for direct support of those units. Divisions and Corps lost their artillery which was brought into an Artillery Reserve for greater flexibility on the battlefield. As such the Artillery Reserve became the instrument of of the Army commander and served as what we would now call “general support” artillery. The organization allowed Meade to better manage his artillery at Gettysburg and employ it where he needed at the time where it was most required. This ensured that Meade and his subordinate commanders had a good command of fires throughout the battle.
Hunt and his subordinates sought to concentrate their artillery but also to employ cross fires on advancing enemy infantry. During the battle Union artillery was particularly effective during Buford’s delaying action where its skillful employment caused Heth and Pender’s Divisions large number of casualties on July 1st. At Cemetery Hill on the evening of July 1st where Howard’s positioning of batteries on that hill with Steinwehr’s Division ensured that it held. On July 2nd it was used with great effect during the savage fighting at the Peach Orchard, the Wheat Field, Devil’s Den and Little Round Top. However its greatest effect was in decimating Pickett’s Division and supporting units on July 3rd.
The Confederate Artillery was assigned to each Army Corps and although Pendleton was Lee’s Artillery Chief he had little influence on the battle. Instead that authority was dispersed to the artillerymen serving under each Corps commander. While this worked well at the corps level it ensured that Lee had no way of effectively coordinating fires throughout the battle. As such on the third day Porter Alexander, a battalion commander and Longstreet’s senior artilleryman was limited to his First Corps batteries and whatever artillery was lent by A. P. Hill’s Third Corps as the artillery of Second Corps was unavailable and on the wrong side of the battlefield when needed.
At the battery level Union artillery was on the whole organized by type in six gun batteries. Confederate artillery units were organized in four or six gun batteries in which types of guns were often mixed, leading to supply problems and inconsistency in rates of fire and range. Union batteries also had better quality ammunition and gunpowder supplies.
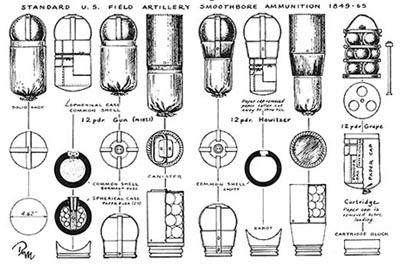


Field Artillery batteries were of two types. Foot Artillery which accompanied the Infantry and Horse Artillery which accompanied the Cavalry. The crews of the Foot Artillery either marched alongside their guns or rode on the caissons. The crews of the Horse Artillery rode horses in order to better keep up with the Cavalry Units they supported.
All the field artillery weapons were line of sight weapons. They had neither the range nor the fire direction capability for indirect fire. Ammunition included solid shot, exploding shells and canister which was used at short range against infantry.
The increase in range and effectiveness of rifled muskets made the job of the artilleryman more dangerous than it had been in previous wars. Thus when employed in the offense or during close assaults artillerymen were exposed to musket fire resulting in heavier casualties among the gun crews.
At Gettysburg the Army of the Potomac about 360 guns, the total number of guns available to Lee and the Army of Northern Virginia varies depending on the source between 262 and 241 guns.
The Union for the most part used weapons made in the United States, whereas the Confederates having few ordnance factories of their own were limited and attempted to obtain weapons from Europe. At Gettysburg it had two of the 2.75 inch Whitworth Breechloading Rifles were the most modern and long range weapons on the battlefield and prefigured the field artillery weapons that would dominate the battlefield in the Twentieth Century.
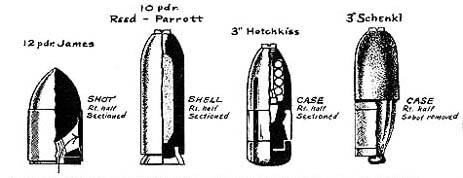
There were three basic types of cannon used at Gettysburg. Rifled cannon, Smoothbores and Howitzers. The bulk of Federal Artillery was made up of rifled cannon, especially the 3” Ordnance Rifle of which Meade had 146 at Gettysburg. There were also 142 of the M 1857 12 pound smoothbore “Napoleon’s” named after Emperor Napoleon III of France. Forty to forty-four percent of the guns available to Lee’s Army of Northern Virginia were Napoleons, of which they had 107 at Gettysburg. The technical details of each type are listed below.
10-Pounder Parrott Rifle, M ’63
Bore Diameter 3.0 in (7.64 cm)
Tube Material Cast and Wrought Iron
Tube Length 78 in (198 cm)
Tube Weight 890 lb (404 kg)
Powder Charge 1 lb (0.45 kg)
Range (5° Elevation) 2,000 yd (1,829 m)
10-Pounder Parrott Rifle, M ’61
Bore Diameter 2.9 in (7.37 cm)
Tube Material Cast and Wrought Iron
Tube Length 78 in (198 cm)
Tube Weight 890 lb (404 kg)
Powder Charge 1 lb (0.45 kg)
Range (5° Elevation) 2,000 yd (1,829 m)
At Gettysburg (total M61 and M63)
60 Union; 42 Confederate
20-Pounder Parrott Rifle
Bore Diameter 3.67 in (9.32 cm)
Tube Material Cast and Wrought Iron
Tube Length 89 in (226 cm)
Tube Weight 1,750 lb (794 kg)
Powder Charge 2 lb (0.91 kg)
Range (5° Elevation) 2,100 yd (1,920 m)
At Gettysburg 24 Union
3.67-Inch Navy Parrott Rifle
Bore Diameter 3.67 in (9.32 cm)
Tube Material Cast and Wrought Iron
Tube Length 89 in (226 cm)
Tube Weight 1,750 lb (794 kg)
Powder Charge 2 lb (0.91 kg)
Range (5° Elevation) 2,100 yd (1,920 m)
At Gettysburg 4 Confederate
Bore Diameter 3.0 in (7.62 cm)
Tube Material Wrought Iron
Tube Length 73 in (185 cm)
Tube Weight 816 lb (370 kg)
Powder Charge 1 lb (0.45 kg)
Range (5° Elevation) 1,835 yd (1,678 m)
At Gettysburg 146 Union; 73 Confederate
14-Pounder James Rifle
Bore Diameter 3.80 in (9.65 cm)
Tube Material Bronze
Tube Length 65 in (165 cm)
Tube Weight 918 lb (416 kg)
Powder Charge 0.75 lb (0.34 kg)
Range (5° Elevation) 1,700 yd (1,554 m)
At Gettysburg 4 Union
12-Pounder (2.75 Inch) Whitworth Breechloading Rifle
Bore Diameter 2.75 in (7 cm)
Tube Material Iron and Steel
Tube Length 104 in (264 cm)
Tube Weight 1,092 lb (495 kg)
Powder Charge 1.75 lb (0.79 kg)
Range (5° Elevation) 2,800 yd (2,560 m)
At Gettysburg 2 Confederate
Blakely Rifle
Bore Diameter 3.4 in (8.64 cm)
Tube Material Steel
Tube Length 59 in (150 cm)
Tube Weight 800 lb (363 kg)
Powder Charge 1 lb (0.45 kg)
Range (5° Elevation) 1,850 yd (1,691 m)
At Gettysburg 3 Confederate
Smoothbore
12-Pounder Napoleon-Federal Manufacture
Bore Diameter 4.62 in (11.73 cm)
Tube Material Bronze
Tube Length 66 in (168 cm)
Tube Weight 1,227 lb (557 kg)
Powder Charge 2.5 lb (1.13 kg)
Range (5° Elevation) 1,619 yd (1480 m)
At Gettysburg 142 Union
12-Pounder Napoleon-Confederate Manufacture
Bore Diameter 4.62 in (11.73 cm)
Tube Material Bronze
Tube Length 66 in (168 cm)
Tube Weight 1,227 lb (557 kg)
Powder Charge 2.5 lb (1.13 kg)
Range (5° Elevation) 1,619 yd (1480 m)
At Gettysburg 107 Confederate
6-Pounder Field Gun
Bore Diameter 3.67 in (9.32 cm)
Tube Material Bronze
Tube Length 60 in (152 cm)
Tube Weight 884 lb (401 kg)
Powder Charge 1.25 lb (0.57 kg)
Range (5° Elevation) 1,523 yd (1,393 m)
At Gettysburg 1 Confederate
Howitzers
12-Pounder Field Howitzer
Bore Diameter 4.62 in (11.73 cm)
Tube Material Bronze
Tube Length 53 in (135 cm)
Tube Weight 788 lb (357 kg)
Powder Charge 1 lb (0.45 kg)
Range (5° Elevation) 1,072 yd (980 m)
At Gettysburg 2 Union; 26 Confederate
24-Pounder Field Howitzer
Bore Diameter 5.82 in (14.78 cm)
Tube Material Bronze
Tube Length 65 in (165 cm)
Tube Weight 1,318 lb (598 kg)
Powder Charge 2 lb (0.91 kg)
Range (5° Elevation) 1,322 yd (1,209 m)
At Gettysburg 4 Confederate
So until tomorrow,
Peace
Padre Steve+







































