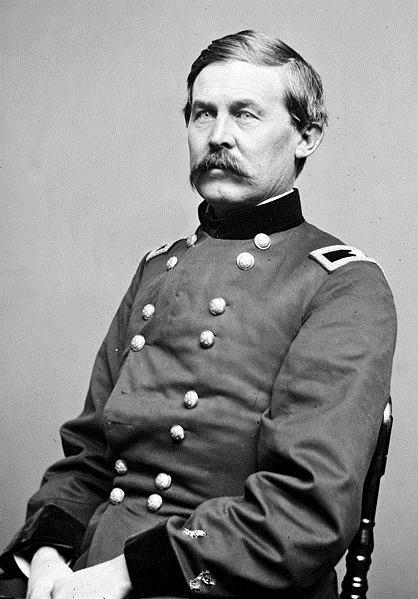
Brigadier General Gouverneur Warren
Throughout this study we have been looking at how leaders at various levels in conduct of campaigns as well as battles make decisions. Likewise we examine the lives and character of those leaders as it applies to their actions at critical points of a battle. In this chapter we will examine three officers whose lives, character and actions at Gettysburg, specifically at Little Round Top exemplify two of the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Desired Leader Attributes, “to anticipate and adapt to surprise and uncertainty” and the principle of Mission Command, to “operate on intent through trust, empowerment and understanding.” It is from those perspectives that we will look at this part of the battle, but we would be amiss if we did not address the nearly mythical status to which this action has risen.
The actions of three men at the Battle of Little Round Top; Brigadier General Gouverneur Warren, the Chief Engineer of the Army of the Potomac, Colonel Strong Vincent, commanding Third Brigade, First Division, V Corps and Colonel Joshua Lawrence Chamberlain, commanding the 20th Maine Infantry Regiment of Vincent’s brigade are very important to the outcome of the battle, but also for what they teach us about leadership and the profession of arms. This chapter focuses on Warren, in particular with his work with the Commander of the Army of the Potomac, George Meade and his actions to secure Little Round Top on July 2nd 1863, the next will deal with Chamberlain and Vincent.
The battle at Little Round Top is an iconic part of American History and in particular for the Army, a key element of how leadership has been studied. It has achieved nearly mythical status due to the actions of Colonel Joshua Chamberlain which have been told many times in history, fiction and in film, particularly Michael Shaara’s classic historical novel The Killer Angels and its film adaptation Gettysburg. While these accounts are certainly inspiring and allow us to experience the emotion and near spiritual quality of what Chamberlain writes, there is much more to learn.
That near spiritual quality and mythic status that we accord Gettysburg is important, for in large part it is why we come to the battlefield, and why we study. Chamberlain said it well many years after Gettysburg at the dedication of the Maine Monuments:
“In great deeds, something abides. On great fields, something stays. Forms change and pass; bodies disappear; but spirits linger, to consecrate ground for the vision-place of souls… generations that know us not and that we know not of, heart-drawn to see where and by whom great things were suffered and done for them, shall come to this deathless field, to ponder and dream; and lo! the shadow of a mighty presence shall wrap them in its bosom, and the power of the vision pass into their souls.” [1]
So as we endeavor to look at the actions of these leaders on that fateful day it is important to recognize that we cannot totally separate those actions that helped decide the battle from the mythos that surrounds the story. [2] Likewise, it important to acknowledge that we cannot separate their character and the totality of military leaders lives from their actions on a particular battlefield. Unlike Chamberlain Warren does not engender myth, and that is why he is often overlooked by many casual students and observers of the Battle of Gettysburg.
For the purposes of this study it is important to note that Warren was not a commander during this action, he was, like most senior officers today, a staff officer. Many times students of military history and theory are inclined to dismiss the contributions of staff officers because they do not have the overall responsibility of a battle, or the glamour of the limelight of the commanders that they serve under. However, for military professionals, especially those serving on senior staffs who prepare campaign plans, contingency plans and crisis plans the study of officers like Warren is essential.
The Federal Army at Gettysburg, like its Confederate opponent had a wide variety of officers serving in its ranks. Many of its senior officers were graduates of West Point. Many had served together in Mexico and in the various campaigns against Native American tribes. Those who stayed in the Army during the long “peace” between the Mexican War and the outbreak of the Civil War endured the monotony, boredom and often miserable conditions of isolated army posts, long family separations, as well as low pay, slow promotion and often low social status.[3] In light of such conditions, many resigned their commissions to undertake various professional, business or academic pursuits; in fact Samuel Huntington noted that in the years before the Civil War that “West Point produced more railroad presidents than generals.” [4] However, on the outbreak of the war returned to service whether in the service of the Union, or the Confederate States.
When the war began the Army underwent a massive expansion, which it met through and the call of up militia and raising new units from the various states. In the expansion many officers were appointed who had no prior military service, or if they did it was performed years or even decades before the war. Some of these men were simply patriots who rallied to the flag, others due to a sense of righteousness about their cause, while others were political opportunists or appointees. In the north this was a particular problem as “professional officers were pushed aside and passed over in the Union, the higher commissions going, in the first stages of the war at least to officers called back into service or directly appointed from civilian life, many of them “political” appointees.” [5]
At times the lack of experience, training and sometimes the poor character of these men was tragic. However, many of these men performed as well or better than some of their regular army counterparts at various levels of command. At the same time a good number of Regular Army officers were allowed to assist states in the formation and training of these new units, one of whom was Gouverneur Warren. Gettysburg would provide opportunity for the best and worst of all of these types of officers to succeed or fail. In this chapter we will look at one of the regular officers and two of the volunteer whose lives intersected on July 2nd 1863.
Brigadier General Gouverneur Warren was typical of the many professional officers of the old army. An 1850 graduate of West Point, Warren was a bright student who had absorbed the teachings of his professor, Dennis Hart Mahan “as the core of his own military thought, both in his senior year in college and through reinforcement as a faculty member.” [6] Warren was commissioned as a Brevet Second Lieutenant and because of his high standing in his class was assigned to Corps of Topographical Engineers. He spent his first seven years in a number of assignments which took him throughout much of the country.
Warren’s work involved exploring and mapping for various enterprises including the project to help tame the Mississippi River, and the exploration of the Great Plains and Black Hills where he developed a sympathy for the various Sioux tribes he encountered noting on completion of his mission in 1858, writing that “He had never heard a Sioux chief “express an opinion in regard to what was due them in which I do not concur” and that “many of them view the extinction of their race as an inevitable result of the operation of present causes, and do so with all the feelings of despair with which we should contemplate the extinction of our nationality.” [7] Following his years in the west he returned as faculty to West Point where he as an Assistant Professor, shared mathematics instructional duties with Oliver O. Howard and resumed his relationship with his former professor Mahan. [8]
On the outbreak of war Warren was granted leave from his duties at West Point to serve as Lieutenant Colonel of Volunteers in the 5th New York Infantry Regiment, also known as Duryee’s Zouaves. Where Duryee was appointed as a Brigadier General, Warren became its Colonel, serving with it during the Peninsula campaign where he was eventually given command of a provisional brigade and promoted to Brigadier General, serving as a Brigade Commander in at Second Manassas, Antietam and Fredericksburg.
At Chancellorsville he was pulled from his brigade duties by Hooker who employed him with good effect to assist his engineering staff, first with mapping and then building the fortifications that stopped the ferocious Confederate storm on the second day of battle. [9] In less than 48 hours Warren’s troops “threw up five miles of the most formidable entrenchments yet constructed under battlefield conditions.” [10] Edward Alexander, Longstreet’s artillery officer noted that when the Confederates came upon the fortifications after Hooker’s withdraw that “they were amazed at the strength and completeness of the enemy’s fortifications….” [11] Following the battle Warren was appointed as Chief Engineer of the Army of the Potomac on May 12th 1863 by Hooker. When Hooker was relieved of command and was replaced by Meade on June 28th 1863, he was kept in that position by his fellow engineer Meade rather than being promoted to a division or being assigned as Meade’s Chief of Staff. As this turned out it was a wise choice.
Warren along with Major General Winfield Scott Hancock arrived at Cemetery Hill on the night of July 1st. As Meade organized his defenses he not only depended on his advice about the ground, but “consulted him constantly at headquarters or sent him off on matters of highest importance.” [12] Meade respected Warren and had offered Warren the chance to serve as his Chief of Staff, a position that Warren, like Seth Williams, the Adjutant General declined that offer indicating that he had “too much work in their departments to take on the burdens of a new job.” [13] Lee appreciated Warren’s “calm, absorbed, and earnest manner, his professional skill and sound judgment.”[14] These qualities would serve both men and the army well on July 2nd.
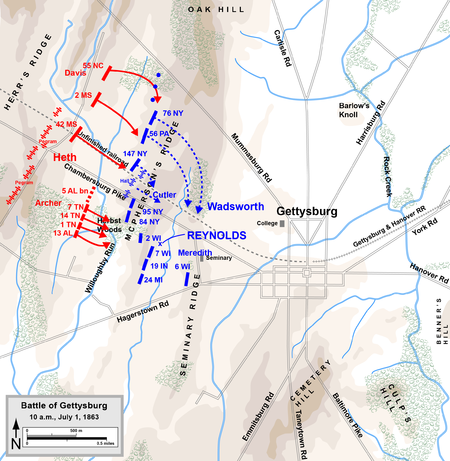
When Sickles moved III Corps forward during the afternoon without permission moved his Corps forming a vulnerable salient at the Peach Orchard leaving the southern flank in the air, Meade was aghast. Warren who from his reconnaissance of the previous day and the morning knew the position better than anyone recognized that “something was badly awry on Sickles’ Third Corps front – matters there were “not all straight.” [15] He had sent an officer to discover to investigate Sickles’ front and that officer reported that the section of Cemetery Ridge assigned to III Corps “was not occupied.” [16]
Meade and Warren discussed the situation and realized that III Corps “could hardly be said to be in position” [17] and knowing VI Corps was now close at hand order V Corps, at the time his only reserve into the position vacated by Sickles. They went forward and seeing the empty spaces Warren told Meade “here is where our line should be” to which Meade replied: “It’s too late now.” [18] Warren, whose familiarity with the whole of the battlefield gave him concern about Sickles’ corps dispositions suggest that Meade send him to the Federal left, “to examine the condition of affairs.” [19]
Meade concurred with his Engineer and in dispatching him he also gave Warren the authority to take charge as needed saying “I wish you would ride over there and if anything serious is going on, attend to it.” [20] Again Meade’s choice of Warren for the task demonstrated the trust that is essential in command. The two officers worked together seamlessly and as Coddington described their relationship that day: “Meade chose him to act as his alter ego in crucial moments of the battle, and Warren rendered services for which Meade and the country were to be eternally grateful.” [21] Warren would not see Meade again “until the attack had spent its force.” [22]
Hunt noted that “The duty could not have been in better hands.” [23] When Warren arrived on Little Round Top he found it unoccupied save for a few signal corps soldiers. Warren immediately recognized the tactical value of Little Round Top and noted that it was “the key of the whole position.” [24] Warren saw that the Confederates were massing not more than a mile away and that there were no troops on the hill to stop them. He believed that an area “of woods on the near side of the Emmitsburg Road as “an excellent place for the enemy to form out of sight” [25] which was exactly what Major General John Bell Hood’s division was doing, as Henry Hunt noted “The enemy at the time lay concealed, awaiting signal for the assault…” [26] To test his suspicions Warren sent a messenger to Captain James Smith’s 4th New York artillery battery on Devil’s Den to fire a single shot into the woods. Warren described the situation:
“As the shot went whistling through the air the sound of it reached the enemy’s troops and caused every one to look in the direction of it. This motion revealed to me the glistening gun-barrels and bayonets of the enemy’s line of battle, already formed and far outflanking the position of any of our troops; so that the line of his advance from the right to Little Round Top was unopposed. I have been particular in telling this, as the discovery was intensely thrilling to my feelings, and almost appalling.” [27]
Upon confirming his fears Warren resorted to ruse and action. He order the “signalmen to keep up their wigwag activity, simply as a pretense of alertness, whether they had any real signals to transmit or not…” [28] He also sent messengers to Meade, Sickles and Sykes, the commander of V Corps asking Meade to “Send at least a division to me” [29] instructing the messenger, Lieutenant Randall Mackenzie to tell Meade “that we would at once have to occupy that place very strongly.” [30] Sickles refused on account of how badly stretched his lines were, however George Sykes of V Corps responded sending Captain William Jay to find Barnes commander of his 1st Division. The messenger could not find Barnes, but instead came across the commander of the division’s 3rd Brigade Colonel Strong Vincent. Vincent knew that Barnes was self-medicating his “pre-battle anxieties out of a black commissary quart bottle” and was already “hollow from skull to boots” and demanded “What are your orders? Give me your orders.” [31] Upon learning that Sykes wanted a brigade to proceed to Little Round Top Vincent responded immediately to take the initiative and ordered his four regiments up Little Round Top without waiting for permission. Vincent told Sykes messenger “I will take the responsibility myself of taking my brigade there.” [32]
Meade’s choice of Warren was demonstrated in how Warren continued to act with alacrity and decisiveness throughout the afternoon. “As the Union line began to crumble on Little Round Top, Warren, vested with the authority of Meade’s chief representative, emerged as the right man at the right place at the right time.” [33] Warren did not stop with sending messengers, but seeing the danger building he noted that the northwest face of the hill was still unoccupied and open to attack. Warren forgot “all about a general’s dignity” he “sprinted down the east slope of the hill like a rabbit.” [34] There he found Brigadier General Stephen Weed’s brigade which he had previously commanded. Since he did not see Weed, but he found Colonel Patrick O’Rorke of the 140th New York and ordered him to follow him up the hill, saying “Paddy…give me a regiment.” [35] When O’Rorke said that Weed expected him to be following him Warren took the responsibility telling O’Rorke “Bring them up on the double quick, and don’t stop for aligning. I’ll take responsibility.” [36] O’Rorke followed with his gallant regiment with the rest of the brigade under Weed following. Warren’s actions were fortuitous as the 140th New York and Lieutenant Charles Hazlett’s battery of the 5th Artillery arrived at the crest just in time to repulse the advancing Confederates. In the fight the brigade would take fearful casualties and by the end of the battle, Weed, O’Rorke and Hazlett would all be dead, but with Vincent’s brigade they held on and saved the Union line.[37]
Warren continued to urge on the Federal troops despite being wounded, in the words of a reporter who observed him in “a most gallant and heroic manner, riding with utmost confidence over fields swept by the enemy’s fire, seemingly everywhere present, directing, aiding, and cheering the troops.” [38] Once he was assured that Little Round Top was secure he proceeded to rejoin Meade “near the center of the battlefield where another crisis was at hand.” [39]
Warren distinguished as a Corps commander until he ran afoul of the fiery General Phillip Sheridan in 1865. Sheridan relieved Warren of command of V Corps following the Battle of Five Forks where Sheridan believed that Warren’s Corps had moved too slowly in the attack. The relief was brutal and ruined his career. Warren was a professional soldier and took the relief hard. Unfortunately as a topographic engineer he was an outsider to many in the army and not fully appreciated by Grant or Sheridan who in their haste at Five Forks destroyed his career.
After the war Warren resigned his commission as a Major General of Volunteers and returned to his permanent rank as a Major of Engineers. He served another 17 years doing engineeringduty and was promoted to Lieutenant Colonel in 1879, but his past always haunted him, even his sleep. He wrote his wife while supervising a major bridge construction project over the Mississippi River in 1867: “I wish I did not dream so much. They make me sometimes to dread to go to sleep. Scenes from the war, are so constantly recalled, with bitter feelings I wish never to experience again. Lies, vanity, treachery, and carnage.” [40]
He sought a Court of Inquiry to exonerate himself but this was refused until President Grant left office. The Court eventually exonerated him but he died three months before the results were published. Embittered he directed that he be buried in civilian clothes and without military honors. His funeral was attended by his friends Winfield Scott Hancock and Samuel Crawford, his oldest army friend and mentor Andrew Humphreys was called away before the service due to the sudden illness of his son. [41] The Washington Post noted that Warren “had gone “where neither the malevolence nor the justice of this world can reach him. He had enough of the former; and denial of the latter not only embittered his closing months of his life, but undoubtedly hastened his end.” [42]
Warren’s actions on that hot and muggy July 2nd exemplified the leadership qualities that we as an institution strive for, and from a leadership perspective demonstrate how the Chairman’s Desired Leader Attributes and the principles of Mission Command: “the ability to operate on intent through trust, empowerment and understanding” should work in a relationship between seniors and subordinates. But his life also serves to remind us of the ethics of our profession. Loomis Langdon, who served as the official recorder for the board of inquiry wrote of Warren:
“I had never met General Warren till he came before his Court of Inquiry…I learned to value his good opinion – and while I admired him for his great patience, his wonderful energy, habit of concentration, his vast learning and untiring application, I loved him for his tenderness, gentleness and charity, even to those whom he believed had combined to do him a cruel wrong; and I admired him for his nobleness of character and his courage and unselfish patriotism.” [43]
It is easy for military professionals to become totally focused in our profession, especially the details of planning and process to forget the humanity of those that we serve alongside. Warren is one of those complex figures who are not easy to categorize. His biographer Jordan wrote that:
“Warren was a man with fine intellect, widely read, and of keen sensibilities. He was also an excellent engineer, mapmaker, and scientist. He was a soldier who cared much for the safety and welfare of the men under him, and he was sickened by the appalling carnage of the war in which he took such a prominent part. He was arrogant and proud, and he hesitated hardly at all in putting down those of his colleagues he regarded as inferiors. His mind’s eye took in much beyond what was his immediate concern, but this gift worked against him in the hierarchical realm of military life. Warren was prone to long sieges of depression, and he himself agreed that others found him morose and unsmiling…” [44]
In reading military history is far too easy to isolate and analyze a commander’s actions in battle and ignore the rest of their lives. I think that this does a great disservice to the men themselves. In time of war gives up something of themselves and sometimes even heroes like Gouverneur Warren are destroyed by the actions of institutions that they serve.
Notes
[1] Chamberlain, Joshua Lawrence. Chamberlain’s Address at the dedication of the Maine Monuments at Gettysburg, October 3rd 1888 retrieved from http://www.joshualawrencechamberlain.com/maineatgettysburg.php 4 June 2014
[2] Note: My use of the terms myth, mythology or mythos should not be considered negative, and the use of the terms does not mean that there is not some degree of fact or truth in them. The definitions of the term mythos are important to understanding my use of the term here, first it denotes a traditional or recurrent narrative theme or plot structure of a story, and secondly a set of beliefs or assumptions about something. (See the Oxford American Dictionary.)
[3] Taylor, John M. Duty Faithfully Performed: Robert E Lee and His CriticsBrassey’s, Dulles VA 1999 pp.37-38.
[4] Huntington, Samuel P. The Soldier and the State: The Theory and Politics of Civil-Military Relations The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, Cambridge MA and London 1957 p.199
[5] Ibid. Huntington. The Soldier and the State: The Theory and Politics of Civil-Military Relations p.213
[6] Jordan, David M. Happiness is Not My Companion: The Life of G.K. Warren Indiana University Press, Bloomington Indiana 2001 p.6
[7] Ibid. Jordan Happiness is Not My Companion: The Life of G.K. Warren p.30
[8] Ibid. Jordan Happiness is Not My Companion: The Life of G.K. Warren p.33
[9] Sears, Stephen W. ChancellorsvilleHoughton Mifflin Co. Boston and New York 1996 p.372
[10] Hagerman, Edward. The American Civil War and the Origins of Modern Warfare. Midland Book Editions, Indiana University Press. Bloomington IN. 1992 p.91
[11] Alexander, Edward Porter Military Memoirs of a Confederate: A Critical Narrative 1907 republished 2013 by Pickle Partners Publishing, Amazon Kindle Edition location 7007
[12] Coddington, Edwin B. The Gettysburg Campaign: A Study in Command, A Touchstone Book, Simon and Schuster New York, 1968 p.332
[13] Sears, Stephen W. Gettysburg. Houghton Mifflin Co. Boston and New York 2003 pp.129-130
[14] Ibid. Coddington, The Gettysburg Campaign: A Study in Command, p.332
[15] Ibid. Sears Gettysburg p.262
[16] Tredeau, Noah Andre. Gettysburg: A Testing of Courage, Harper Collins Publishers, New York 2002 p.319
[17] Ibid. Tredeau. Gettysburg: A Testing of Courage, p.319
[18] Ibid. Tredeau. Gettysburg: A Testing of Courage, p.320
[19] Ibid. Jordan Happiness is Not My Companion: The Life of G.K. Warren p.90
[20] Ibid. Tredeau. Gettysburg: A Testing of Courage, p.320
[21] Ibid. Coddington, The Gettysburg Campaign: A Study in Command, p.388
[22] Guelzo, Allen C. Gettysburg: The Last Invasion Vintage Books a Division of Random House, New York 2013 p.260
[23] Hunt, Henry. The Second Day at Gettysburg in Battles and Leaders of the Civil War Volume III, The Tide Shifts. Edited by Robert Underwood Johnson and Clarence Clough Buel Castle, Secaucus NJ p. 307
[24] Ibid. Jordan Happiness is Not My Companion: The Life of G.K. Warren p.92
[25] Ibid. Jordan Happiness is Not My Companion: The Life of G.K. Warren p.92
[26] Ibid. Hunt The Second Day at Gettysburg in Battles and Leaders of the Civil War Volume III, The Tide Shifts. p. 307
[27] Pfanz, Harry F. Gettysburg: The Second Day. University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill 1987 p.206
[28] Foote, Shelby, The Civil War, A Narrative. Volume Two Fredericksburg to Meridian Random House, New York 1963 p.503
[29] Ibid. Jordan Happiness is Not My Companion: The Life of G.K. Warren p.92
[30] Ibid. Guelzo Gettysburg: The Last Invasion Vintage p.261
[31] Ibid. Guelzo Gettysburg: The Last Invasion Vintage p.262
[32] Longacre, Edward Joshua Chamberlain: The Soldier and the Man Combined Publishing Conshohocken PA 1999 p.127
[33] Ibid. Coddington, The Gettysburg Campaign: A Study in Command, p.395
[34] Swanberg, W.A. Sickles the IncredibleStan Clark Military Books, Gettysburg PA 1957 p.214
[35] Ibid. Jordan Happiness is Not My Companion: The Life of G.K. Warren p.93
[36] Ibid. Foote The Civil War, A Narrative. Volume Two Fredericksburg to Meridian p.504
[37] Ibid. Jordan Happiness is Not My Companion: The Life of G.K. Warren pp. 93-94
[38] Ibid. Coddington, The Gettysburg Campaign: A Study in Command, p.388
[39] Ibid. Coddington, The Gettysburg Campaign: A Study in Command, p.396
[40] Ibid. Jordan Happiness is Not My Companion: The Life of G.K. Warren p.249
[41] Ibid. Jordan Happiness is Not My Companion: The Life of G.K. Warren p.309
[42] Ibid. Jordan Happiness is Not My Companion: The Life of G.K. Warren p.308
[43] Ibid. Jordan Happiness is Not My Companion: The Life of G.K. Warren p.309
[44] Ibid. Jordan Happiness is Not My Companion: The Life of G.K. Warren preface pp.x-xi