“Danger is part of the friction of war. Without an accurate conception of danger we cannot understand war. That is why I have dealt with it here.” Carl Von Clausewitz [1]
When commanders send their troops into battle to execute the plans of their staff, they cannot forget that as Clausewitz noted that War is the province of danger and that:
“In the dreadful presence of suffering and danger, emotion can easily overwhelm intellectual conviction, and in the psychological fog it is so hard to form clear and complete insights that changes in view become more understandable and excusable….No degree of calm can provide enough protection: new impressions are too powerful, too vivid, and always assault the emotions as well as the intellect.” [2]
To re-engage our understanding of this issue is important, especially in the application of Mission Command where as General Martin Dempsey noted that “Understanding equips decision makers at all levels with the insight and foresight to make effective decisions, to manage the associated risks, and to consider second and subsequent order effects.” [3] The current and recent wars fought by the United States and its NATO and coalition allies have shielded many military professionals from this aspect of war, but it is still present and we should not ignore it. As noted in the 2006 edition of the Armed Forces Officer:
“The same technology that yields unparalleled success on the battlefield can also detach the warrior from the traditional ethos of the profession by insulating him or her from many of the human realities of war.” [4]
“The nature of the warrior leader is driven by the requirements of combat” [5]and courage, both “courage in the face of the danger, and the courage to accept responsibility” [6] are of paramount importance. In an era where the numbers of soldiers that actually experience combat or served in true combat conditions where the element of danger is ever present is shrinking, we can at least gain part of that understanding through the study of history, campaigns and battles and by actually walking the battlefields, and considering the effects of terrain, weather, exhaustion and the imagining danger faced in confronting an enemy on the field of battle. As such the Battle of Gettysburg and the climactic event of Pickett’s Charge on July 3rd is a good place to reimagine the element of danger.
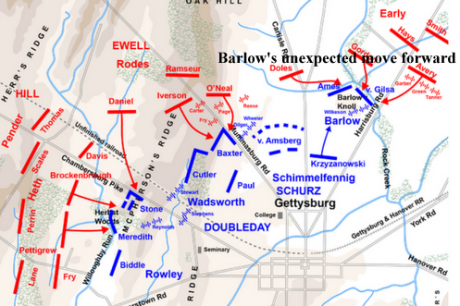
Porter Alexander’s artillery had begun it’s bombardment at 1:07 p.m. and as it did and the Union artillery commenced a deliberate counter-fire the Confederate infantry behind Seminary Ridge began to take a beating. Unlike the Confederate barrage which had mainly sailed over the Union troops on Cemetery Ridge causing few causalities, “a large proportion” of the Union “long shots landed squarely in the ranks of the gray soldiers drawn up to await the order to advance.” [7] Estimates vary but the waiting Confederates lost between 300-500 killed and wounded, the most affected was Kemper’s brigade of Pickett’s division which lost about 250 men, or 15% of its strength. [8] Other units lost significant numbers, with those inflicted on Pettigrew’s brigades further depleting their already sparse numbers.
Composed of Pickett’s fresh division from First Corps, Heth’s battered division now under Pettigrew which had already taken close to 40% casualties. Of the two brigades of Pender’s division now commanded by Trimble, Lane’s which was fresh but Scales brigade, now under command of Colonel William Lowrence had suffered greatly on July 1st; its “casualty rate was 63% and it had lost its commander and no fewer than fifty-five field and company grade officers.” [9] And now, these battered the units began to take casualties from well directed Federal fire. George Stewart wrote: “In most armies, such a battered unit would have been sent to the rear for reorganization, but here it was being selected for a climactic attack!” [10]
“The Confederate losses mounted at an alarming rate. The psychological impact of artillery casualties was great, for the big guns not only killed but mangled bodies, tore them apart, or disintegrated them.” [11] A survivor wrote his wife days later: “If the crash of worlds and all things combustible had been coming in collision with each other, it could not have surpassed it seemingly. To me it was like the “Magazine of Vengeance” blown up.” [12] A soldier of Kemper’s brigade recalled “The atmosphere was rent and broken by the rust and crash of projectiles…The sun, but a few minutes before so brilliant, was now darkened. Through this smoky darkness came the missiles of death…the scene beggars description…Many a fellow thought his time had come…Great big, stout hearted men prayed, loudly too….” [13] Colonel Joseph Mayo of the 3rd Virginia regiment was heavily hit, one of its survivors wrote “when the line rose up to charge…it appeared that as many were left dead and wounded as got up.” [14]
On the opposite ridge Union forces were experiencing the same kind of intense artillery fire. But these effects were minimized due to the prevalent overshooting of the Confederate artillery as well as the poor quality of ammunition. This resulted in few infantry casualties with the worst damage being taken by a few batteries of artillery at the angle. Soldiers behind the lines took the worst beating, but “the routing of these non-combatants was of no military significance,” [15] This did create some problems for the Federals as Meade was forced to abandon their headquarters and the Artillery Reserve was forced to relocate “a little over a half mile to the rear.” [16] The effects of this on operations were minimal as Brigadier General Robert Tyler commanding the Artillery Reserve “posted couriers at the abandoned position, should Hunt want to get in touch with him.” [17]
Despite the fusillade Meade maintained his humor and as some members of his staff tried to find cover on the far side of the little farmhouse quipped:
“Gentlemen, are you trying to find a safe place?…You remind me of the man who drove the oxen team which took ammunition for the heavy guns to the field at Palo Alto. Finding himself in range, he tipped up his cart and hid behind it. Just then General Taylor came along and shouted “You damned fool, don’t you know you are no safer there than anywhere else?” The driver responded, “I don’t suppose I am general, but it kind of feels so.” [18]
Despite the unparalleled bombardment, the likes which not had been seen on the American continent, the Confederate artillery had little actual effect on the charge. The Prussian observer travelling with Lee’s headquarters “dismissed the barrage as a “Pulververschwindung,”…a waste of powder. [19] The Federal infantry remained in place and ready to meet the assault, Hunt replaced his damaged batteries and even more importantly Lieutenant Colonel Freeman McGilvery’s massive battery was lying undetected where it could deliver devastating enfilade fire as were Rittenhouse’s batteries on Little Round Top and Osborne’s on Cemetery Hill. These guns, unaffected by the Confederate bombardment were poised to wreak destruction on the men of the three Confederate divisions.
Unlike the Federal Army which had its large pool of artillery battalions in the Artillery Reserve with which to replace batteries that had taken casualties or were running low on ammunition, and “soon the drivers of the caissons found that the heavy fire had exhausted their supply of shot and shell, and the had to go even farther to get it from the reserve train. As a result some of the guns remained mute and their gunners stood helpless during the cannonade and charge, for Alexander had no batteries in reserve to replace them.” [20] The reason for this was that the Confederates had reorganized their artillery before Chancellorsville with all batteries assigned directly to the three infantry corps leaving the army without a reserve, and because Brigadier General William Pendleton had relocated the artillery trains further to the rear without informing Alexander or Longstreet. He had also ordered the eight guns of the Richardson’s artillery away without notifying anyone, guns which Alexander was counting on to support the attack. At about 2:20 p.m. Alexander, knowing that he was running short of ammunition sent a note to Picket and Pettigrew advising them:
“General: If you are to advance at all, you must come at once or we will not be able to support you as we ought. But the enemy’s fire has not slackened and there are still 18 guns firing from the cemetery.” [21]
About twenty minutes later Alexander saw some of the guns along Cemetery Ridge begin to limber up and depart, and noticed a considerable drop off in Federal fire. Now confident that his guns had broken the Federal resistance, at 2:40 sent word to Pickett “For God’s sake come quick or my ammunition will not let me support you.” [22] However, what Alexander did not realize was that to conserve ammunition for the Confederate infantry charge Henry Hunt had ordered those batteries to withdraw and was replacing them with fresh batteries and had ordered an “immediate cessation and preparation for the assault to follow.” [23]
The message reached Pickett and Pickett immediately rode off to confer with Longstreet. Pickett gave the message to Longstreet who read it “and said nothing. Pickett said, “General, shall I advance!” Longstreet, knowing it had to be, but unwilling to give the word, turned his face away. Pickett saluted and said “I am going to move forward, sir” galloped off to his division and immediately put it in motion.” [24]
A few minutes later Longstreet rode to find Alexander. Meeting him at 2:45 and Alexander informed him of the shortage of ammunition, which upset him enough that he “seemed momentarily stunned” [25] by this news Longstreet told Alexander, “Stop Pickett immediately and replenish your ammunition.” [26] But Alexander now had to give Longstreet even worse news telling him “I explained that it would take too long, and the enemy would recover from the effect of our fire was then having, and too that we had, moreover, very little to replenish it with.” [27] Longstreet continued to ride with Alexander and again eyed the Federal positions on Cemetery Ridge with his binoculars and said “I don’t want to make this attack,” pausing between sentences as if thinking aloud. “I believe it will fail- I do not know how it can succeed- I would not make it even now, but Gen. Lee has ordered it and expects it.” [28] Alexander, who as a battalion commander now in charge of First Corps artillery was uncomfortable, he later wrote:
“I had the feeling that he was on the verge of stopping the charge, & that with even slight encouragement he would do it. But that very feeling kept me from saying a word, or either assent I would not willingly take any responsibility in so grave a matter & I had almost a morbid fear of causing any loss of time. So I stood by, & looked on, in silence almost embarrassing.” [29]
While Longstreet was still speaking Pickett’s division swept out of the woods to begin the assault, Alexander knew that “the battle was lost if we stopped. Ammunition was too low to try anything else, for we had been fighting for three days. There was a chance, and it was not my part to interfere.” [30]
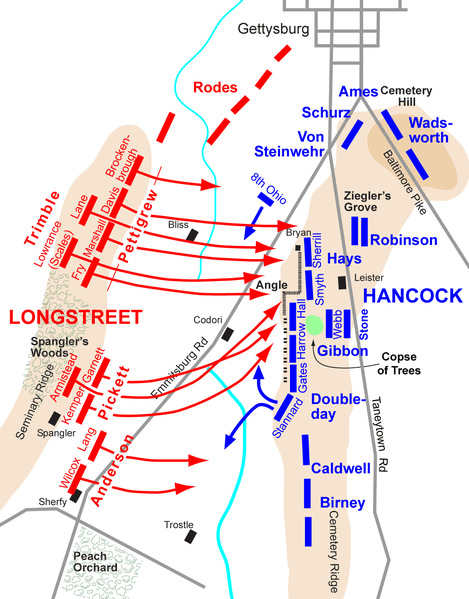
Despite this Pickett and many of his soldiers were confident of success, and “no officer reflected the men’s confidence better than George Pickett. There was no fatalism in him. Believing that his hour of destiny had come and expecting to take fortune at its flood, he rode down the slop like a knight in a tournament.” [31] Pickett was “an unforgettable man at first sight” [32] Pickett was exceptionally undistinguished in the West Point class of 1846, graduating last in the class, but “fought valiantly in a number of battles” [33] during the Mexican War alongside James Longstreet. Like many he officers he resigned his commission in 1861 and received a colonelcy in the new Confederate army. During the Seven Days battles he commanded a brigade, which was now commanded by Richard Garnett and was wounded at Gaines Mill. Promoted to Major General in the summer of 1862 Pickett received command of the division formerly commanded by David R. Jones. The division was sent to peripheral areas and took no part in the battles of late 1862 or Chancellorsville. Reduced from its five brigade strength due to the insistence of Jefferson Davis to leave forces to protect Richmond the division was built around the brigades of James Kemper, Lewis Armistead and Richard Garnett.
When Pickett’s division as well as those of Pettigrew and Trimble swept out of the wood to begin the attack the last chance to stop it ended. As Pickett’s brigades moved out he encouraged them shouting “Remember Old Virginia!” or to Garnett’s men “Up, men, and to your posts! Don’t forget today that you are from Old Virginia!” [34] But when Garnett asked if there were any final instructions Pickett was told “I advise you to make the best kind of time in crossing the valley; it’s a hell of an ugly looking place over yonder.” [35] Armistead called out to his soldiers, “Men, remember who you are fighting for! Your homes, your firesides, and your sweethearts! Follow Me!” [36]Armistead’s example had a major impact on his brigade, men were inspired, as one later wrote “They saw his determination, and they were resolved to follow their heroic leader until the enemy’s bullets stopped them.” [37] about 500 yards to Pickett’s left Pettigrew exhorted his men “for the honor of the good old North State, forward.” [38]
Pickett’s division “showed the full length of its long gray ranks and shining bayonets, as grand as a sight as ever a man looked on.” [39] The sight was impressive on both sides of the line, a Confederate Captain recalling the “glittering forest of bayonets” the two half mile wide formations bearing down “in superb alignment.” [40] even impressing the Federals. Colonel Philippe Regis de Trobriand, a veteran of many battles in Europe and the United States recalled “it was a splendid sight,” [41] and another recalled that the Confederate line ‘gave their line an appearance of being irresistible.” [42]
But the Federals were confident. Having withstood the Confederates for two days and having survived the artillery bombardment the Union men eagerly awaited the advancing Confederates. Directly facing the Confederate advance in the center of the Union line was the division of John Gibbon. The cry went out “Here they come! Here they come! Here comes the infantry!” [43] To the left of Gibbon Alexander Hays called to his men “Now boys look out…now you will see some fun!” [44]
The Confederates faced difficulties as they advanced, and not just from the Union artillery which now was already taking a terrible toll on the advancing Confederates. Stuck by the massed enfilade fire coming from Cemetery Hill and Little Round Top continued their steady grim advance. Carl Schurz from his vantage point on Cemetery Hill recalled:
“Through our field-glasses we could distinctly see the gaps torn in their ranks, the grass dotted with dark spots- their dead and wounded….But the brave rebels promptly filled the gaps from behind or by closing up on their colors, and unasked and unhesitatingly they continued with their onward march.” [45]
Pettigrew’s division was met by fire which enveloped them obliquely from Osborne’s 39 guns on Cemetery Hill. On the left flank a small regiment, the 8th Ohio lay in wait. Seeing an opportunity the commander Lieutenant Colonel Franklin Sawyer deployed his 160 men in a single line, took aim at Brockenbrough’s Virginia brigade some two hundred yards ahead of the Emmitsburg Road, and opened a devastating fire. “Above the boiling clouds the Union men could see a ghastly debris of guns, knapsacks, blanket rolls, severed human heads, and arms and legs and parts of bodies tossed into the air by the impact of the shot.” [46] So sudden and unexpected was this that the Confederates panicked and “fled in confusion…” to the rear where they created more chaos in Trimble’s advancing lines as one observed they “Came tearing through our ranks, which caused many men to break.” [47] The effect on Confederate morale was very important, for “the Army of Northern Virginia was not used to seeing a brigade, even a small one, go streaming off to the rear, with all its flags….Even Pickett’s men sensed that something disastrous had happened on the left….” [48]
In one fell swoop Pettigrew was minus four regiments. Brockenbrough was singularly ineffective in leading his men, he “was a nonentity who did not know how to control his recalcitrant rank and file; nor did he have the presence to impress his subordinate officers and encourage them to do his bidding.” [49] The disaster that had overtaken Brockenbrough’s brigade now threated “another important component of Lee’s plan-the protection so necessary for the left flank of the advancing line had collapsed.
Pettigrew’s division continued its advance after Brockenbrough’s brigade collapsed, but the Confederate left was already beginning to crumble. “Sawyer changed front, putting his men behind a fence, and the regiment began firing into the Confederate flank.” [50] with Davis’s brigade now taking the brunt of the storm of artillery shells from Osborne’s guns. This brigade had suffered terribly at the railroad cut on July 1st, especially in terms of field and company grade officers was virtually leaderless, and “the inexperienced Joe Davis was helpless to control them.” [51] To escape the devastating fire Davis ordered his brigade to advance at the double quick which brought them across the Emmitsburg Road ahead of the rest of the division, where they were confronted by enfilade canister fire from Woodruff’s battery to its left, as well as several regiments of Federal infantry and from the 12th New Jersey directly in their front. A New Jersey soldier recalled “We opened on them and they fell like grain before the reaper, which nearly annihilated them.” [52] Davis noted that the enemy’s fire “commanded our front and left with fatal effect.” [53] Davis saw that further continuing was hopeless and ordered his decimated brigade “to retire to the position originally held.” [54]
Pettigrew’s remain two brigades continued grimly on to the Emmitsburg Road, now completely devoid of support on their left flank. Under converging fire from Hay’s Federal troops the remaining troops of Pettigrew’s command were slaughtered. Hay’s recalled “As soon as the enemy got within range we poured into them and the cannon opened with grape and canister [, and] we mowed them down in heaps.” [55] The combination of shot, shell, canister and massed musket fire “simply erased the North Carolinian’s ranks.” [56] Pettigrew was wounded, Colonel Charles Marshall killed 50 yards from the stone wall and “only remnants of companies and regiments remained unscathed.” [57] Soon the assault of Pettigrew’s division was broken:
“Suddenly Pettigrew’s men passed the limit of human endurance and the lines broke apart and the hillside covered with men running for cover, and the Federal gunners burned the ground with shell and canister. On the field, among the dead and wounded, prostrate men could be seen holding up handkerchiefs in sign of surrender.” [58]
Trimble’s two brigades fared no better. Scales brigade, now under the command of Colonel W. Lee Lowrence “never crossed the Emmitsburg Road but instead took position along it to fire at the enemy on the hill. The soldiers from North Carolina who two days before had marched without flinching into the maw of Wainwright’s cannon on Seminary Ridge could not repeat the performance.” [59] Trimble was severely wounded in the leg and sent a message to Lane to take command of the division. The order written in the third person added a compliment to his troops: “He also directs me to say that if the troops he had the honor to command today for the first time couldn’t take that position, all hell can’t take it.” [60] Lane attempted to rally the troops for one last charge when one of his regimental commanders exploded telling him “My God, General, do you intend rushing your men into such a place unsupported, when the troops on the right are falling back?” [61] Lane looked at the broken remains of Pettigrew’s division retiring from the field and ordered a retreat. Seeing the broken remnants of the command retreating, an aide asked Trimble if the troops should be rallied. Trimble nearly faint from loss of blood replied: “No Charley the best these brave fellows can do is to get out of this,” so “let them get out of this, it’s all over.” [62] The charge was over on the Confederate left.
The concentrated Federal fire was just as effective and deadly on the Confederate right. Kemper’s brigade, on the right of Pickett’s advance was mauled by the artillery of Rittenhouse on Little Round Top, which “tracked their victims with cruel precision of marksmen in a monstrous shooting gallery” and the overs “landed their shots on Garnett’s ranks “with fearful effect.” [63]
As the Confederates advanced Pickett was forced to attempt to shift his division to the left to cover the gap between his and Pettigrew’s division. The move involved a forty-five degree oblique and the fences, which had been discounted by Lee as an obstacle which along the Emmitsburg Road “virtually stopped all forward movement as men climbed over them or crowed through the few openings.” [64] Pickett’s division’s oblique movements to join with Pettigrew’s had presented the flank of his division to McGilvery’s massed battery. The movement itself had been masterful, the execution of it under heavy fire impressive; however it meant the slaughter of his men who were without support on their right flank.
As Pickett’s division advanced into the Plum Run Valley they were met by the artillery of Freeman McGilvery, who wrote that the “execution of the fire must have been terrible, as it was over a level plain, and the effect was plain to be seen. In a few minutes, instead of a well-ordered line of battle, there were broken and confused masses, and fugitives fleeing in every direction.” [65]
Kemper’s brigade which had the furthest to go and the most complicated maneuvering to do under the massed artillery fire suffered more damage. The swale created by Plum Run was a “natural bowling alley for the projectiles fired by Rittenhouse and McGilvery.” [66] was now flanked by Federal infantry as it passed the Condori farm. The Federal troops were those of the Vermont brigade commanded by Brigadier General George Stannard. These troops were nine month volunteers recruited in the fall of 1862 and due to muster our in a few days. They were new to combat, but one of the largest brigades in the army and 13th Vermont “had performed with veteran like precision the day before” [67] leading Hancock to use them to assault the Confederate right. The Vermonters were positioned to pour fire into the Confederate flank, adding to the carnage created by the artillery, and the 13th and 16th Vermont “pivoted ninety degrees to the right and fired a succession of volleys at pistol range on the right of Pickett’s flank.” [68]
Kemper had not expected this, assuming that the Brigades of Wilcox and Perry would be providing support on the flank. As he asked a wounded officer of Garnett’s brigade if his wound was serious, the officer replied that he soon expected to be a prisoner and asked Kemper “Don’t you see those flanking columns the enemy are throwing on our right to sweep the field?” [69] Kemper was stunned but ordered his troops to rush federal guns, but “they were torn to pieces first by the artillery and then by the successive musketry of three and a half brigades of Yankee infantry.” [70] Kemper was fearfully wounded in the groin, no longer capable of command. His brigade was decimated and parts of two regiments had to refuse their line to protect the flank, and those that continued to advance had hardly any strength left with which to succeed, the Confederate left was no for all intents and purposes out of the fight.
Now that fight was left in the hands of Armistead and Garnett’s brigades, and at this moment in the battle, the survivors of those units approached the stone wall and the angle where they outnumbered the Federal defenders, one regiment of which, the 71st Pennsylvania had bolted to the rear.
The survivors of Garnett’s brigade, led by their courageous but injured commander, riding fully exposed to Federal fire on his horse crossed the Emmitsburg Road and pushed forward overwhelming the few Federals remaining at the wall. They reached the outer area of the angle “which had been abandoned by the 71st Pennsylvania” and some of his men “stood on the stones yelling triumphantly at their foes.” [71] Armistead, leap over the wall shouting to his men “Come on boys! Give them the cold steel”…and holding his saber high, still with the black hat balanced on its tip for a guidon, he stepped over the wall yelling as he did so: “Follow me!” [72]
However, their triumph was short lived; the 72nd Pennsylvania was rushed into the gap by the brigade commander Brigadier General Alexander Webb. The climax of the battle was now at hand and “the next few minutes would tell the story, and what that story would be would all depend on whether these blue-coated soldiers really meant it…. Right here there were more Confederates than Federals, and every man was firing in a wild, feverish haste, with smoke settling down thicker and thicker.” [73] The 69th Pennsylvania, an Irish regiment under Colonel Dennis O’Kane stood fast and their fire slaughtered many Confederates. Other Federal regiments poured into the fight, famous veteran regiments the 19th and 20th Massachusetts, the 7th Michigan and the remnants of the 1st Minnesota who had helped stop the final Confederate assault on July 2nd at such fearful cost.
Dick Garnett, still leading his troops “muffled in his dark overcoat, cheered his troops, waving a black hat with a silver cord” [74] when he was shot down, his frightened horse running alone off the battlefield, a symbol of the disaster which had befallen Pickett’s division. Armistead reached Cushing’s guns where he was hit by several bullets and collapsed mortally wounded. “Armistead had been the driving force behind the last effort, there was no one else on hand to take the initiative. Almost as quickly as it had come crashing in, the Rebel tide inside the outer angle ebbed back to the wall.” [75]
For a time the Confederate survivors engaged Webb’s men in a battle at the wall itself in a stubborn contest. A Federal regimental commander wrote “The opposing lines were standing as if rooted, dealing death into each other.” [76] The Federals launched a local counterattack and many Confederates elected to surrender rather than face the prospect of retiring across the battlefield that was still swept by Federal fire.
Webb had performed brilliantly in repulsing the final Confederate charge and “gained for himself an undying reputation. Faced with defeat, he accepted the challenge and held his men together through great personal exertion and a willingness to risk his life.” [77] For his efforts he was belatedly awarded the Medal of Honor.
Webb, like John Buford on July 1st, Strong Vincent, Freeman McGilvery and George Sears Greene on July 2nd, was instrumental in the Union victory. Hancock said of Webb “In every battle and on every important field there is one spot to which every army [officer] would wish to be assigned- the spot upon which centers the fortunes of the field. There was but one such spot at Gettysburg and it fell to the lot of Gen’l Webb to have it and to hold it and for holding it he must receive the credit due him.” [78]
The survivors of Pickett, Pettigrew and Trimble’s shattered divisions began to retreat, Lee did not yet understand that his great assault had been defeated, but Longstreet, who was in a position to observe the horror was. He was approached by Lieutenant Colonel Arthur Fremantle, a British observer from the Coldstream Guards. Fremantle did not realize that the attack had been repulsed, having just seen one of Longstreet’s regiments “advancing through the woods in good order” and unwisely bubbled “I would not have missed this for anything.” [79] Longstreet replied with a sarcastic laugh “The devil you wouldn’t” barked Longstreet. “I would have liked to have missed this very much; we’ve attacked and been repulsed. Look there.” [80] Fremantle looked out and “for the first time I then had a view of the open space between the two positions, and saw it covered with Confederates slowly and sulkily returning towards us in small broken parties, under a heavy fire of artillery.” [81] Henry Owen of the 18th Virginia wrote that the retreating men “without distinction of rank, officers and privates side by side, pushed, poured and rushed in a continuous stream, throwing away guns, blankets, and haversacks as they hurried on in confusion to the rear.” [82]
It was a vision of utter defeat. Pickett, who had seen his division destroyed and had been unable to get it additional support was distraught. An aide noted that Pickett was “greatly affected and to some extent unnerved” [83] by the defeat. “He found Longstreet and poured out his heart in “terrible agony”: “General, I am ruined; my division is gone- it is destroyed.” [84] Lee had come up by now and attempted to comfort Pickett grasping his hand and telling him: “General, your men have done all that they could do, the fault is entirely my own” and instructed him that he “should place his division in the rear of this hill, and be ready to repel the advance of the enemy should they follow up their advantage.” [85] The anguished Pickett replied, “General Lee, I have no division now. Armistead is down, Garnett is down and Kemper is mortally wounded.” [86]

Pickett’s charge was over, and with it the campaign that Lee had hoped would secure the independence of the Confederacy was effectively over, and the Battle of Gettysburg lost. “Lee’s plan was almost Burnside-like in its simplicity, and it produced a Fredericksburg with the roles reversed.” [87]
It was more than a military defeat, but a political one as well for with it went the slightest hope remaining of foreign intervention. As J.F.C. Fuller wrote “It began as a political move and it had ended in a political fiasco.” [88]
[1] Clausewitz, Carl von. On War Indexed edition, edited and translated by Michael Howard and Peter Paret, Princeton University Press, Princeton NJ 1976 p.114
[2] Ibid. Clausewitz On War p.108
[3] Dempsey, Martin Mission Command White Paper 3 April 2012 p.5 retrieved ( July 2014 from http://www.dtic.mil/doctrine/concepts/white_papers/cjcs_wp_missioncommand.pdf
[4] ___________. The Armed forces OfficerU.S. Department of Defense Publication, Washington DC. January 2006 p.18
[5] Ibid. The Armed Forces Officer p.18
[6] Ibid. Clausewitz On War p.101
[7] Foote, Shelby, The Civil War, A Narrative. Volume Two Fredericksburg to Meridian Random House, New York 1963 p.548
[8] Gottfried, Bradley The Artillery of Gettysburg Cumberland House Publishing, Nashville TN 2008 p.
[9] Sears, Stephen W. Gettysburg. Houghton Mifflin Co. Boston and New York 2003 p.387
[10] Stewart, George R. Pickett’s Charge: A Micro-History of the Final Attack at Gettysburg, July 3rd 1863Houghton Mifflin Company Boston 1959
[11] Hess, Earl J. Pickett’s Charge: The Last Attack at Gettysburg University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill and London 2001 p.153
[12]Wert, Jeffery D. Gettysburg Day Three A Touchstone Book, New York 2001 p.181
[13] Dowdy, Clifford. Lee and His Men at Gettysburg: The Death of a Nation Skyhorse Publishing, New York 1986, originally published as Death of a Nation Knopf, New York 1958 p.294
[14] Ibid. Wert Gettysburg Day Three p.179
[15] Ibid. Stewart Pickett’s Charge p.132
[16] Coddington, Edwin B. The Gettysburg Campaign: A Study in Command, A Touchstone Book, Simon and Schuster New York, 1968 p.496
[17] Ibid. Coddington The Gettysburg Campaign p.496
[18] Huntington, Tom Searching for George Gordon Meade: The Forgotten Victor of GettysburgStackpole Books, Mechanicsburg PA 2013 p.171
[19] Ibid. Hess Pickett’s Charge p.163
[20] Ibid. Coddington The Gettysburg Campaign p.499
[21] Trudeau, Noah Andre. Gettysburg: A Testing of Courage, Harper Collins Publishers, New York 2002 p.459
[22] Ibid. Coddington The Gettysburg Campaign p.500
[23] Hunt, Henry The Third Day at Gettysburg in Battles and Leaders of the Civil Waredited by Bradford, Neil Meridian Press, New York 1989 p.374
[24] Alexander, Edwin Porter. The Great Charge and the Artillery Fighting at Gettysburg, in Battles and Leaders of the Civil Waredited by Bradford, Neil Meridian Press, New York 1989 p.364
[25] Ibid. Coddington The Gettysburg Campaign p.501
[26] Ibid. Alexander The Great Charge and the Artillery Fighting at Gettysburg p.365
[27] Ibid. Alexander The Great Charge and the Artillery Fighting at Gettysburg p.365
[28] Ibid. Trudeau. Gettysburg: A Testing of Courage pp.474-475
[29] Ibid. Alexander The Great Charge and the Artillery Fighting at Gettysburg p.365
[30] Alexander, Edward Porter. Fighting for the Confederacy: The Personal Recollections of General Edward Porter Alexander edited by Gary Gallagher University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill 1989 p.261
[31] Ibid. Dowdy Lee and His Men at Gettysburg p.313
[32] Ibid. Wert Gettysburg Day Three p.109
[33] Ibid. Hess Pickett’s Charge p.37
[34] Guelzo, Allen C. Gettysburg: The Last InvasionVintage Books a Division of Random House, New York 2013 p.408
[35] Ibid. Hess Pickett’s Charge p.166
[36] Ibid. Hess Pickett’s Charge p.167
[37] Ibid. Hess Pickett’s Charge p.167
[38] Ibid. Trudeau. Gettysburg: A Testing of Courage p.483
[39] Ibid. Alexander The Great Charge and the Artillery Fighting at Gettysburg p.365
[40] Ibid. Foote The Civil War, A Narrative. Volume Two p.553
[41] Ibid. Guelzo Gettysburg: The Last Invasion p.407
[42] Ibid. Hess Pickett’s Charge p.193
[43] Ibid. Hess Pickett’s Charge p.193
[44] Ibid. Guelzo Gettysburg: The Last Invasion p.411
[45] Ibid. Sears Gettysburg p.422
[46] Catton, Bruce The Army of the Potomac: Glory Road Doubleday and Company, Garden City New York, 1952 p.318
[47] Ibid. Sears Gettysburg p.423
[48] Ibid. Stewart Pickett’s Charge: A Micro-History of the Final Attack at Gettysburg pp.193-194
[49] Ibid. Hess Pickett’s Charge p.187
[50] Ibid. Stewart Pickett’s Charge: A Micro-History of the Final Attack at Gettysburg p.193
[51] Ibid. Dowdy Lee and His Men at Gettysburg p.311
[52] Ibid. Trudeau. Gettysburg: A Testing of Courage p.494
[53] Ibid. Sears Gettysburg p.425
[54] Ibid. Trudeau. Gettysburg: A Testing of Courage p.494
[55] Ibid. Trudeau. Gettysburg: A Testing of Courage p.502
[56] Ibid. Wert Gettysburg Day Three p.216
[57] Ibid. Wert Gettysburg Day Three p.218
[58] Ibid. Catton The Army of the Potomac: Glory Road p.318
[59] Ibid. Trudeau. Gettysburg: A Testing of Courage p.504
[60] Ibid. Stewart Pickett’s Charge: A Micro-History of the Final Attack at Gettysburg pp.238-239
[61] Ibid. Trudeau. Gettysburg: A Testing of Courage p.504
[62] Ibid. Guelzo Gettysburg: The Last Invasion p.425
[63] Ibid. Foote The Civil War, A Narrative. Volume Two p.555
[64] Ibid. Coddington The Gettysburg Campaign p.503
[65] Ibid. Gottfried The Artillery of Gettysburg p.217
[66] Ibid. Hess Pickett’s Charge p.220
[67] Ibid. Coddington The Gettysburg Campaign p.515
[68] Ibid. Coddington The Gettysburg Campaign p.515
[69] Ibid. Trudeau. Gettysburg: A Testing of Courage p.502
[70] Ibid. Sears Gettysburg p.448
[71] Ibid. Trudeau. Gettysburg: A Testing of Courage p.505
[72] Ibid. Foote The Civil War, A Narrative. Volume Two p.562
[73] Ibid. Catton The Army of the Potomac: Glory Road p.319
[74] Ibid. Dowdy Lee and His Men at Gettysburg p.317
[75] Ibid. Trudeau Gettysburg p.508
[76] Ibid. Sears Gettysburg p.451
[77] Ibid. Coddington The Gettysburg Campaign p.528
[78] Ibid. Coddington The Gettysburg Campaign p.528
[79] Fremantle, Arthur Three Months in the Southern States, April- June 1863 William Blackwood and Sons, Edinburgh and London 1863 Amazon Kindle edition p.285
[80] Wert, Jeffry D. General James Longstreet The Confederacy’s Most Controversial Soldier, A Touchstone Book, Simon and Schuster, New York and London 1993 p.292
[81] Ibid. Fremantle Three Months in the Southern States p.287
[82] Ibid. Sears Gettysburg p.456
[83] bid. Hess Pickett’s Charge p.326
[84] Ibid. Guelzo Gettysburg: The Last Invasion p.428
[85] Ibid. Guelzo Gettysburg: The Last Invasion p.428
[86] Ibid. Hess Pickett’s Charge p.326
[87] Millet, Allan R. and Maslowski, Peter, For the Common Defense: A Military History of the United States The Free Press a Division of Macmillan Inc. New York, 1984 p.206
[88] Fuller, J.F.C. Grant and Lee: A Study in Personality and Generalship, Indiana University Press, Bloomington IN 1957 pp.200-201