 The author with Marines at Point du Hoc, Normandy in 2004
The author with Marines at Point du Hoc, Normandy in 2004
Every year about this time I try to write about D-Day. Last year I posted several articles as I had in 2009 as well. This year I spent more time on the Battle of Midway writing three articles. Today I have been on the road much of the day and as I drove back to my Island Hermitage I began to think about what I wanted to do this year. When I have decided to do is to re-post a short research paper that I did for one of my Master’s degree courses tonight and follow it with some articles over the week on specific aspects and personalities of the campaign. What I hope is that people that are not familiar with the campaign as well as those that are can use this as a portal to other resources on the web and in print.
I have visited Normandy once in 2004 on a trip with the Marines of the Marine Security Force Company Europe that took me to Belleau Wood as well as Normandy. In both places I had the good fortune to be able to explain aspects of both battles, at Normandy discussing the invasion from the German side of the fence. The Normandy battlefields are well worth visiting. Hopefully in the next few years I will get a chance to go back and do some serious exploring.
Introduction
 General Dwight D Eisenhower Commander in Chief Allied Forces Europe
General Dwight D Eisenhower Commander in Chief Allied Forces Europe
The American landings on Omaha Beach were critical to the success of the Allied invasion northwestern Europe in the overall Overlord plan. Without success at Omaha there would have been a strong chance that the German 7th Army and Panzer Group West could have isolated the remaining beachheads, and even if unsuccessful at throwing the Allies into the sea could have produced a stalemate that would have bled the Allies white. This quite possibly could have led to a political and military debacle for the western allies which would have certainly changed the course of World War II and maybe the course of history.[i] This is not to say the Germans would have won the war, but merely to state that a defeat on Omaha could have changed the outcomes of the war significantly. Subsequent to the successful landing there were opportunities both for the Allies and the Germans to change the way that the campaign unfolded, thus the battles leading up to the breakout at Avranches are critical to its development and the subsequent campaign in France.
OVERLORD: The Preparations
 Eisenhower’s Key Lieutenants: Patton, Bradley and Montgomery
Eisenhower’s Key Lieutenants: Patton, Bradley and Montgomery
The planning for the Normandy invasion began in earnest after the QUADRANT conference in Quebec in August 1943. The timetable for the operation was established at the Tehran conference where Stalin sided with the Americans on the need for an invasion of France in the spring of 1944.[ii] Prior to this there had been some planning by both the British and Americans for the eventual invasion initially named ROUNDUP. These preparations and plans included a large scale raid at Dieppe in 1942 which ended in disaster but which provided needed experience in what not to do in an amphibious assault on a heavily defended beach. The failure at Dieppe also darkened the mood of the Allies, the British in particular to the success of such operations, bringing to mind the failed Gallipoli campaign of 1915 as well as the opposed landings at Salerno and the USMC experience at Tarawa.[iii] Despite this the Americans led by General Marshall pushed for an early invasion of northwest Europe. Churchill and the British due to their weakness in land power pushed for land operations in the Mediterranean, and even in Norway as an option to the assault in France. The conflicted mindset of the Allies left them in the position of planning almost exclusively for the success of the initial landings and build up to the near exclusion of planning for the subsequent campaign once they landed. This especially included what one writer described as “the maze of troubles awaiting behind the French shore.”[iv]
 Field Marshal Erwin Rommel, Commander of Army Group B
Field Marshal Erwin Rommel, Commander of Army Group B
Despite conflicts between the Americans and British political and military leadership the planning for the Normandy landings detailed in NEPTUNE and OVERLORD moved ahead. General Dwight Eisenhower was appointed as the commander of SHAEF with his major subordinates for Land, Air and Sea which caused consternation on both sides of the Atlantic.[v] [vi] The planned operation was expanded from the initial 3 division assault on a narrow front to a minimum 5 division assault on a broad front across Normandy[vii]supplemented by a strong airborne force.[viii] Overall the plan as it developed reflected a distinctly “American willingness to confront the enemy head-on in a collision which Britain’s leaders had sought for so long to defer.”[ix] It is ironic in a sense that the British avoidance of the head on attack was based on their known lack of manpower. Britain had few infantry reserves to sustain the war effort and the Americans only late recognized their own deficiency in both quantity and quality of infantry forces on which their strategy depended. That the western allies, so rich in material and natural resources would be so deficient in infantry manpower was a key constraint on the subsequent campaign in France and Germany. The shortage of infantry forces would cause great consternation among the Allies as the campaign in France wore on.
The Germans too faced manpower shortages due to the immense losses sustained on the Eastern front, those lost in Africa and those tied down in Italy, the Balkans and Norway as well as the drain caused by Luftwaffe Field Divisions and troops diverted into the Waffen-SS. The German Army resorted to smaller divisions and the created many “static” divisions manned by elderly or invalid Germans to plug the gaps along the Atlantic wall. The Germans were also forced to recruit “Volksdeutsch” and foreign “volunteers” to fill out both Wehrmacht and Waffen-SS formations.
 German fortifications at the Pas de Calais
German fortifications at the Pas de Calais
Prior to the final decision to mount an invasion the Allied planners had contended with the location of the assault in northwestern France. The Pas de Calais provided a direct route was rejected because it was where the Germans would expect the strike to occur and because it was where the German defenses were strongest. The fiasco at Dieppe had provided ample proof of what could happen when making an assault into a heavily fortified port. Likewise the mouth of the Seine near Le Harve was rejected because of the few beaches suitable for landing and because the forces would be split on both sides of the river. Brittany was excluded due to its distance from the campaigns objectives in Germany.[x]This left Normandy which offered access to a sufficient number of ports and offered some protection from the weather. Normandy offered options to advance the campaign toward the “Breton ports or Le Harve as might be convenient.”[xi] Omaha beach, situated on the center right of the strike would be crucial to the success of the assault situated to the left of UTAH and the right of the British beaches.
 Rommel inspecting beach obstacles
Rommel inspecting beach obstacles
Once Normandy was selected as the location for the strike by the Allies, the planning sessions remained contentious. This was especially true when the Allies debated the amount and type of amphibious lift that could be provided for the landings, particularly the larger types of landing ships and craft to support the Normandy invasion and the planned invasion of southern France, Operation ANVIL. The increase in OVERLORD requirements for landing craft had an impact in the Mediterranean and resulted in ANVIL being postponed until later in the summer.
 “Dummy” Sherman Tank: The Allies created a fictional Army Group to deceive German planners
“Dummy” Sherman Tank: The Allies created a fictional Army Group to deceive German planners
As part of their preparations the Allies launched a massive deception campaign, Operation FORTITUDE. This operation utilized the fictitious First Army Group under the “command” of General George Patton. Patton was still smarting from his relief of command of 7th Army following slapping commanded an “Army Group” which incorporated the use of dummy camp sites, dummy tanks, aircraft and vehicles, falsified orders of battle and communications to deceive German intelligence.[xii] The success of this effort was heightened by the fact that all German intelligence agents in the U.K. had been neutralized or turned by the British secret service. Additionally the Luftwaffe’s limited air reconnaissance could only confirm the pre-invasion build ups throughout England without determining the target of the invasion.[xiii] The German intelligence chief in the west, Colonel Baron von Roenne “was deceived by FORTITUDE’s fantasy invasion force for the Pas de Calais.”[xiv] Despite this Commander of the 7thArmy recognized by 1943 that Normandy was a likely Allied target and efforts were made to shift 7th Army’s center of gravity from Brittany to Normandy. The one potential German success in getting wind of when the Allied landings would occur was lost when German intelligence discovered two lines of Verlaine’s “Chason d’ Automme” in June 1944 which were to alert the French Resistance of the invasion. The security section of 15th Army heard them transmitted on the afternoon of 5 June and notified General Jodl at OKW, but no action was taken to alert forces on the coast.[xv] Allied intelligence was aided by ULTRA intercepts of coded German wireless transmissions. However this was less of a factor than during the African and Italian campaigns as more German communications were sent via secure telephone and telegraph lines vice wireless.[xvi] Allied deception efforts were for the most part successful in identifying German forces deployed in Normandy. However they were uncertain about the location of the 352nd Infantry Division which had been deployed along OMAHA and taken units of the 709th Infantry Division under its command when it moved to the coast.[xvii]
 US Army Air Corps B-17s were part of the strategic air campaign to isolate the German beach defenses
US Army Air Corps B-17s were part of the strategic air campaign to isolate the German beach defenses
The Allied air campaign leading up to the invasion was based on attempting to isolate the invasion site from German reinforcements. Leigh-Mallory the Air Chief developed the “TRANSPORTATION PLAN” which focused efforts on destroying the French railroad infrastructure.[xviii] A more effective effort was led by General Brereton and his Ninth Air Force which was composed of medium bombers and fighters. Brereton’s aircraft attacked bridges and rapidly achieved success in crippling German efforts to reinforce Normandy.[xix] Max Hastings gives more credit to the American bombing campaign in Germany to crippling the German defense in the west. General Spaatz and the 8th Air Force destroyed German production capacity in oil and petroleum as well as the degraded the German fighter force. The American daylight raids so seriously degraded the German fighter force that it could not mount effective resistance to the invasion.[xx] Russell Weigley also notes that Albert Speer the Reich Armaments Minister said that “it was the oil raids of 1944 that decided the war.”[xxi]
 US Navy LST’s being loaded for the invasion
US Navy LST’s being loaded for the invasion
Planning and preparations for OMAHA were based around getting the 1st and 29th Infantry Divisions ashore and them securing a beachhead “twenty-five kilometers wide and eight or nine kilometers deep.”[xxii] American preparations were thorough and ambitious, but the American assault would go through the most heavily defended sector of German defenses in Normandy. The landing beaches were wide and bordered by dunes which were nearly impassable to vehicles and “scrub covered bluffs thirty to fifty meters high…rough and impassable to vehicles even to tracked vehicles except at a few places. The exits were unimproved roads running through four or five draws that cut the bluffs.”[xxiii] Dug in along those bluffs was the better part of the 352nd Division. The Americans compounded their selection of a difficult and heavily defended landing zone the Americans failed to take advantage of many of the “gadgets” that were offered by the British which in hindsight could have aided the Americans greatly. The Americans made use of two battalions of DD (Dual Drive) tanks but turned down the offer of flail tanks, flamethrower tanks, and engineer tanks, the “funnies” developed by General Hobart and the British 79th Armored Division.[xxiv]
 Dual Drive amphibious tanks were included as part of the US invasion package
Dual Drive amphibious tanks were included as part of the US invasion package
Weigley believes that the American view of “tanks as instruments of mobility rather than of breakthrough power.” Likewise the Americans victories in the First World War were won by infantry with little tank support.[xxv] In this aspect the Americans were less receptive to utilizing all available technology to support their landings, something that when considering the fact that Americans were great lovers of gadgets and technology. The British use of the Armor, including the “Funnies” on the beaches to provide direct fire into German strong points lessened their infantry casualties on D-Day. Due to this lack of armor support on the beach American forces on OMAHA had little opportunity to exercise true combined arms operations during the initial landings.[xxvi]
 Rommel with Artillerymen of the 21st Panzer Division in Normandy
Rommel with Artillerymen of the 21st Panzer Division in Normandy
German preparations for an Allied landing in Normandy were less advanced than the Pas de Calais. However they had made great strides since late 1943. Field Marshal Rommel greatly increased defensive preparations along the front, including the Normandy beaches. One of Rommel’s initiatives was to deploy Panzer Divisions near the coast where they could rapidly respond to an invasion. However Rommel did not get everything that he wanted. The OKW only allotted him two Panzer Divisions to be deployed near the Normandy beaches. Only one of these the 21st Panzer Division was deployed near Caen in the British sector. One wonders the result had the 12th SS Panzer Division been deployed behind OMAHA. [xxvii]
OMAHA: The Landings
 The venerable USS Nevada, resurrected from the mud of Pearl Harbor bombarding German positions at Utah Beach
The venerable USS Nevada, resurrected from the mud of Pearl Harbor bombarding German positions at Utah Beach
Like the rest of the Allied invasion forces the 1st and 29th U.S. Infantry Divisions set sail from their embarkation ports with the intent of landing on June 5th. General Bradley, commanding the First Army until the American XII Army Group would be activated accompanied the invasion force. The OMAHA landing was under the command of General Gerow and his V Corps while VII Corps led by the 4th Infantry Division landed at Utah supported by airdrops of the 82nd and 101st Airborne Divisions inland. American command and control during the invasion was exercised from sea as in the Pacific, although General Officers were to go ashore with each of the American divisions. A severe channel storm disrupted the plan to land on the 5th and Eisenhower delayed the invasion one day catching a break in the weather and electing to go on the 6th.[xxviii] This delay while uncomfortable for the embarked troops caused the Germans to believe that no invasion would take place until the next favorable tide and moon cycle later in the month.[xxix] The assumption that no invasion was possible ensured that a number of key senior German leaders, including Rommel were absent from the invasion front when the Allies landed.[xxx]
 US Troops ride a LCVP toward Omaha
US Troops ride a LCVP toward Omaha
The landing beaches at OMAHA stretched about 6500 meters from Colleville-Sur-Mer to Vierville-Sur-Mere in the west. The beaches are wide with bluffs overlooking them and a seawall between the beaches and the bluffs. Additionally several small towns dot the beach. To the west of the town of Vierville, a prominent height overlooked the entire beachhead. Named Pont du Hoc, it was believed to house a 150mm battery sighted where it could enfilade the OMAHA landing zones. The Americans assigned to the 2nd Ranger Battalion to make a seaborne assault to land, scale the cliffs and take the battery. Companies from this battalion made a heroic landing and scaled the cliffs to capture the strongpoint only to discover that the guns had not been emplaced. The Rangers took heavy casualties and held their isolated beachhead against German counterattacks until relieved by the 29th Division on the morning of June 8th.[xxxi]
 Landing craft passing the USS Augusta in heavy seas heading toward Omaha Beach
Landing craft passing the USS Augusta in heavy seas heading toward Omaha Beach
H-Hour for OMAHA was 0630. Unfortunately the assault troops were transferred to their LCVP landing craft 16-20 kilometers from the beach. The result was a long and dangerous ride in the small craft for the infantry. Most of the infantry were completely soaked in sea spay and seasick before going ashore and they carried loads far above what they normally would carry into battle.[xxxii] The Armor support was one battalion of DD tanks, the 741stArmored Battalion, supporting the 16th Infantry Regiment of 1st Infantry Division. These were also launched too far out and nearly all of the tanks were swamped and lost before firing a shot in anger.[xxxiii] Other American support units needed to provide firepower on the beach were equally unfortunate. Weigley notes that at OMAHA “at least 10 of the LCVPs sank” as did “the craft carrying almost all of the 105mm howitzers that were to be the first artillery ashore after the tanks.”[xxxiv] The losses would cripple the assault on OMAHA and nearly cause its abandonment.
As the soldiers of the American divisions on OMAHA came ashore they faced German defenders of the 352nd, 716th and a regiment of the 709th Infantry Division, the latter under the tactical command of the 352nd. Without the bulk of their tanks artillery and lacking close air support the Americans struggled across the beaches and were cut down in large numbers before being pinned down behind the sea wall.[xxxv] With the Americans pinned down on the beach unable to advance, the time tables for the reinforcing waves became snarled amid the German beach obstacles which had not been cleared. This was in large part due to 40% casualties among the Combat Engineers and the loss of all but five bulldozers.[xxxvi] Naval officers were frustrated in their attempts to provide naval gunfire support by the lack of identifiable targets on the beaches. Yet German strongpoint’s were “knocked out by either by superbly directed vigorous gunfire from destroyers steaming as close as 800 yards offshore, or by determined action from Rangers or infantry.[xxxvii]
 US Infantry struggles ashore at Omaha
US Infantry struggles ashore at Omaha
Soldiers ashore discovered that they were not facing the static 716th Division but the veteran 352nd Division as well.[xxxviii] Only the leadership and actions of Brigadier General Norman Cota the 29th Division’s Deputy Commander and Colonel Charles Canham of the 116th Infantry kept the situation from complete collapse. They were able to rally their troops. Under their leadership small units from the 116th which had its linage back to the “Stonewall Brigade” as well as elements of the 16th and 18th Infantry Regiments began to move forward. Surviving junior leaders began to lead survivors through the dunes and up the bluffs to attack German defenders of the roads leading up from the beach from the flank and rear. A mid-day break in the weather allowed some close tactical air support giving the troops badly needed support.
 US 1st Infantry Division Troops at the Omaha sea wall
US 1st Infantry Division Troops at the Omaha sea wall
With the situation desperate General Bradley considered the evacuation of OMAHA. At sea events were as confused as Bradley and his staff attempted to make sense of what was going on. Even later in the evening there was discussion of diverting all further reinforcements from OMAHA to the British beaches.[xxxix]At 1330 hours “Gerow signaled Bradley: “Troops formerly pinned down on beaches…advancing up heights behind beaches.”[xl] By the end of the day Bradley’s aid Major Hansen noted Bradley’s comments to Collins: “They are digging in on Omaha beach with their fingernails. I hope they can push in and get some stuff ashore.” And Montgomery: “Someday I’ll tell Gen[eral] Eisenhower just how close it was for a few hours.”[xli]
 German Fallschirmjaeger Trüppen in Normandy, the German Parachute forces fighting in an infantry role were very effective in the Normandy campaign
German Fallschirmjaeger Trüppen in Normandy, the German Parachute forces fighting in an infantry role were very effective in the Normandy campaign
The landings at OMAHA succeeded at a cost of over 2000 casualties. Critical to the success of the landings were the German inability to reinforce their defending troops on the beach. Likewise the weakness of the units available to mount the standard counterattack that was critical to German defensive plans on D-Day itself kept the Germans from driving the Americans back into the Channel. The 352nd Division fought superbly under the full weight of V Corps and the British XXX Corps on its right suffering heavy casualties as they contested every inch of ground. The 716th Division composed of second rate troops melted under the onslaught. Allied air supremacy played a key role as sorties by the 8th and 9th Air Forces helped keep German reinforcements from arriving and interdicted counter attacks inland. Weigley credits the Allied air superiority with the success of the landings and with limiting casualties.[xlii]Von Rundstedt and other German commanders in France were limited by the delay and refusal of Hitler and OKW to release Panzer reserves when needed most early on June 6th. By the close of D-Day allied forces had secured the five invasion beaches but not achieved their objectives of taking Caen and Bayuex. Since the forces on the various beachheads had not linked up the beaches would have been extremely vulnerable had the Germans been able to mount a rapid counterattack by Panzers and strong infantry formations as they had at Salerno.
Major Battles to the Breakout at Avranches
Securing the Beachheads
 P-47 firing rockets at a ground target. Close air support was vital to Allied forces in Normandy
P-47 firing rockets at a ground target. Close air support was vital to Allied forces in Normandy
It took the V and VII Corps nearly a week to secure the beachheads. German forces including the stalwart 352nd Division resisted stubbornly and mounted sharp local counterattacks which kept the Americans off balance. Elements of the 29th Division and the 90th Division began to push inland and to expand the beachhead toward UTAH. Opposed by the 352nd Division and elements of the 91st Airlanding Division and other non-divisional units the fighting revealed the inexperience of the American infantry formations and the uneven quality of their leadership. As the Americans tackled the Germans in the labyrinth of the Bocage country the defensive skill of the Germans cost many American lives and delayed the joining of the beachheads. On the 13th the link up was solid enough to enabling the Americans to conduct the follow up operations needed to expand the beachhead, secure Cherbourg and clear the Cotentin.
 A Panther tank of the Panzer Lehr Division in Normandy
A Panther tank of the Panzer Lehr Division in Normandy
In some American divisions the hard fighting triggered a leadership crisis. The lack of success of the 90th Division led General “Lightening Joe” Collins of VII Corps relieve the division commander and two regimental commanders of command, a portent of things to come with other American units.[xliii] As the V and VII corps pushed into the “Bocage” they were followed by a massive build up of troops and equipment delivered to the beaches and to the artificial “Mulberry” harbors. Despite their numeric superiority, air supremacy and massive Naval gunfire support and facing the weakened 352nd, 91st and the 6thParachute Regiment and other less than quality formations, survivors of the static divisions, the Americans made painfully slow progress as they moved off the beachhead and into the Bocage.[xliv]
The Capture of Cherbourg
 US Soldiers of the 29th Division surrender to German Fallschirmjaeger in Normandy
US Soldiers of the 29th Division surrender to German Fallschirmjaeger in Normandy
Once the beachheads had been consolidated the Americans turned their attention toward Cherbourg. Cherbourg was the major naval port at the far northwest tip of the Cotentin. D-Day planners counted on its swift capture and rehabilitation to serve as a supply port for the Allied forces. The 9th Division drove south to the coast near Barneville on the 18th of June cutting off the German forces covering the approaches to Cherbourg.[xlv] This put the Germans in a bind as the 7th Army “had to split its forces in the peninsula in order to hold the fortress a little longer and thus to gain time for the establishment of the southern front on the Cotentin peninsula.[xlvi] The German forces arrayed before Cherbourg waged a desperate defense centered around the 243rd Infantry Division and other assorted battle groups of LXXXIV Corps, whose commander General Marcks one of the best German Generals was killed in action on 12 June.[xlvii] The U.S. VII Corps under Collins with the 9th, 4th and 79th Divisions pushed up the peninsula capturing Cherbourg on June 29th. Bradley pushed hard for the capture of the port as the Mulberries had been ravaged by a severe Channel storm the week prior. The port of Cherbourg was thoroughly demolished by German engineers and would not be fully operational for months. The loss of the Mulberries and delay in Cherbourg’s availability meant that few supplies were landed on the beaches would “hinder the escape from the constricting land of the hedgerows into which the Americans had come in search of a port.[xlviii]
The Battle of Caumont Gap
V Corps under Gerow made a cautious advance by phase lines toward Caumont, St Lo and Carentan. The deliberate advance by the Corps toward a line weakly held by the Reconnaissance battalion of the 17th SS Panzer Grenadier Division was directed by Bradley who did not want to divert attention from the effort against Cherbourg. After capturing Caumont V Corps halted and continued aggressive patrolling to deceive the Germans while digging in.[xlix] The possibility existed that a strong push against the weak German line could have led to an opportunity to envelope the German line west of Caen. This was a missed opportunity that in part led to the bloody and controversial campaign to capture Caen.[l]
British efforts around Caen
 German Panzer Ace Waffen SS Captain Michale Wittman single handedly destroyed a British Battalion at Villers Bocage in his Tiger Tank
German Panzer Ace Waffen SS Captain Michale Wittman single handedly destroyed a British Battalion at Villers Bocage in his Tiger Tank
Montgomery had ambitious plans to break out of Normandy by capturing Caen on D-Day and driving toward Falaise and Argentan. The British plans for this were frustrated by the rapid reinforcement of the sector by the Germans and the activities of 21st Panzer, Panzer Lehr, and the 12th SS Panzer Divisions. A flanking maneuver at Villers-Bocage was frustrated by a few Tiger tanks led by the legendary Waffen SS Panzer commander Captain Michael Wittman whose tanks devastated a British Armored battalion.[li]
 Wreckage of a British Battalion at Villers Bocage
Wreckage of a British Battalion at Villers Bocage
A series of disastrous attacks toward Caen (EPSOM, CHARNWOOD and GOODWOOD) strongly supported by air strikes and Naval gunfire finally succeeded in taking that unfortunate city on July 18th but failed to take the heights beyond the town.[lii]
 British operations like Operation Epsom met setback after setback against dug in German forces outside of Caen
British operations like Operation Epsom met setback after setback against dug in German forces outside of Caen
Against crack well dug in German forces the British took heavy casualties in tanks and infantry seriously straining their ability to conduct high intensity combat operations in the future.[liii] The one benefit, which Montgomery would claim after the war as his original plan was that German forces were fixed before Caen and ground down so they could not be used against Bradley’s breakout in the west at St Lo.[liv]
Clearing the Bocage: The Battle of the Cotentin Plain
Other German forces arrived, and reinforced the Caumont gap which no longer “yawned invitingly in front of V Corps.” [lv] Bradley wished to push forward rapidly to achieve a breakthrough in the American sector.[lvi] Facing the most difficult terrain in France amid the Bocage and swamps that limited avenues of approach to the American divisions committed to the offensive. The Americans now faced their old foe the 352nd division as well various elements of II Parachute Corps, the 17th SS Panzer Grenadier and Panzer Lehr Divisions. American tanks and infantry made slow progress and incurred high losses as they dueled the Germans at close range. In the VIII Corps sector alone the attack “consumed twelve days and 10,000 casualties to cross eleven kilometers of the Bocage…the achievements of the VII and XIX Corps were no better than comparable.[lvii]
St. Lo
 US Tanks advancing with German prisoners moving back to US lines at St Lo
US Tanks advancing with German prisoners moving back to US lines at St Lo
St. Lo was a key to Bradley’s breakout efforts. His Army had to capture it and the roads leading out of it to launch Operation COBRA along the coast. The task of capturing St. Lo was assigned to GEROW’S V Corps and Corlett’s XIX Corps. They faced opposition from the tough paratroops of the German 3rd Parachute Division of II Parachute Corps. The 2nd, 29th, 30th and 83rd Divisions fought a tough battle advancing eleven kilometers again with high numbers of casualties especially among the infantry to secure St. Lo on 18 July.[lviii] They finally had cleared the hedgerows. St Lo epitomized the struggle that the American Army had to overcome in the Bocage. Hard fighting but outnumbered German troops in excellent defensive country exacted a terrible price in American blood despite the Allied control of the skies.[lix]
Operation COBRA
 US 155mm Howitzers in Normandy, the Germans had profound respect for American Artillery, a respect that they did not share for American Infantry or Armor forces
US 155mm Howitzers in Normandy, the Germans had profound respect for American Artillery, a respect that they did not share for American Infantry or Armor forces
With the Bocage behind him Bradley desired to push the Germans hard. COBRA was his plan to break out of Normandy. Bradley ably assisted by Collins they realized that the better terrain, road networks favored a breakout. American preparations included a technical advance that allowed tanks to plow through hedgerows. This was the “Rhino” device fashioned by American troops which was installed on 3 of every 5 First Army Tanks for the operation.[lx] VII Corps was to lead the attack which was to begin on July 24th. American planning was more advanced than in past operations. Collins and Bradley planned for exploitation operations once the breakthrough had been made. A massive air bombardment would precede the attack along with an artillery barrage by Collins corps artillery which was reinforced by additional battalions. A mistake by the heavy bombers in the 24th resulted in the American troops being hit with heavy casualties and a postponement of the attack until the 25th.[lxi] The following day the attack commenced. Another mistake by the bombers led to more American casualties[lxii] but VII Corps units pressed forward against the determined resistance of the survivors of Panzer Lehr and the remnants of units that had fought the Americans since the invasion began. Although it was a “slow go” on the 25th Bradley and his commanders were already planning for and beginning to execute the breakout before the Germans could move up reinforcements. The 26th of June brought renewed attacks accompanied by massive air strikes.
While not much progress was made on the 26th, the Americans discovered on the 27th that the German forces were retreating. The capture of Marigny allowed VIII Corps to begin exploitation down the coastal highway to Coutances. On the 27th General Patton was authorized to take immediate command of VIII Corps a precursor to the activation of his 3rdArmy. COBRA ripped a hole in the German line and inflicted such heavy casualties on the German 7th Army that it could do little to stop the American push.[lxiii] As the American forces pushed forward they reinforced their left flank absorbing the local German counterattacks which were hampered by the Allied close air support.
Avranches and Beyond
 US Forces advance through the ruins of St Lo
US Forces advance through the ruins of St Lo
As the breakthrough was exploited the command of the forces leading it shifted to Patton and the newly activated 3rd Army. By the 28th VIII Corps led by the 4th and 6th Armored Divisions had reached Avranches and established bridgeheads over the See River with additional bridges being captured intact on the 30th.[lxiv] The capture of Avranches allowed the Americans to begin exploitation operations into Brittany and east toward the Seine. Weigley notes that for the first time in the campaign that in Patton the Americans finally had a commander who understood strategic maneuver and would use it to great effect.[lxv]
Conclusion
The American campaign in Normandy cost the U.S. Army a great deal. It revealed weaknesses in the infantry, the inferiority of the M4 Sherman tank to most German types, problems in tank-infantry cooperation and also deficiencies in leadership at senior, mid-grade and junior levels. Heavy casualties among infantry formations would lead to problems later in the campaign. Numerous officers were relieved including Division and Regimental commanders. Nonetheless during the campaign the Americans grew in their ability to coordinate air and ground forces and adapt to the conditions imposed on them by their placement in the Cotentin. The deficiencies would show up in later battles but the American Army learned its trade even impressing some German commanders on the ground in Normandy.[lxvi]
[i] See the alternative history of by Peter Tsouras Disaster at D-Day: The Germans Defeat the Allies, June 1944, Greenhill Books, London 1994. Tsouras describes the defeat of the Omaha landings and the effect on the course of the campaign leading to the overthrow of Hitler and a negotiated armistice in the west. While this outcome could be rigorously debated other outcomes could have led to the fall of the Roosevelt and Churchill governments and their replacement by those not committed to unconditional surrender or a continuation of the war that brought about more German missile attacks on the U.K. and the introduction of other advanced German weapons that could have forced such a settlement. Another option could have led to the dropping of the Atomic Bomb on a German city vice Hiroshima.
[ii] Weigley, Russell F. Eisenhower’s Lieutenants: The Campaign of France and Germany, 1944-1945, Indiana University Press, Bloomington IN, 1981 p.33
[iii] Ibid pp. 34-35
[iv] Ibid p.35
[v] General Montgomery 21st Army group and Land Forces, Admiral Sir Bertram Ramsey as Allied Naval Expeditionary Force and Air Marshall Sir Trafford Leigh-Mallory as Commander in Chief Allied Expeditionary Air Force. Weigley p.43
[vi] Max Hastings in Overlord: D-Day and the Battle for Normandy Vintage Books, New York, 1984, comments that many in Britain wondered if Eisenhower with the lack of actual battle experience could be a effective commander and that Eisenhower was disappointed in the appointment of Leigh-Mallory and Ramsey, and had preferred Alexander over Montgomery, pp. 28-29.
[vii] Ibid. Weigley p.40. Montgomery was the first to object to the 3 division narrow front invasion rightly recognizing that seizing Caen with its road junctions could provide a springboard for the campaign into open country.
[viii] Ibid. p.37
[ix] Hastings, Max. Overlord: D-Day and the Battle for Normandy Vintage Books, New York, 1984 p.29 Hastings finds the irony in the selection of the British officers to execute the plan that reflected the American way of thinking.
[x] The Germans agreed with this in their planning leaving Brittany very lightly defended. See Isby, David C. Ed. “The German Army at D-Day: Fighting the Invasion.” p.27 The report of General Blumentritt, Chief of Staff OB West noted that only 3 divisions were assigned to Brittany.
[xi] Ibid. Weigley, pp. 39-40
[xii] Ibid. p.73
[xiii] See Isby p. 69. General Max Pemsel of 7th Army noted that “During the spring of 1944, Seventh Army received only tow good photographs of British southern ports, which showed large concentrations of landing craft.”
[xiv] Ibid. Hastings p.63. Hastings comments also about the success of using the turned Abwehr agents.
[xv] Warlimont, Walter. “Inside Hitler’s Headquarters: 1939-1945.” Translated from theGerman by R.H. Barry. Presidio Press, Novao CA, English Edition Copyright 1964 Wiedenfeld and Nicholson Ltd. Pp.422-423
[xvi] Ibid. Weigley pp. 53-54
[xvii] Ibid. p. 67
[xviii] Ibid. pp.57-64 Weigley spends a great deal of time on the wrangling between Eisenhower, Leigh Mallory and Spaatz on the nature of the plan, the allocation of forces both strategic and tactical assigned to carry it out and its success, or in the light of postwar analysis the lack of effect that it had on German operations.
[xix] Ibid. p.67-68.
[xx] Ibid. Hastings pp. 43-44 In large part due to the long range P-51 Mustang which accompanied the American bombing raids beginning in 1943. Another comment is that the campaign drew the German fighters home to defend Germany proper and prevented their use in any appreciable numbers over the invasion beaches.
[xxi] Ibid. Weigley p.69
[xxii] Ibid. p.89
[xxiii] Ibid. pp. 88-89
[xxiv] Ibid. p.87
[xxv] Ibid. Weigley also talks about the rejection of General Corlett’s ideas to use Amtracks used by the Marines in the Pacific to land on less desirable, but less defended beaches to lessen casualties on the beaches and the need for additional support equipment even on smooth beaches. One of Corlett’s criticisms was that too little ammunition was allotted to supporting the landings and not enough supporting equipment was provided. pp. 46-47
[xxvi] Hastings notes that with the strength and firepower of the German forces on OMAHA that many of these vehicles had they been employed would like have ended up destroyed further cluttering the beachhead. “Overlord” p.102
[xxvii] The battle over the deployment of the Panzer Divisions is covered by numerous historians. The source of the conflict was between Rommel who desired to place the Panzer Divisions on the Coast under his command due to the fear that Allied air superiority would prevent the traditional Panzer counterthrust, General Gyer von Schweppenburg commander of Panzer Group West (Later the 5th Panzer Army) and Field Marshal Von Rundstedt who desired to deploy the divisions order the command of Rundstedt for a counter attack once the invasion had been launched, a strategy which was standard on the Eastern Front, and Hitler who held most of the Panzer reserve including the SS Panzer Divisions under his control at OKW. Hitler would negotiate a compromise that gave Rommel the satisfaction of having three Panzer Divisions deployed behind coast areas in the Army Group B area of responsibility. 21stPanzer had those duties in Normandy.
[xxviii] Ibid. p.74-75
[xxix] Von Luck, Hans. “Panzer Commander“ Dell Publishing, New York, 1989 pp. 169-170. Von Luck a regiment commander in 21st Panzer noted that General Marcks of 84th Corps had predicted a 5 June invasion at a conference May 30th.
[xxx] Almost every D-Day historian talks about the weather factor and its effect on the German high command’s reaction to the invasion. Rommel was visiting his wife for her birthday and planned to make a call on Hitler. Others including commanders of key divisions such as the 91st Airlanding Division were off to a war game in Rennes and the 21st Panzer Division to Paris.
[xxxi] Ibid. Weigley p. 96
[xxxii] See Cornelius Ryan, “The Longest Day” Popular Library Edition, New York 1959. pp. 189-193 for a vivid description of the challenges faced by soldiers going from ship to landing craft and their ride in to the beaches.
[xxxiii] Ibid. Weigley. p.78 Weigley talks about the order for the tanks to be carried ashore on their LCTs that did not get transmitted to the 741st.
[xxxiv] Ibid.
[xxxv] Ibid. Weigley p. 87 The weather prevented the aerial bombardment from being effective. Because the bombers could not see their targets they dropped their bomb loads further inland, depriving the infantry of support that they were expecting. Naval gunfire support had some effect but had to be lifted as the troops hit the beach leaving much of that support to come from Destroyers and specially equipped landing craft which mounted rockets and guns.
[xxxvi] Ibid. Hastings. pp. 90-91.
[xxxvii] Ibid. p.99
[xxxviii] Ibid. Weigley p.80
[xxxix] Ibid. p.101 Also see Weigley p.80
[xl] Ibid. p.99
[xli] Ibid. Weigley. p.95
[xlii] Ibid. p.94
[xliii] Ibid. p.99 Both Weigley and Hastings make note of the failure of both the Americans and British to train their troops to fight in the bocage once they had left the beaches.
[xliv] Ibid. Hastings. pp.152-153
[xlv] Ibid. Weigley p.101
[xlvi] Isby, David C., Ed. “Fighting in Normandy: The German Army from D-Day to Villers-Bocage.” Greenhill Books, London, 2001. p.143
[xlvii] Ibid. Hastings p.173 Allied fighter bombers exacted a fearful toll among German commanders. The Commanders of the 243rd and 77th Divisions fighting in the Cotentin were also killed by air attacks on the 17th and 18th. Further east facing the British the commander of the 12th SS Panzer Division, Fritz Witt on the 17th.
[xlviii] Ibid. Weigley. p.108
[xlix] Ibid. p.111-112.
[l] Ibid.
[li] The efforts of the 51st Highland Division and 7th Armored Division were turned aside by the Germans in the area and were dramatized by the destruction of a British armored battalion by SS Captain Michael Wittman and his platoon of Tiger tanks. See Hastings pp.131-135.
[lii] The British 8th Corps under General O’Connor lost 270 tanks and 1,500 men on 18 July attempting to crack the German gun line on the ridge beyond Caen. Weigley, pp.145-146.
[liii] Hastings comments about the critical British manpower shortage and the pressures on Montgomery to not take heavy casualties that could not be replaced. Overlord. pp.241-242.
[liv] Ibid. Weigley pp.116-120
[lv] Ibid. p.122
[lvi] Ibid. p121 Bradley told Eisenhower “when we hit the enemy this time we will hit him with such power that we can keep going and cause a major disaster.”
[lvii] Ibid. 134
[lviii] Ibid. Weigley. pp. 138-143. Weigley notes of 40,000 U.S. casualties in Normandy up to the capture of St. Lo that 90% were concentrated among the infantry.
[lix] Weigley quotes the 329th Regiment, 83rd Division historian “We won the battle of Normandy, [but] considering the high price in American lives we lost. P.143. This is actually a provocative statement that reflects America’s aversion to massive casualties in any war.
[lx] Ibid. p.149
[lxi] Ibid. p. 152
[lxii] Ibid. pp. 152-153. Among the casualties were the command group of the 9th Division’s 3rd Battalion 47th Infantry and General Leslie McNair who had come to observe the assault.
[lxiii] Ibid. pp.161-169. Weigley notes the advances in U.S. tactical air support, the employment of massive numbers of U.S. divisions against the depleted German LXXXIV Corps, and the advantage that the “Rhino” device gave to American tanks by giving them the ability to maneuver off the roads for the first time.
[lxiv] Ibid. pp.172-173.
[lxv] Ibid. p.172
[lxvi] Ibid. Isby, David C. “Fighting in Normandy,” p.184, an officer of the 352nd Division referred to the American soldier “was to prove himself a in this terrain an agile and superior fighter.”
Bibliography
Carell, Paul. “Invasion: They’re Coming!” Translated from the German by E. Osers, Bantam, New York 1964.
Hastings, Max. Overlord: D-Day and the Battle for Normandy Vintage Books, New York, 1984
Isby, David C. Ed. “The German Army at D-Day: Fighting the Invasion.” Greenhill Books, London 2004
Isby, David C., Ed. “Fighting in Normandy: The German Army from D-Day to Villers-Bocage.” Greenhill Books, London, 2001.
Ryan, Cornelius, “The Longest Day” Popular Library Edition, New York 1959
Tsouras, Peter. “Disaster at D-Day: The Germans Defeat the Allies, June 1944,”Greenhill Books, London 1994.
Von Luck, Hans. “Panzer Commander“ Dell Publishing, New York, 1989
Warlimont, Walter. “Inside Hitler’s Headquarters: 1939-1945.” Translated from theGerman by R.H. Barry. Presidio Press, Novao CA, English Edition Copyright 1964 Wiedenfeld and Nicholson Ltd. Warlimont, Walter. “Inside Hitler’s Headquarters: 1939-1945.” Translated from theGerman by R.H. Barry. Presidio Press, Novao CA, English Edition Copyright 1964 Wiedenfeld and Nicholson Ltd.
Weigley, Russell F. Eisenhower’s Lieutenants: The Campaign of France and Germany, 1944-1945, Indiana University Press, Bloomington IN, 1981

























































 Eisenhower and 101st Airborne
Eisenhower and 101st Airborne LST-325 at Normandy, Specialized Landing Ships and Craft were in High Demand and Short Supply in June 1944
LST-325 at Normandy, Specialized Landing Ships and Craft were in High Demand and Short Supply in June 1944 Omaha Beach
Omaha Beach Outnumbered Paratroops of II Fallschirmjaeger Corps Delayed US Forces Considerably in Normandy
Outnumbered Paratroops of II Fallschirmjaeger Corps Delayed US Forces Considerably in Normandy  8th Air Force Bombers Helped Hit German Oil Production Facilities and caused the Luftwaffe to spend its fighter squadrons over Germany than France
8th Air Force Bombers Helped Hit German Oil Production Facilities and caused the Luftwaffe to spend its fighter squadrons over Germany than France Landing craft passing USS Augusta
Landing craft passing USS Augusta Dual Drive or DD Tanks took heavy Losses at Omaha
Dual Drive or DD Tanks took heavy Losses at Omaha 1st Infantry Divison Troops at the Omaha Beach Sea Wall
1st Infantry Divison Troops at the Omaha Beach Sea Wall Panzers and Grenadiers in Normandy
Panzers and Grenadiers in Normandy
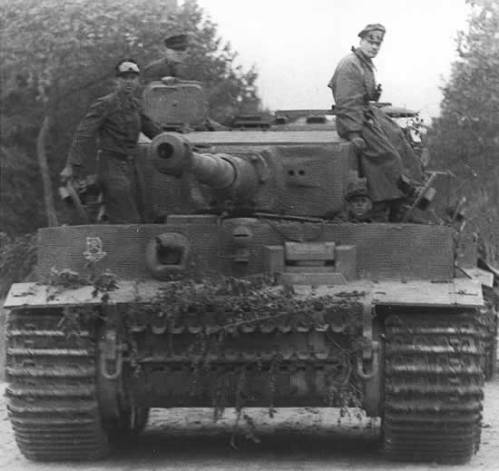 Tiger Tank and Crew in Normandy
Tiger Tank and Crew in Normandy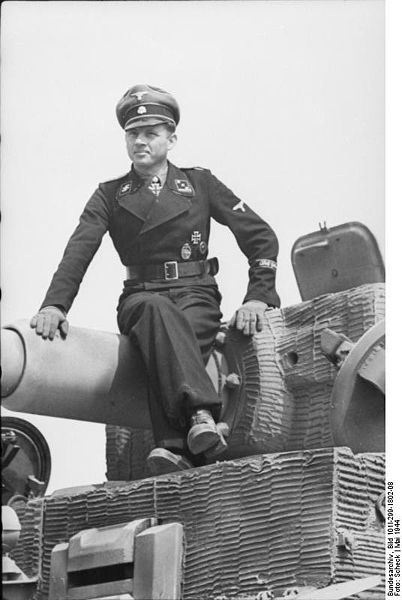 Panzer Ace Captain Michael Wittmann on His Tiger Tank
Panzer Ace Captain Michael Wittmann on His Tiger Tank US Tanks and German Prisoners at St Lo
US Tanks and German Prisoners at St Lo Hitler’s FW-200 Prior to his Ill-fated vist to Army Group Center
Hitler’s FW-200 Prior to his Ill-fated vist to Army Group Center Goering meeting Diplomats following Hitler’s State Funeral
Goering meeting Diplomats following Hitler’s State Funeral Erich Von Manstein at the Front
Erich Von Manstein at the Front Sturmgechuten and SdKfw 251 APCs moving into position
Sturmgechuten and SdKfw 251 APCs moving into position Soviet Tanks and AT Guns at Kupiansk
Soviet Tanks and AT Guns at Kupiansk Mk IV Panzers
Mk IV Panzers  T-34 towing disabled T-34 near Orel
T-34 towing disabled T-34 near Orel SS Panzer Troops and Tigers prepping for battle
SS Panzer Troops and Tigers prepping for battle German Tank Commader as Panzers mop up
German Tank Commader as Panzers mop up Goering Surrenders himself
Goering Surrenders himself 